Generate search queries with Gemini
This document explains how you can use Gemini to generate search queries from the Gemini pane or when using Google Security Operations search.
For best results, we recommend using the Gemini pane to generate search queries.
Generate a search query using the Gemini pane
- Sign in to Google SecOps.
- Click the Gemini logo to open the Gemini pane.
Enter a natural language prompt and press Enter. The natural language prompt must be in English.
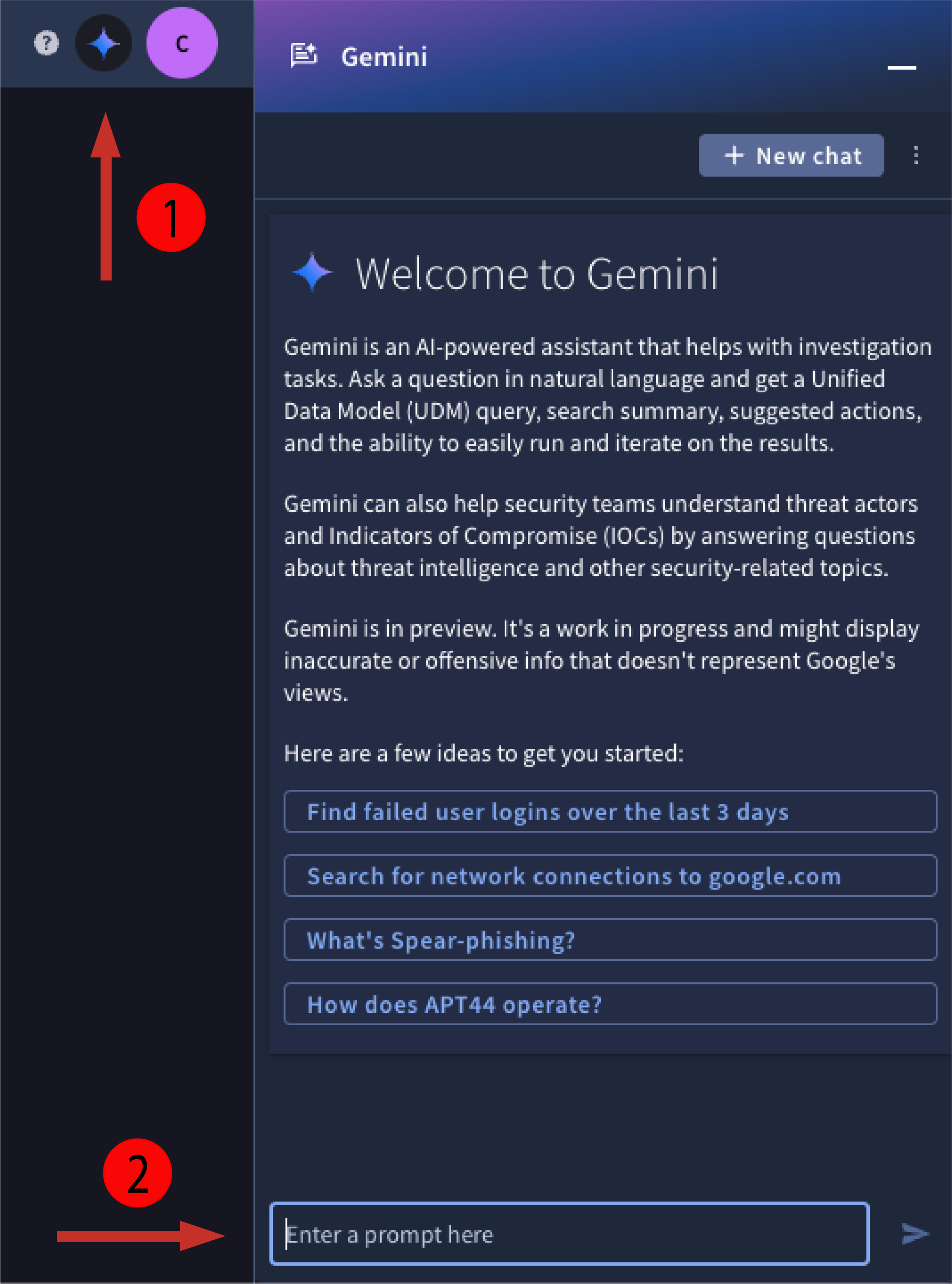
Figure 1. Open Gemini pane and enter prompt.
Review the generated search query. The search query uses YARA-L 2.0 syntax. If the generated search query meets your requirements, click Run search. Gemini produces a results summary along with suggested actions.
Example search prompts and follow-up questions
Show me all failed logins for the last 3 daysGenerate a rule to help detect that behavior in the future
Show me events associated with the principle user izumi.nWho is this user?
Search for all of the events associated with the IP 198.51.100.121 in the last 3 hoursList all of the domains in the results setWhat types of events were returned?
Show me events from my firewall in the last 24 hoursWhat were the 16 unique hostnames in the results set?What were the 9 unique IPs associated with the results set?
Generate a search query using natural language
Using the Google SecOps search feature, you can enter a natural language query about your data, and Gemini can translate this into a search query to run against UDM events.
For better results, we recommend using the Gemini pane to generate search queries.
To use a natural language search to create a search query, complete the following steps:
- Sign in to Google SecOps.
- Go to Investigation > SIEM Search.
Enter a search statement in the natural language query bar and click Generate Query. You must use English for the search.
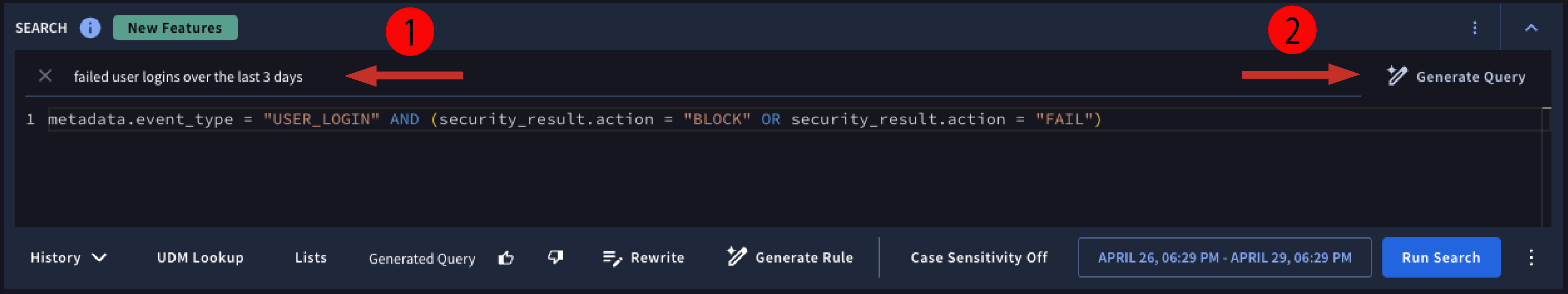
Figure 2. Enter a natural language search and click Generate Query.
The following statements are examples that might generate a useful search:
- network connections from 10.5.4.3 to google.com
- failed user logins over the last 3 days
- emails with file attachments sent to john@example.com or jane@example.com
- all Cloud service accounts created yesterday
- outbound network traffic from 10.16.16.16 or 10.17.17.17
- all network connections to facebook.com or tiktok.com
- service accounts created in Google Cloud yesterday
- Windows executables modified between 8 AM and 1 PM on May 1, 2023
- all activity from winword.exe on lab-pc
- scheduled tasks created or modified on exchange01 during the last week
- email messages that contain PDF attachments
- emails sent by or sent from admin@acme.com on September 1
- any files with the hash 44d88612fea8a8f36de82e1278abb02f
- all activity associated with user "sam@acme.com"
- yesterday
- within the last 5 days
- on Jan 1, 2023
Review the generated search query. The syntax is Overview of YARA-L 2.0.
Optional: Adjust the search time range.
Click Run Search.
Review the search results to determine if the event is present. If needed, use search filters to narrow the list of results.
Provide feedback about the query using the Generated Query feedback icons. Select one of the following:
- If the query returns the expected results, click thumb_up Thumbs Up.
- If the query does not return the expected results, click thumb_down Thumbs Down.
- Optional: Include additional detail in the Feedback field.
To submit a revised search query that helps improve results:
- Edit the search query that was generated.
- Click Submit.
- If you didn't rewrite the query, you're prompted to edit the query.
- If you did rewrite the query, the revised search query is sanitized for sensitive data and used to improve results.
If the search statement includes a time-based term, the time picker is automatically adjusted to match. For example, this would apply to the following searches:
If the search statement can't be interpreted, you see the following
message:
"Sorry, no valid query could be generated. Try asking a
different way."
Delete a chat session
You can delete your chat conversation session or delete all chat sessions. Gemini maintains all user conversation histories privately and adheres to Google Cloud's responsible AI practices. User history is never used to train models.
- In the Gemini pane, select Delete chat from the menu at the top right.
- Click Delete chat at the bottom right to delete the current chat session.
- Optional: To delete all chat sessions, select Delete all chat sessions and then click Delete all chats.
Provide feedback
You can provide feedback to responses generated by the Gemini AI investigation assistance. Your feedback helps Google improve the feature and the output generated by Gemini.
- In the Gemini pane, click thumb_up Thumb Up or thumb_down Thumb Down.
- Optional: Click thumb_down Thumb Down and provide feedback.
- Click Send feedback.
Need more help? Get answers from Community members and Google SecOps professionals.
