Pengantar clone tabel
Dokumen ini memberikan ringkasan tentang clone tabel di BigQuery. Dokumen ini ditujukan bagi pengguna yang sudah memahami BigQuery dan tabel BigQuery.
Clone table adalah salinan ringan yang dapat ditulis dari tabel lain (disebut tabel dasar). Anda hanya dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan data dalam clone tabel yang berbeda dengan tabel dasar, sehingga pada awalnya tidak ada biaya penyimpanan untuk clone tabel. Selain model penagihan untuk penyimpanan, dan beberapa metadata tambahan untuk tabel dasar, clone tabel mirip dengan tabel standar. Anda dapat membuat kueri, membuat salinannya, menghapusnya, dan seterusnya.
Kasus penggunaan umum untuk clone tabel mencakup:
- Membuat salinan tabel produksi yang dapat Anda gunakan untuk pengembangan dan pengujian.
- Membuat sandbox bagi pengguna untuk menghasilkan analisis dan manipulasi data mereka sendiri, tanpa menyalin semua data produksi secara fisik. Hanya data yang diubah yang akan ditagih.
Setelah Anda membuat clone tabel, clone tersebut akan terpisah dari tabel dasar. Setiap perubahan yang dibuat pada tabel dasar atau clone tabel tidak akan diterapkan di tabel lain.
Jika Anda memerlukan salinan tabel yang bersifat hanya baca dan ringan, sebaiknya gunakan snapshot tabel.
Metadata clone tabel
Clone tabel memiliki metadata yang sama dengan tabel standar, ditambah berikut ini:
- Project, set data, dan nama tabel dasar clone tabel.
- Waktu operasi clone tabel. Jika perjalanan waktu digunakan untuk membuat clone tabel, maka ini adalah stempel waktu perjalanan waktu.
Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES.
Operasi clone tabel
Secara umum, Anda menggunakan clone tabel dengan cara yang sama seperti menggunakan tabel standar, termasuk operasi berikut:
- Membuat kueri
- Kontrol akses
- Mendapatkan metadata
- Partisi dan pengelompokan
- Menggunakan skema
- Menghapus
Namun, pembuatan clone tabel berbeda dengan pembuatan tabel standar. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat Membuat clone tabel.
Biaya penyimpanan
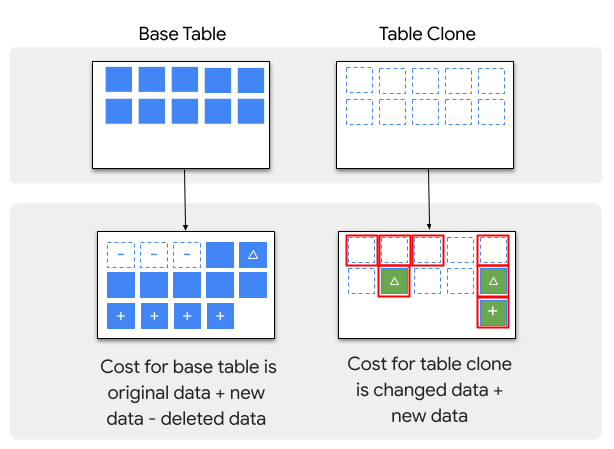
Biaya penyimpanan berlaku untuk clone tabel tetapi BigQuery hanya mengenakan biaya untuk data dalam clone tabel yang belum ditagihkan ke tabel lain:
Saat clone tabel dibuat, awalnya tidak ada biaya penyimpanan untuk clone tabel tersebut.
Jika data ditambahkan atau diubah dalam clone tabel, Anda akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan data yang ditambahkan atau diperbarui.
Jika data dihapus dalam clone tabel, Anda tidak akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan data yang dihapus.
Jika data diubah atau dihapus dalam tabel dasar yang juga ada dalam clone tabel, Anda akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan clone tabel dari data yang diubah atau dihapus. Jika ada beberapa clone yang berisi data yang diubah atau dihapus, Anda hanya dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan yang digunakan oleh clone terlama.
Jika data ditambahkan ke tabel dasar setelah clone tabel dibuat, Anda tidak akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan data tersebut dalam clone tabel, tetapi Anda akan dikenai biaya untuk penyimpanan tersebut di tabel dasar.
Perbedaan antara biaya penyimpanan clone tabel dan tabel dasar ditampilkan dalam gambar berikut:
Untuk informasi lebih lanjut, lihat Harga penyimpanan BigQuery.
Batasan
- Anda dapat meng-clone tabel antar-set data dalam project yang sama, dan di antara set data dalam project yang berbeda. Namun, set data tujuan untuk clone tabel harus berada di region yang sama dan dalam organisasi yang sama dengan tabel yang sedang di-clone. Misalnya, Anda tidak dapat meng-clone tabel dari set data yang berbasis di Uni Eropa ke set data yang berbasis di AS.
- Anda tidak dapat membuat clone data tabel karena data tabel tersebut jauh lebih lama dari durasi periode perjalanan waktu untuk set data tabel tersebut.
- Anda tidak dapat membuat clone tampilan atau tampilan terwujud.
- Anda tidak dapat membuat clone tabel eksternal.
- Jika Anda meng-clone tabel yang memiliki data di penyimpanan yang dioptimalkan untuk tulis (buffering streaming untuk baris yang baru-baru ini di-streaming), data di penyimpanan yang dioptimalkan untuk tulis tidak disertakan dalam tabel clone.
- Jika Anda meng-clone tabel yang memiliki data dalam perjalanan waktu, data dalam perjalanan waktu tidak disertakan dalam clone tabel.
- Clone tabel tidak dapat dibedakan dari tabel standar di panel Explorer. Namun, Anda dapat mengetahui clone tabel dari tabel standar dengan melihat detail tabel. Detail clone tabel memiliki bagian Info Tabel Dasar yang tidak disertakan pada tabel standar.
- Anda tidak dapat menggunakan operasi clone untuk menambahkan data ke tabel yang ada. Misalnya, Anda tidak dapat menggunakan setelan flag
--append_table=truedan--clone=truedalam perintahbq cpyang sama. Untuk menambahkan data saat menduplikasi tabel, gunakan operasi penyalinan. - Saat Anda membuat clone tabel, namanya harus mematuhi aturan penamaan yang sama seperti saat Anda membuat tabel.
- Pembuatan clone tabel tunduk pada batas BigQuery pada tugas penyalinan.
- Waktu yang diperlukan BigQuery untuk membuat clone tabel dapat bervariasi secara signifikan di berbagai operasi karena penyimpanan yang mendasarinya dikelola secara dinamis.
Kuota dan batas
Clone tabel memiliki kuota dan batas yang sama dengan tabel standar. Untuk mengetahui informasi lebih lanjut, lihat kuota dan batas tabel. Clone tabel juga memiliki batas clone tabel yang berlaku.

