Pengantar snapshot tabel
Dokumen ini merupakan pengantar snapshot tabel BigQuery. Dokumen ini merupakan bagian pertama dari serangkaian dokumen yang menjelaskan cara menggunakan snapshot tabel BigQuery, termasuk cara membuat, memulihkan, memperbarui, mendapatkan informasi tentang, dan membuat kueri snapshot tabel. Serangkaian dokumen tersebut ditujukan untuk pengguna yang sudah memahami BigQuery dan tabel BigQuery.
Snapshot tabel
Snapshot tabel BigQuery menyimpan isi tabel (disebut tabel dasar) pada waktu tertentu. Anda dapat menyimpan snapshot tabel terkini, atau membuat snapshot tabel sebagaimana keadaan tabel pada suatu waktu dalam tujuh hari terakhir. Snapshot tabel dapat memiliki masa berlaku; ketika jumlah waktu yang dikonfigurasi telah berlalu sejak snapshot tabel dibuat, BigQuery akan menghapus snapshot tabel tersebut. Anda dapat membuat kueri snapshot tabel seperti halnya tabel standar. Snapshot tabel bersifat hanya baca, tetapi Anda dapat membuat (memulihkan) tabel standar dari snapshot tabel, lalu mengubah tabel yang dipulihkan.
Manfaat menggunakan snapshot tabel meliputi hal berikut:
Menyimpan data selama lebih dari tujuh hari. Dengan perjalanan waktu BigQuery, Anda hanya dapat mengakses data tabel dari tujuh hari yang lalu atau setelahnya. Dengan snapshot tabel, Anda dapat mempertahankan data tabel dari suatu titik waktu tertentu selama yang Anda inginkan.
Meminimalkan biaya penyimpanan. BigQuery hanya menyimpan byte yang berbeda antara snapshot dan tabel dasarnya, sehingga snapshot tabel biasanya menggunakan lebih sedikit ruang penyimpanan daripada salinan tabel penuh.
Jika Anda memerlukan salinan tabel yang ringan dan dapat diubah, sebaiknya gunakan clone tabel.
Kontrol akses untuk snapshot tabel
Kontrol akses untuk snapshot tabel mirip dengan kontrol akses untuk tabel. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat Mengontrol akses ke resource dengan IAM.
Membuat kueri snapshot tabel
Pembuatan kueri untuk data snapshot tabel dilakukan dengan cara yang sama seperti pembuatan kueri jenis tabel BigQuery lainnya. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, baca artikel Membuat kueri data BigQuery.
Biaya penyimpanan
Biaya penyimpanan berlaku untuk snapshot tabel, tetapi BigQuery hanya mengenakan biaya untuk data dalam snapshot tabel yang belum ditagihkan ke tabel lain:
Ketika snapshot tabel dibuat, awalnya tidak ada biaya penyimpanan untuk snapshot tabel.
Jika data baru ditambahkan ke tabel dasar setelah snapshot tabel dibuat, Anda tidak perlu membayar untuk penyimpanan data yang ada dalam snapshot tabel tersebut.
Jika data diubah atau dihapus dalam tabel dasar yang juga ada dalam snapshot tabel, tagihan berikut akan terjadi:
Anda akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan snapshot tabel dari data yang diubah atau dihapus.
Jika tabel dasar ditagih sebagai penyimpanan fisik, biaya perjalanan waktu dan failsafe tidak akan ditagih ke tabel dasar. Saat snapshot dihapus, Anda akan ditagih untuk perjalanan waktu dan failsafe.
Jika ada beberapa snapshot yang berisi data yang diubah atau dihapus, Anda hanya akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan yang digunakan oleh snapshot terlama.
Saat Anda menyalin snapshot atau clone tabel dalam region yang sama atau dari satu region atau multi-region ke region lainnya, salinan lengkap tabel akan dibuat. Hal ini akan menimbulkan biaya penyimpanan tambahan.
Perbedaan antara biaya penyimpanan tabel dasar dan snapshot tabel ditunjukkan dalam gambar berikut:
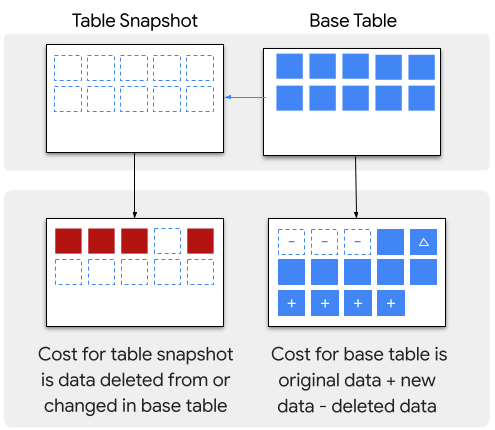
Untuk informasi lebih lanjut, lihat Harga penyimpanan BigQuery.
Batasan
Suatu snapshot tabel harus berada di region yang sama, dan dalam organisasi yang sama dengan tabel dasarnya. Jika Anda memilih set data di region yang berbeda, BigQuery akan membuat salinan tabel di set data target di region tersebut.
Snapshot tabel bersifat hanya baca; Anda tidak dapat memperbarui data dalam snapshot tabel kecuali jika Anda membuat tabel standar dari snapshot tersebut dan kemudian memperbarui datanya. Anda hanya dapat memperbarui metadata snapshot tabel; misalnya, deskripsi, tanggal habis masa berlaku, dan kebijakan aksesnya.
Anda hanya dapat mengambil snapshot data tabel sebagaimana keadaan data tabel tersebut pada tujuh hari yang lalu atau setelahnya, karena adanya batas tujuh hari untuk perjalanan waktu.
Anda tidak dapat mengambil snapshot dari suatu tabel virtual atau tampilan terwujud.
Anda tidak dapat mengambil snapshot dari tabel eksternal.
Anda tidak dapat menimpa snapshot tabel atau tabel yang sudah ada saat membuat snapshot tabel.
Jika Anda mengambil snapshot tabel yang memiliki data di dalam penyimpanan yang dioptimalkan untuk tulis (buffering streaming), data di penyimpanan yang dioptimalkan untuk tulis tidak disertakan dalam snapshot tabel.
Jika Anda mengambil snapshot tabel yang memiliki data di dalam perjalanan waktu, data dalam perjalanan waktu tidak disertakan dalam snapshot tabel.
Jika Anda mengambil snapshot dari tabel berpartisi yang menetapkan masa berlaku partisi, informasi habis masa berlaku partisi tidak akan disimpan di dalam snapshot. Tabel yang di-snapshot justru menggunakan masa berlaku partisi default dari set data tujuan. Untuk menyimpan informasi masa berlaku partisi, salin tabel.
Kuota dan batas
Untuk mengetahui informasi tentang kuota dan batas yang berlaku untuk snapshot tabel, lihat Kuota dan batas snapshot tabel.
Langkah berikutnya
- Membuat snapshot tabel.
- Memulihkan snapshot tabel.
- Memperbarui deskripsi, tanggal habis masa berlaku, atau kebijakan akses untuk snapshot tabel.
- Membuat snapshot bulanan dari suatu tabel menggunakan akun layanan yang menjalankan kueri terjadwal.
- Mengotomatiskan snapshot di tingkat set data.

