Topik ini hanya dimaksudkan sebagai contoh. Panduan ini menjelaskan cara mendapatkan sertifikat TLS dari certificate authority (CA) Let's Encrypt. Langkah-langkah ini disediakan terutama sebagai contoh untuk diikuti jika Anda tidak memiliki cara siap pakai lain untuk mendapatkan pasangan sertifikat/kunci yang diotorisasi oleh CA. Contoh ini menunjukkan cara membuat sertifikat menggunakan CA Let's Encrypt, klien Certbot, dan Cloud DNS Google Cloud Platform.
Tempat Anda dapat menggunakan sertifikat ini
Anda harus memberikan sertifikat TLS untuk gateway masuk Runtime yang diekspos di luar cluster.
Lihat juga Koneksi eksternal.Persyaratan
Anda memerlukan nama domain yang diperoleh melalui registrar nama domain. Anda dapat mendaftarkan nama domain melalui Google Domains atau registrar domain lain pilihan Anda.
Mengonfigurasi Cloud DNS
Untuk mendapatkan sertifikat TLS resmi, Anda harus memiliki nama domain yang memenuhi syarat. Langkah-langkah berikut menjelaskan cara menggunakan Google Cloud DNS untuk mendapatkan nama domain dan mengelola server domain Anda.- Buka konsol Google Cloud dan login ke akun Anda.
- Pilih project tempat Apigee hybrid diinstal.
- Jika Anda belum melakukannya, aktifkan Cloud DNS API. Lihat Mengaktifkan API.
- Buat alamat IP statis:
- Jika Anda menggunakan GKE, ikuti petunjuk di
Mengonfigurasi alamat IP eksternal statis untuk membuat alamat IP statis yang dapat digunakan proses eksternal
untuk berkomunikasi dengan ingress runtime campuran. Anda dapat memberi alamat nama apa pun
yang diinginkan, misalnya:
apigee-hybrid-runtime. Setelah selesai, Anda akan menggunakan nomor IP dalam konfigurasi cluster pada langkah berikutnya. Contoh:34.66.75.196 - Jika Anda menggunakan Anthos GKE, ikuti petunjuk dalam dokumentasi Anthos GKE untuk membuat alamat IP statis.
- Jika Anda menggunakan GKE, ikuti petunjuk di
Mengonfigurasi alamat IP eksternal statis untuk membuat alamat IP statis yang dapat digunakan proses eksternal
untuk berkomunikasi dengan ingress runtime campuran. Anda dapat memberi alamat nama apa pun
yang diinginkan, misalnya:
- Dapatkan IP Eksternal yang baru saja Anda cadangkan.
- Buat kumpulan data untuk endpoint ingress Istio runtime. Ini adalah alamat untuk melakukan panggilan API ke gateway campuran. Masukkan IP Eksternal yang Anda dapatkan di langkah sebelumnya dan tambahkan awalan ke nama domain, seperti
example-endpoint. Untuk mengetahui petunjuknya, lihat Membuat data baru.- Membuat zona publik terkelola. Untuk mengetahui petunjuknya, lihat Membuat zona publik terkelola.
- Buat kumpulan data baru dengan:
- DNS Name: Nama endpoint yang akan dikomunikasikan dengan panggilan API eksternal, seperti
api-servicesatauexample-endpoint - Resource Record Type: A
- TTL dan TTL Unit: Terima default
- Alamat IP: IP statis yang Anda buat.
- DNS Name: Nama endpoint yang akan dikomunikasikan dengan panggilan API eksternal, seperti
- Tampilan Detail zona akan mencantumkan empat server DNS sebagai data NS untuk zona baru Anda. Salin data data DNS, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam contoh berikut:
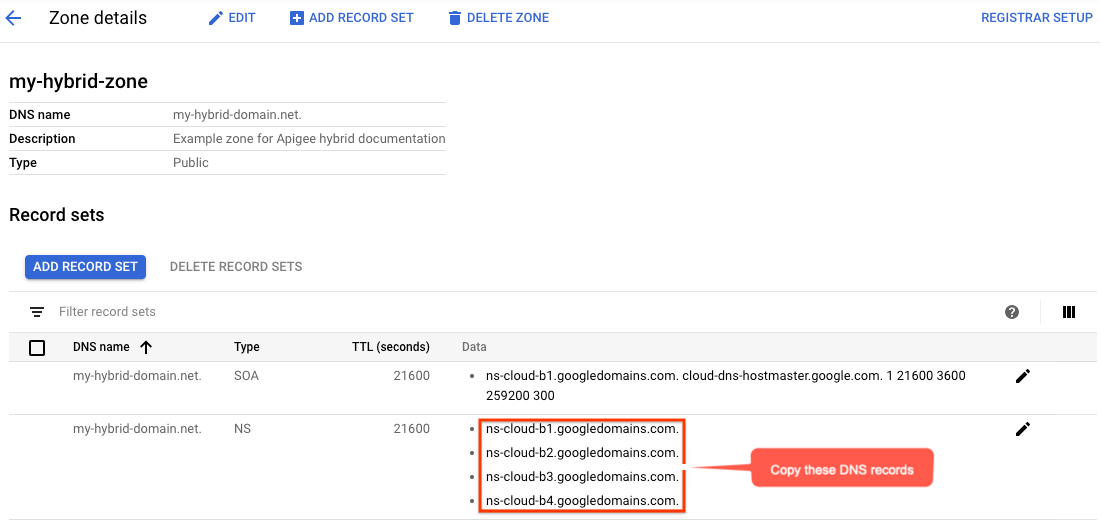
- Kembali ke halaman domain Anda di registrar (misalnya, Google Domains).
- Pilih domain Anda.
- Pilih DNS.
- Di bagian Server Nama, klik Edit.
Masukkan server nama domain yang Anda salin dari halaman Network Services Cloud DNS. Contoh:
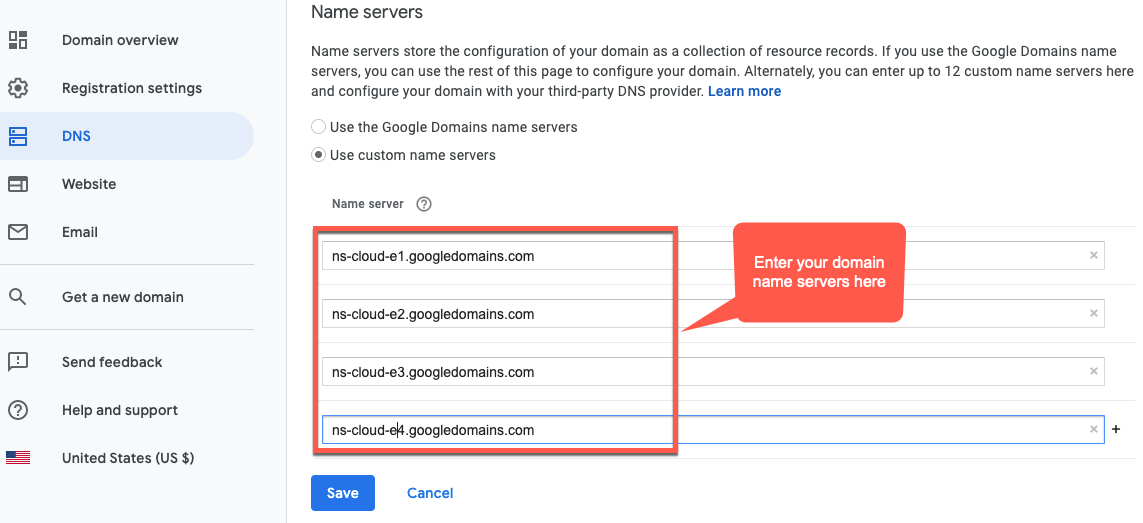
Sekarang, Google Cloud DNS akan mengelola data DNS untuk domain Anda.
Menginstal Certbot di VM
Setelah menyiapkan Cloud DNS untuk mengelola server domain, Anda akan menginstal klien Certbot dengan plugin dns_google di Cloud VM. Klien ini memungkinkan Anda mendapatkan sertifikat resmi untuk domain dari endpoint Let's Encrypt.
- Buka konsol Google Cloud dan login dengan akun yang Anda buat di Langkah 1: Membuat akun Google Cloud.
- Pilih project yang Anda buat di Langkah 2: Membuat project Google Cloud.
- Pilih IAM & admin > Service accounts.
Tampilan Akun layanan menampilkan daftar akun layanan project.
- Untuk membuat akun layanan baru, klik +Create Service Account di bagian atas tampilan.
Tampilan Detail akun layanan akan ditampilkan.
- Di kolom Nama akun layanan, masukkan nama akun layanan.
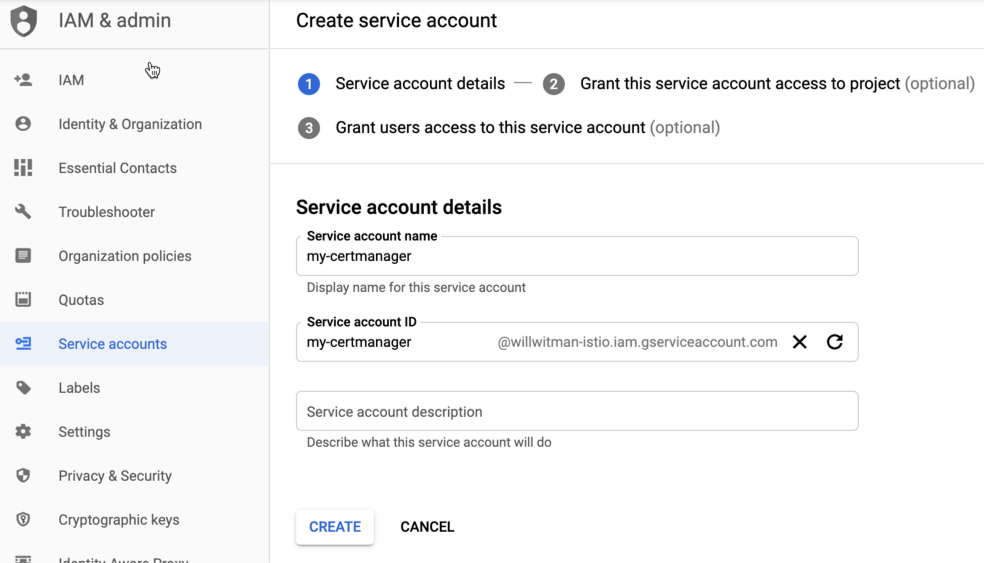
Anda dapat menambahkan deskripsi secara opsional di kolom Deskripsi akun layanan. Deskripsi membantu mengingatkan Anda tentang tujuan penggunaan akun layanan tertentu.
- Klik Buat.
Google Cloud akan membuat akun layanan baru dan menampilkan tampilan Izin akun layanan. Gunakan tampilan ini untuk menetapkan peran ke akun layanan baru Anda.
- Klik menu drop-down Select a role.
- Pilih peran Project Owner.
- Klik Lanjutkan.
- Klik Selesai.
- Di konsol Google Cloud, pilih Compute Engine > VM Instances.
- Buat instance VM bernama certmanager.
- Di bagian Boot Disk, pilih CentOS7 dan 20 GB untuk drive persisten SSD.
- Tetapkan Akun Layanan ke akun yang Anda buat di atas.
- Instal Certbot dan plugin dns_google di mesin, lalu jalankan klien Certbot:
sudo su -yum -y install yum-utilsyum install certbot -yyum install certbot-dns-google -ycertbot certonly --dns-google -d *.your_domain_name,*.your_domain_name --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directoryContoh:
sudo su -yum -y install yum-utilsyum install certbot -yyum install certbot-dns-google -ycertbot certonly --dns-google -d *.apigee-hybrid-docs.net,*.apigee-hybrid-docs.net --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - Anda kini dapat menemukan file sertifikat dan kunci pribadi yang diotorisasi di direktori ini:
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain_name/Contoh:
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/apigee-hybrid-docs.netlscert.pem chain.pem fullchain.pem privkey.key README - Salin file
fullchain.pemdanprivkey.keyke komputer lokal Anda. - Opsional: Buat secret Kubernetes dengan pasangan kunci/sertifikat. Lihat petunjuk di Opsi 2: Kubernetes Secret di Mengonfigurasi TLS dan mTLS di ingress Istio.
- Perbarui file penggantian Anda agar mengarah ke sertifikat dan kunci pribadi.
Contoh:
... envs: - name: test serviceAccountPaths: synchronizer: "your_keypath/synchronizer-manager-service-account.json udca: "your_keypath/analytic-agent-service-account.json virtualhosts: - name: my-env-group sslCertPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/fullchain.pem" sslKeyPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/privkey.key"
Atau jika menggunakan secret Kubernetes:
... envs: - name: test serviceAccountPaths: synchronizer: "your_keypath/synchronizer-manager-service-account.json udca: "your_keypath/analytic-agent-service-account.json virtualhosts: - name: my-env-group tlsMode: SIMPLE # Note: SIMPLE is the default, MUTUAL is also an available value. sslSecret: myorg-test-policy-secret" ...
- Terapkan perubahan pada konfigurasi
envs:Helm
Jalankan
helm upgrade untuk setiap lingkungan yang ingin Anda perbarui. helm upgrade ENV_NAME apigee-env/ \ --namespace apigee \ --set env=ENV_NAME \ --atomic \ -f OVERRIDES_FILE.yaml
apigeectl$APIGEECTL_HOME/apigeectl apply -f OVERRIDES_FILE.yaml --env ENV_NAME
atau, untuk mengupdate komponen untuk semua lingkungan:
$APIGEECTL_HOME/apigeectl apply -f OVERRIDES_FILE.yaml --all-envs
Menguji konfigurasi
Men-deploy dan menguji proxy. Lihat Mem-build ringkasan proxy API pertama Anda.

