Este tópico é apenas um exemplo. Ele explica como conseguir um certificado TLS da autoridade de certificação (CA, na sigla em inglês) Let's Encrypt (em inglês). Essas etapas são fornecidas principalmente como um exemplo a ser seguido se você não tiver outra maneira pronta de obter um par de certificado/chave autorizado por uma CA. No exemplo, mostramos como gerar certificados usando a CA Let's Encrypt, o cliente Certbot e o Cloud DNS do Google Cloud Platform.
Onde usar essas credenciais
Você precisa fornecer credenciais TLS para dois gateways de entrada do Istio expostos fora do cluster:
| Gateway | Requisito de TLS |
|---|---|
| Gateway de entrada do MART | Requer um par de chave/certificado TLS autorizado. |
| Gateway de entrada do ambiente de execução | É possível usar um par de certificado/chave autoassinado ou credenciais TLS autorizadas. |
Requisitos
Você precisará de um nome de domínio proveniente de um registrador de nomes de domínio. É possível registrar um nome de domínio por meio do Google Domains ou outro registro de domínios da sua escolha.
Configurar o Cloud DNS
Para conseguir credenciais TLS autorizadas, você precisa ter um nome de domínio qualificado. As etapas a seguir explicam como usar o Google Cloud DNS para conseguir um nome de domínio e gerenciar seus servidores de domínio.- Abra o Console do Google Cloud e faça login com a conta que você criou na Etapa 1: criar uma conta do Google Cloud.
- Selecione o projeto criado na Etapa 2: criar um projeto do GCP.
- Ative a API Cloud DNS. Consulte Como ativar APIs.
- Crie dois endereços IP estáticos:
- Se você estiver no GKE, siga as instruções em
Como reservar um endereço IP externo estático para criar
dois endereços IP estáticos. É possível atribuir os nomes a qualquer nome, como
apigee-hybrid-marteapigee-hybrid-runtime. Quando terminar, você terá dois números de IP para usar na configuração do cluster na próxima etapa. Por exemplo:35.225.131.189e34.66.75.196. - Se você estiver no Anthos GKE, siga as instruções na documentação do Anthos GKE para criar dois endereços IP estáticos.
- Se você estiver no GKE, siga as instruções em
Como reservar um endereço IP externo estático para criar
dois endereços IP estáticos. É possível atribuir os nomes a qualquer nome, como
- Crie uma zona pública gerenciada. Para mais instruções, consulte Criar uma zona pública gerenciada.
- Consiga o IP externo reservado para o
apigee-hybrid-mart. - Cria um conjunto de registros para o endpoint MART. Insira o IP externo que você recebeu na etapa anterior
e adicione um prefixo ao nome do domínio, como
mart. Para mais instruções, consulte Criar um novo registro.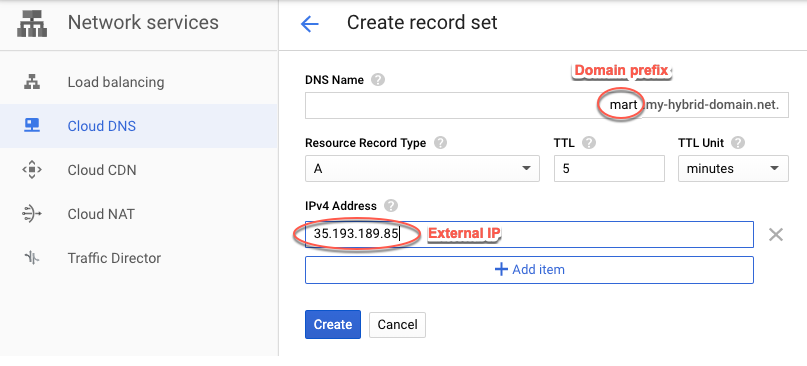
- Receba o IP externo reservado para
apigee-hybrid-runtime. - Crie um conjunto de registros para o endpoint de entrada do Istio. Esse é o endereço para fazer
chamadas de API para o gateway híbrido. Insira o IP externo que você recebeu na etapa anterior
e adicione um prefixo ao nome do domínio, como
apitest. Para mais instruções, consulte Criar um novo registro.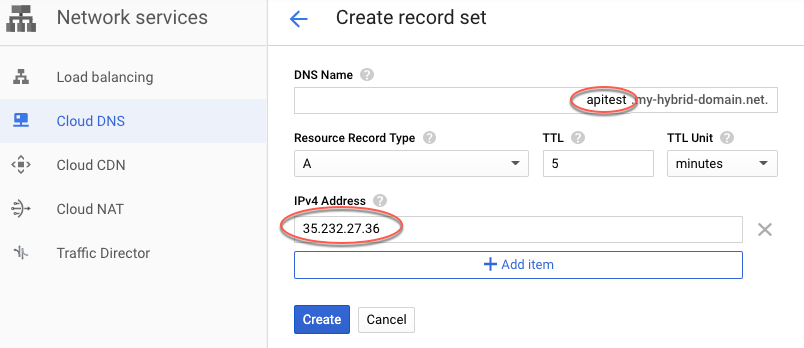
- Copie os dados do registro DNS, conforme mostrado no exemplo a seguir:
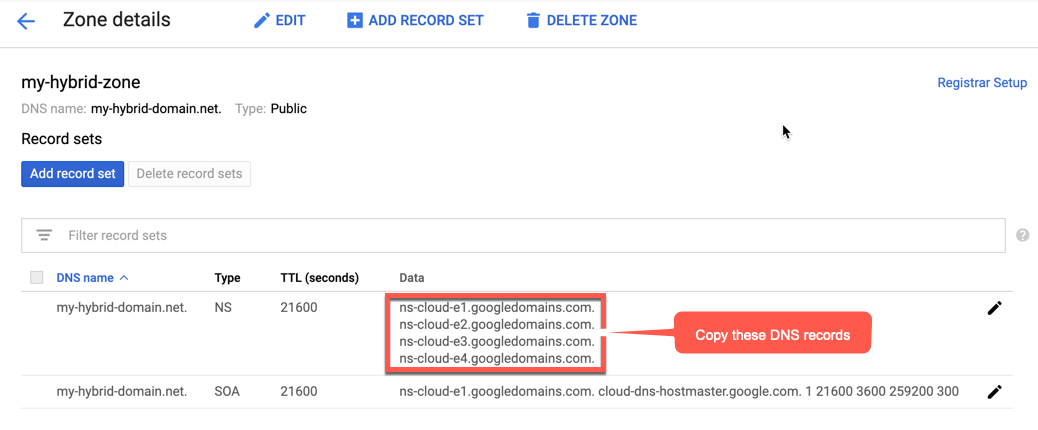
- Volte para a página do seu domínio no Google Domains.
- Selecione seu domínio.
- Selecione DNS.
- Na seção "Servidores de nomes", clique em Editar.
Insira os servidores de nomes de domínio que você copiou da página Serviços de rede do Cloud DNS.
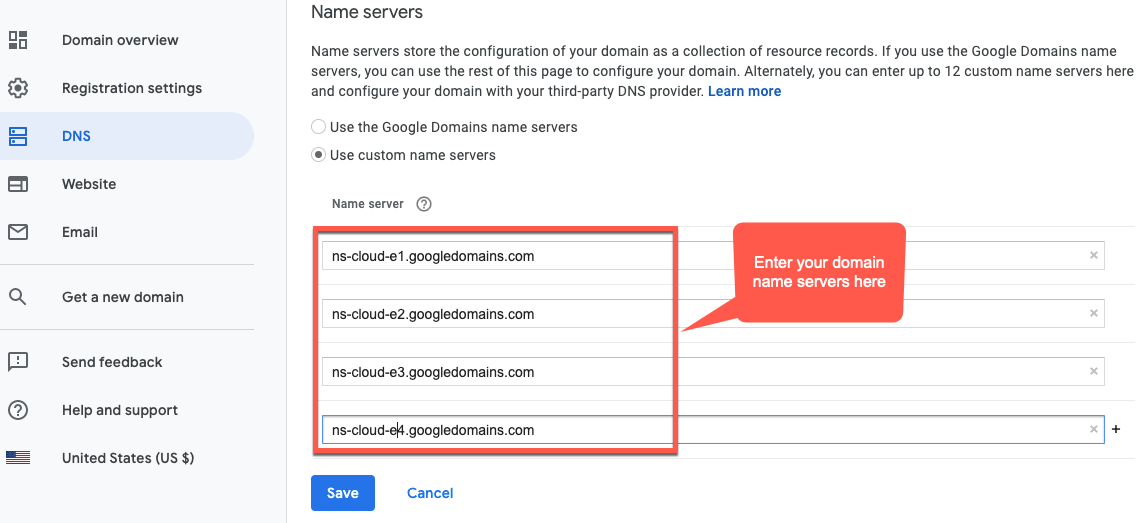
Agora o Google Cloud DNS gerenciará os registros DNS do seu domínio.
Instalar o Certbot em uma VM
Agora que o Cloud DNS está configurado para gerenciar os servidores de domínio, instale o cliente Certbot com o plug-in dns_google em uma VM do Cloud. O cliente permite que você receba certificados autorizados para seu domínio a partir de um endpoint Let's Encrypt.
- Abra o Console do Google Cloud e faça login com a conta que você criou na Etapa 1: criar uma conta do Google Cloud.
- Selecione o projeto criado na Etapa 2: criar um projeto do GCP.
- Selecione IAM e administrador > Contas de serviço.
A visualização "Contas de serviço" exibe uma lista das contas de serviço do projeto.
- Para criar uma nova conta de serviço, clique em +Criar conta de serviço na parte superior
da visualização.
A visualização Detalhes da conta de serviço é exibida.
- No campo Nome da conta de serviço, insira o nome da conta de serviço.
Se quiser, adicione uma descrição no campo Descrição da conta de serviço. As descrições são úteis para lembrar você sobre como uma conta de serviço específica é usada.
- Clique em Criar
O GCP cria uma nova conta de serviço e exibe a visualização Permissões da conta de serviço. Use essa visualização para atribuir um papel à sua nova conta de serviço.
- Clique na lista suspensa Selecionar um papel.
- Selecione o papel Proprietário do projeto.
- Clique em Continuar.
- Clique em Concluído.
- No console do GCP, selecione Compute Engine > Instâncias de VM.
- Crie uma instância de VM chamada certmanager.
- Na seção "Disco de inicialização", escolha CentOS7 e 20 GB para a unidade permanente SSD.
- Defina a conta de serviço como a que você criou acima.
- Instale o Certbot e o plug-in dns_google
na máquina e execute o cliente do Certbot:
sudo su -yum -y install yum-utilsyum install certbot -yyum install certbot-dns-google -ycertbot certonly --dns-google -d *.your_domain_name,*.your_domain_name --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directoryExemplo:
sudo su -yum -y install yum-utilsyum install certbot -yyum install certbot-dns-google -ycertbot certonly --dns-google -d *.apigee-hybrid-docs.net,*.apigee-hybrid-docs.net --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - Agora é possível encontrar o certificado autorizado e os arquivos de chave privada nesse diretório:
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain_name/Exemplo:
cd /etc/letsencrypt/live/apigee-hybrid-docs.netlscert.pem chain.pem fullchain.pem privkey.pem README - Copie os arquivos
fullchain.pemeprivkey.pempara sua máquina local. - Atualize seu arquivo de modificação para apontar para o certificado e a chave privada. Para o
hostAliases, use o nome do DNS que você criou anteriormente.Exemplo:
... envs: - name: test serviceAccountPaths: synchronizer: "your_keypath/synchronizer-manager-service-account.json udca: "your_keypath/analytic-agent-service-account.json virtualhosts: - name: default hostAliases: ["apitest.apigee-hybrid-docs.net"] sslCertPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/fullchain.pem" sslKeyPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/privkey.pem" routingRules: - env: test mart: nodeSelector: key: cloud.google.com/gke-nodepool value: apigee-runtime sslCertPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/fullchain.pem" sslKeyPath: "$HOME/hybrid/apigee-hybrid-setup/tls/privkey.pem" replicaCountMin: 1 replicaCountMax: 1 hostAlias: "mart.apigee-hybrid-docs.net" - Aplique as alterações:
Se você alterou a configuração
mart, aplique as alterações:apigeectl apply -f your_overrides_file -c mart
Se você alterou a configuração
envs, aplique as alterações:apigeectl apply -f your_overrides_file -c runtime
Testar a configuração
Implante e teste um proxy, conforme explicado em Criar e implantar um novo proxy de API.
