Troubleshoot IAM permissions in BigQuery
This document shows you how to troubleshoot issues with
Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions in BigQuery. IAM
permission issues typically result in Access Denied errors like the following:
Access Denied: Project PROJECT_ID: User does not have bigquery.jobs.create permission in project PROJECT_ID.Access Denied: Project PROJECT_ID: User does not have bigquery.datasets.get permission on dataset DATASET.User does not have permission to query table PROJECT_ID:DATASET.TABLE.Access Denied: Table PROJECT_ID:DATASET.TABLE: User does not have permission to query table PROJECT_ID:DATASET.TABLE, or perhaps it does not exist.Access Denied: User PRINCIPAL does not have permission to perform bigquery.tables.getData on resource 'projects/PROJECT_ID/datasets/DATASET/tables/TABLE'.
Before you begin
- To troubleshoot a principal's access to a BigQuery resource, ensure that you have the required IAM permissions.
Gather information about the issue
The first step in troubleshooting a resource access issue is to determine the permission that is missing, the IAM principal that was denied access, and the resource the principal was attempting to access.
Get information from the error or job history
To get information about the principal, the resource, and the permissions, examine the output from the bq command-line tool, the API response, or BigQuery in the Google Cloud console.
For example, if you attempt to run a query with insufficient permissions, you see an error like the following on the Job information tab in the Query results section of the Google Cloud console.
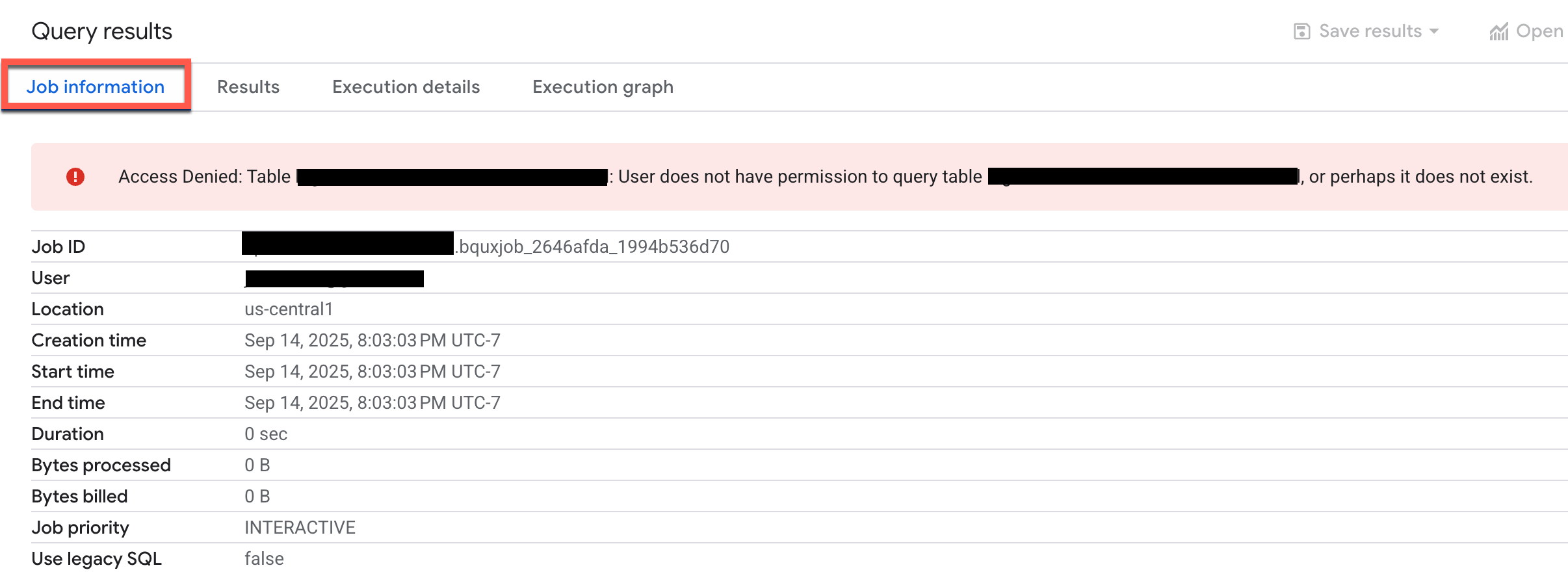
Examine the error to determine the principal, the resource, and the permissions.
In some cases, you may be able to request missing permissions directly from the error message. For more information, see Troubleshoot permission error messages in the IAM documentation.
Get information from the Cloud Audit Logs
If the error message is generic, missing information, or if the action failed in a background process, use the Cloud Audit Logs Logs Explorer to get information about the error.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Logs Explorer page.
Alternatively, from the navigation menu, choose Monitoring > Logs Explorer.
In the Logs Explorer, for the logs scope, choose Project logs.
In the query window, enter the following query to get permission-related errors from the BigQuery data access logs:
resource.type="bigquery_resource" AND logName="projects/PROJECT_ID/logs/cloudaudit.googleapis.com%2Fdata_access" AND protoPayload.status.message:"Access Denied" OR protoPayload.status.message:"Permission denied" OR protoPayload.status.code=7
Replace PROJECT_ID with your project ID.
In the query results, expand the log entry that corresponds to your failed operation.
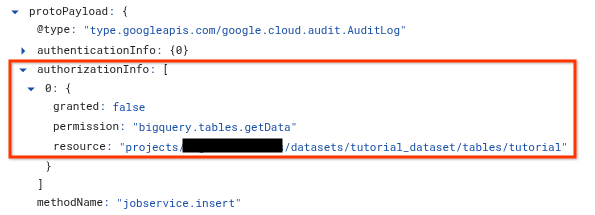
In the
protoPayloadsection, expand theauthorizationInfoarray, and then expand each node in theauthorizationInfoarray.The
authorizationInfoarray shows every permission check performed during the API call.To see cause of the error, look for the
granted: falseentry. Thegranted: falseentry shows the following information:permission: The IAM permission string that was checked. For example,bigquery.tables.getData.resource: The fully qualified name of the resource that the principal attempted to access. For example,projects/myproject/datasets/mydataset/tables/mytable.principalEmail(if available): Referenced inprotoPayload.authenticationInfo, this is the principal that attempted the action.
Use the Policy Analyzer for allow policies
Policy Analyzer for allow policies lets you find out which IAM principals have what access to which BigQuery resources based on your IAM allow policies.
After you gather information about the permissions error, you can use the Policy Analyzer to understand why the principal lacks the required access. This tool analyzes all relevant policies, memberships in Google Groups, and inheritance from parent resources such as a project, a folder, and your organization.
To use Policy Analyzer for allow policies, you create an analysis query, specify a scope for the analysis, and then run the query.
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Policy Analyzer page.
Alternatively, from the navigation menu, choose IAM & Admin > Policy Analyzer.
Click Create Custom Query.
On the Configure your query page, enter the information you gathered previously:
In the Select the scope section, in the Select query scope field, verify that your current project appears or click Browse to choose another resource.
In the Set the query parameters section, for Parameter 1, choose Principal, and in the Principal field, enter the email of the user, group, or service account.
Click Add parameter.
For Parameter 2, choose Permission, and in the Permission field, click Select, choose the BigQuery permission, and then click Add. For example, select
bigquery.tables.getData.Click Add parameter.
For Parameter 3, choose Resource, and in the Resource field, enter the fully qualified resource name. The resource name must include the service prefix as in the following examples:
- BigQuery project:
//cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/projects/PROJECT_ID - BigQuery dataset:
//bigquery.googleapis.com/projects/PROJECT_ID/datasets/DATASET - BigQuery table:
//bigquery.googleapis.com/projects/PROJECT/datasets/DATASET/tables/TABLE
- BigQuery project:
In the Custom query pane, click Analyze > Run query.
Examine the query results. The result can be one of the following:
- An empty list. No results confirm that the principal doesn't have the required permission. You'll need to grant the principal a role that provides the correct permissions.
- One or more results. If the analyzer finds an allow policy, some form of access exists. Click View Binding on each result to view the roles that provide access to the resource that the principal is a member of. The policy binding shows whether access is granted through group membership or inheritance, or whether access is denied by an IAM condition or an IAM deny policy.
Find the correct IAM role that grants the required permissions
After you confirm that the principal doesn't have sufficient access, the next step is to find the appropriate predefined or custom IAM role that grants the required permissions. The role you choose should adhere to the principle of least privilege.
If your organization uses custom roles, you can find the correct role by listing all custom roles created in your project or organization. For example, in the Google Cloud console, on the Roles page, you can filter the list by Type:Custom to see only custom roles.
To find the correct predefined IAM role, follow these steps.
Open the BigQuery permissions section of the BigQuery IAM roles and permissions page.
In the Enter a permission search bar, enter the permission you retrieved from the error message, job history, or audit logs. For example,
bigquery.tables.getData.The search results show all predefined BigQuery roles that grant the permission.
Apply the principle of least privilege: in the list of roles, choose the least permissive role that grants the required permissions. For example, if you searched for
bigquery.tables.getDatato grant the ability to query table data, BigQuery Data Viewer is the least permissive role that grants that permission.Grant the principal the appropriate role. For information about how to grant an IAM role to a BigQuery resource, see Control access to resources with IAM.
What's next
- For a list of all BigQuery IAM roles and permissions, see BigQuery IAM roles and permissions.
- For more information on troubleshooting allow and deny policies in IAM, see Troubleshoot policies.
- For more information on the Policy Intelligence Policy Analyzer, see Policy Analyzer for allow policies.
- For more information on the Policy Troubleshooter, see
Use Policy Troubleshooter.
