This topic is intended as an example only. It explains how to obtain a TLS certificate from the certificate authority (CA) Let's Encrypt. These steps are provided primarily as an example to follow if you do not have another ready way to obtain a certificate/key pair that is authorized by a CA. The example shows how to generate certificates using the Let's Encrypt CA, the Certbot client, and Google Cloud Platform Cloud DNS.
Where you can use these credentials
You must provide TLS credentials for two Istio ingress gateways that are exposed outside the cluster:
| Gateway | TLS requirement |
|---|---|
| MART ingress gateway | Requires an authorized TLS certificate/key pair. |
| Runtime ingress gateway | You can use a self-signed certificate/key pair or authorized TLS credentials. |
Requirements
- You will need a domain name obtained through a domain name registrar. You can register a domain name through Google Domains or another domain registrar of your choice.
Configure Cloud DNS
To obtain authorized TLS credentials, you must have a qualified domain name. The following steps explain how to Google Cloud DNS to obtain a domain name and manage your domain servers.- Open the Google Cloud console and log in with the account you created in Step 1: Create a Google Cloud account.
- Select the project that you created in Step 2: Create a GCP project.
- Enable the DNS API. See Enabling APIs.
- Create two static IP addresses:
- If you are on GKE, follow the instructions in
Reserving a static external IP address to create
two static IP addresses. You can give the addresses any name you wish, for example:
apigee-hybrid-martandapigee-hybrid-runtime. When you finish, you will have two IP numbers to use in the cluster configuration in the next step. For example:35.225.131.189and34.66.75.196 - If you are on Anthos GKE, follow instructions in the Anthos GKE documentation to create two static IP addresses.
- If you are on GKE, follow the instructions in
Reserving a static external IP address to create
two static IP addresses. You can give the addresses any name you wish, for example:
- Create a managed public zone. For instructions, see Create a managed public zone.
- Get the External IP you reserved for the
apigee-hybrid-mart. - Create record set for the MART endpoint. Enter the External IP you obtained in the previous
step and add a prefix to the domain name, such as
mart. For instructions, see Create a new record.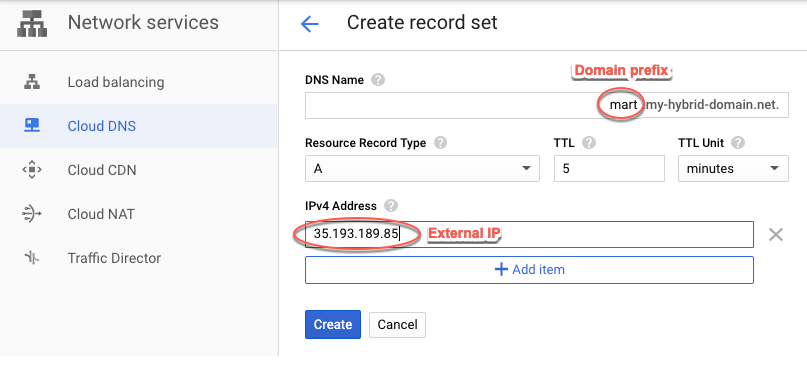
- Get the External IP that you reserved for
apigee-hybrid-runtime. - Create record set for the Istio ingress endpoint. This is the address for making API
calls to the hybrid gateway. Enter the External IP you obtained in the previous
step and add a prefix to the domain name, such as
apitest. For instructions, see Create a new record.
- Copy the DNS record data, as shown in the following example:
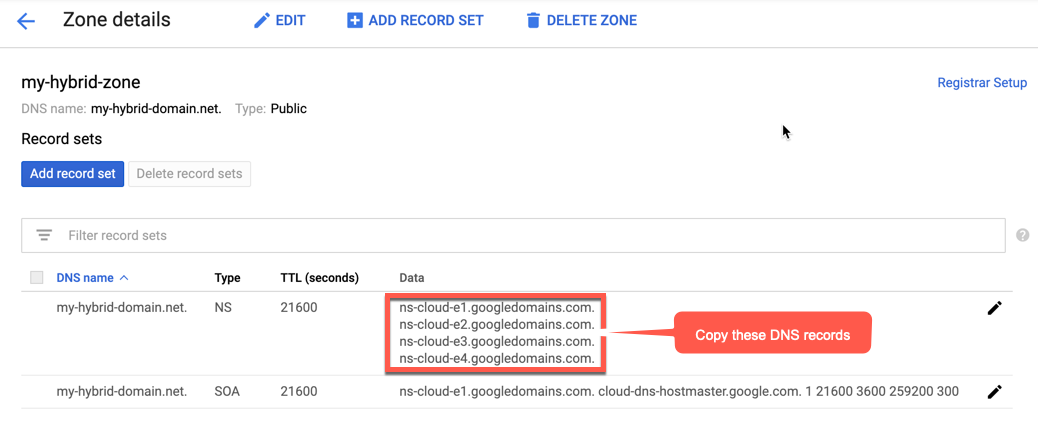
- Return to your domain page at Google Domains.
- Select your domain.
- Select DNS.
- In the Name Servers section, click Edit.
Enter the domain name servers that you copied from the Network Services Cloud DNS page:
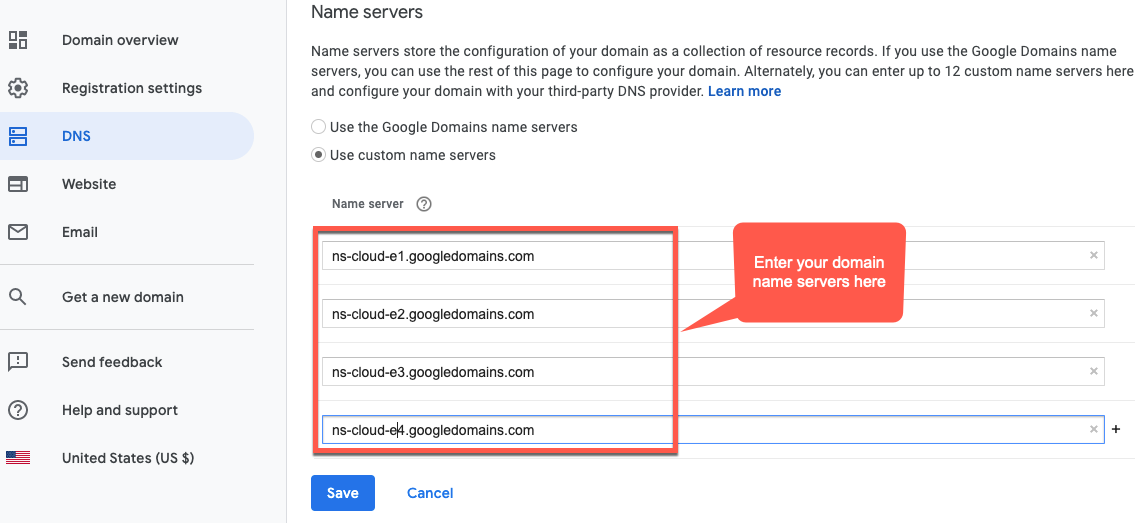
Now, your Google Cloud DNS will manage the DNS records for your domain.
Install Certbot on a VM
Now that you have Cloud DNS set up to manage your domain servers, you will install the Certbot client with the dns_google plugin on a Cloud VM. The client enables you to get authorized certificates for your domain from a Let's Encrypt endpoint.
- Open the Google Cloud console and log in with the account you created in Step 1: Create a Google Cloud account.
- Select the project that you created in Step 2: Create a GCP project.
- Select IAM & admin > Service accounts.
The Service accounts view displays a list of the project’s service accounts.
- To create a new service account, click +Create Service Account at the top of
the view.
The Service account details view displays.
- In the Service account name field, enter the name of the service account.

You can optionally add a description in the Service account description field. Descriptions are helpful at reminding you what a particular service account is used for.
- Click Create.
GCP creates a new service account and displays the Service account permissions view. Use this view to assign a role to your new service account.
- Click the Select a role drop-down list.
- Select the Project Owner role.
- Click Continue.
- Click Done.
- In the GCP console, select Compute Engine > VM Instances.
- Create a VM instance named certmanager.
- Under the Boot Disk section, choose CentOS7 and 20 GB for the SSD persistent drive.
- Set the Service Account to the one you created above.
- Install Certbot and the dns_google
plugin on the machine and run the Certbot client:
sudo su -yum -y install yum-utilsyum install certbot -yyum install certbot-dns-google -ycertbot certonly --dns-google -d *.your_domain_name,*.your_domain_name --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directoryFor example:
sudo su -yum -y install yum-utilsyum install certbot -yyum install certbot-dns-google -ycertbot certonly --dns-google -d *.apigee-hybrid-docs.net,*.apigee-hybrid-docs.net --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - You can now find your authorized certificate and private key files in this directory:
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain_name/For example:
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/apigee-hybrid-docs.netlscert.pem chain.pem fullchain.pem privkey.pem README - Copy the files
fullchain.pemandprivkey.pemto your local machine. - Update your overrides file to point to the certificate and private key. For the
hostAlias, use the DNS name that you created previously.For example:
envs: - name: test sslCertPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/fullchain.pem" sslKeyPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/privkey.pem" hostAlias: "apitest.apigee-hybrid-docs.net" mart: nodeSelector: key: cloud.google.com/gke-nodepool value: apigee-runtime sslCertPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/fullchain.pem" sslKeyPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/privkey.pem" replicaCountMin: 1 replicaCountMax: 1 hostAlias: "mart.apigee-hybrid-docs.net" - Apply the changes:
If you changed the
martconfiguration, apply the changes:apigeectl apply -f your_overrides_file -c mart
If you changed the
envsconfiguration, apply the changes:apigeectl apply -f your_overrides_file -c runtime
Test the configuration
Deploy and test a proxy, as explained in Create and deploy a new API proxy.
