A service account is a special type of account in Google Cloud that enables components and applications of a system to interact with each other and with other APIs. For more information about Google Cloud, see About Google Cloud services.
Apigee hybrid uses Google Cloud service accounts to perform a variety of tasks, including:
- Send log and metrics data
- Pull trace requests
- Connect to API gateway for administrative API requests
- Execute back ups
- Download proxy bundles
While one service account could perform all of these operations, for production environments Apigee recommends that you create multiple service accounts, each assigned to a specific task and each with its own set of permissions. This enhances security by compartmentalizing access and limiting each service account's scope and access privileges. As with user accounts, these permissions are applied by assigning one or more roles to the service account.
Service accounts and roles used by hybrid components
To operate properly, Apigee hybrid requires you to create several service accounts. Each service account requires a specific role or roles that enable it to perform its function.
The following table describes the service accounts for the hybrid components. The names given for each service account are the default names. You can use any names you want, but the names should be easy to identify with each account's purpose.
| Component* | Role | Required for basic install? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
apigee-cassandra |
Storage Object Adminroles/storage.objectAdmin |
Allows Cassandra backups to Cloud Storage, as described in Backup and recovery. | |
apigee-logger |
Logs Writerroles/logging.logWriter |
Allows logging data collection, as described in Logging. Only required for non-GKE cluster installations. | |
apigee-mart |
Apigee Connect Agentroles/apigeeconnect.Agent |
Allows MART service authentication. The Apigee Connect Agent role allows it to communicate securely with the Apigee Connect process, as described in Using Apigee Connect. | |
apigee-metrics |
Monitoring Metric Writerroles/monitoring.metricWriter |
Allows metrics data collection, as described in Metrics collection overview. | |
apigee-runtime |
No role required | Allows the Apigee hybrid runtime to connect to Google services and custom services on Google Cloud, such as Google Authentication, Google Cloud Trace, and Jaeger. | |
apigee-synchronizer |
Apigee Synchronizer Managerroles/apigee.synchronizerManager |
Allows the synchronizer to download proxy bundles and environment configuration data. Also enables operation of the trace feature. | |
apigee-udca |
Apigee Analytics Agentroles/apigee.analyticsAgent |
Allows the transfer of trace, analytics and deployment status data to the management plane. | |
apigee-watcher |
Apigee Runtime Agentroles/apigee.runtimeAgent |
Apigee Watcher pulls virtual hosts related changes for an org from synchronizer and makes necessary changes to configure istio ingress. | |
| * This name is used in the downloaded service account key's filename. | |||
As an alternative, for nonproduction, test, and demo environments, you can use a single service account with all the roles assigned to it. This is not recommended for production environments.
| Component* | Role | Required for basic install? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
apigee-non-prod |
Apigee Analytics Agent, Apigee Connect Agent, Apigee Organization Admin, Apigee Runtime Agent, Apigee Synchronizer Manager, Cloud Trace Agent, Logs Writer, Monitoring Metric Writer, Storage Object Admin | Or all required SAs above | Single service account for demo or test environments. See Install, Part 2, Step 5: Create service accounts. |
In addition to creating the service accounts listed in this table, you will use each accounts
private keys to generate access tokens so that you can access the Apigee APIs. The
create-service-account tool automaticallyl downloads the key files into a directory
on your local machine when it creates or updates the service accounts.
Create the service accounts
There are several ways to create service accounts, including:
- (Recommended)
create-service-accounttool - Google Cloud console
- gcloud SDK
Each of these is described in the following sections.
Use the create-service-account tool
The create-service-account tool is available after you
download and expand apigeectl in the
tools/ directory. It hybrid component-specific service accounts and assigns
the required roles for you. The tool also automatically downloads the service account keys and
stores them on your local machine.
For example, the following command will create all the separate individual service accounts for a
production environment, assign the appropriate IAM roles to each service account, and download
each accounts private key file to the ./service-accounts directory:
./tools/create-service-account --env prod
The following command creates a single service account named apigee-non-prod with all IAM
roles for all hybrid components,
suitable for demo and test environments, but not for production environments:
./tools/create-service-account --env non-prod
For more information on using create-service-account, see
create-service-account reference.
Use the Google Cloud console
You can create service accounts with the Google Cloud console.
To create a service account with the Google Cloud console and generate a key for the service account, do the following:
-
Create a service account:
-
In the Cloud console, go to the Service Accounts page.
- Select your project.
- Click Create Service Account.
-
In the Service account name field, enter a name. The Cloud console fills in the Service account ID field based on this name.
Apigee recommends that you use a name that reflects the service account's role; you can set the name of the service account to be the same name as the component that uses it. For example, set the name of the Logs Writer service account
apigee-logger.For more information about the service accounts names and roles, see Service accounts and roles used by hybrid components.
- Optional: In the Service account description field, enter a description for the service account. Descriptions are helpful at reminding you what a particular service account is used for.
- Click Create and continue.
-
Click the Select a role field and select a role, as described in Service accounts and roles used by hybrid components. If the Apigee roles do not appear in the drop down list, refresh the page.
For example, for the logging component, select the Logs Writer role.
If necessary, enter text to filter the list of roles by name. For example, to list only the Apigee roles, enter
Apigeein the filter field.You can add more than one role to a service account, but Apigee recommends that you only use one role for each of the recommended service accounts. To change the roles of a service account after you have created it, use the IAM page in the Cloud console.
- Click Continue.
Google Cloud displays the Grant users access to this service account view:
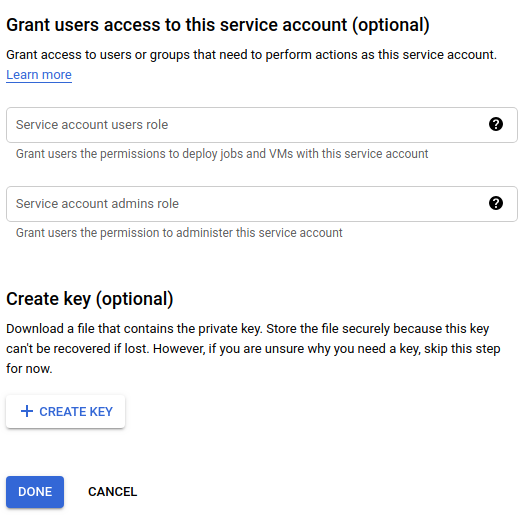
- Under Create key (optional), click Create Key.
Google Cloud gives you the option to download a JSON or P12 key:
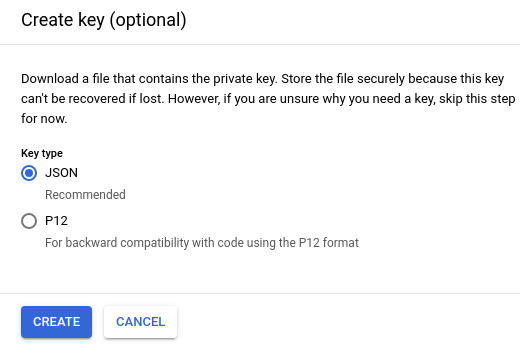
- Select JSON (the default) and click Create.
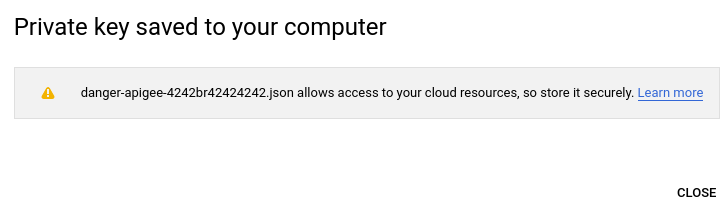
Google Cloud saves the key file in JSON format to your local machine and displays a confirmation when it is successful, as the following example shows:
You will later use some of the service account keys to configure hybrid runtime services. For example, when you configure the hybrid runtime, you will specify the location of the service account keys using the SERVICE_NAME
.serviceAccountPathproperties.These keys are used by the service accounts to get access tokens, which the service account then uses to make requests against the Apigee APIs on your behalf. (But that's not for a while yet; for now, just remember where you saved it.)
- Repeat steps 4 through 11 for each service account listed in
Service accounts and roles used by hybrid components
(except the
apigee-martaccount—which has no role associated with it—so do not assign it a role).When you're finished, you should have the following service accounts (in addition to the defaults, if any):
In the Google Cloud console, service accounts are indicated with the
 icon.
icon.
After you create a service account, if you want to add or remove a role to it, you must use the IAM & Admin view. You cannot manage roles for service accounts in the Service accounts view.
Use the gcloud service account creation APIs
You can create and manage service accounts with the Cloud Identity and Access Management API.
For more information, see Creating and managing service accounts.
Troubleshooting
-
