本页面适用于 Apigee 和 Apigee Hybrid。
查看 Apigee Edge 文档。
![]()
本主题简要介绍 Apigee 系统架构,旨在帮助您了解预配期间会创建哪些组件以及它们在整个系统中的用途。
Apigee 提供两个预配选项:使用 VPC 对等互连和不使用 VPC 对等互连。下面的几个部分将介绍这两个选项。
启用了 VPC 对等互连的架构
本部分介绍当 Apigee 预配了 VPC 对等互连选项时的 Apigee 系统架构。
预配概览
在预配期间,将配置和创建组件,以允许您管理的虚拟专用云网络 (VPC) 与 Apigee 管理的 VPC 网络之间进行双向通信。完成前几个预配步骤后,两个 VPC 已存在,但仍无法来回通信。需要进一步的配置以允许双向通信。请参阅图 1。
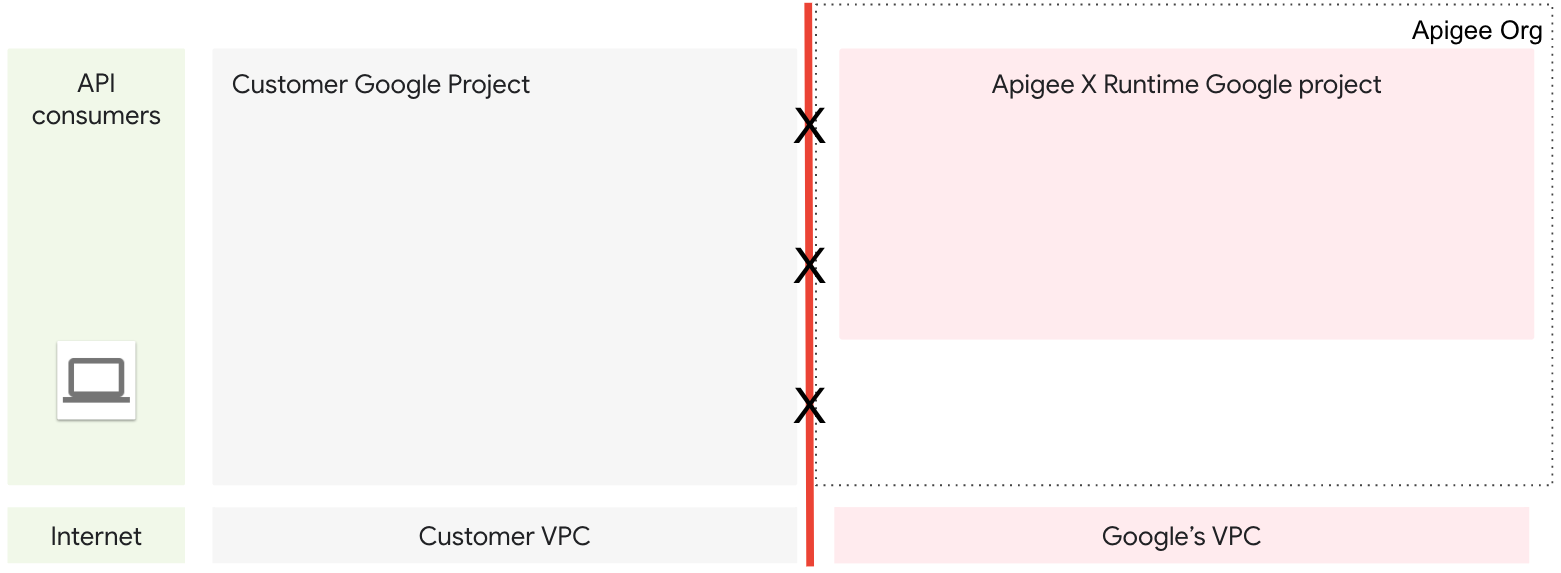
为了实现 VPC 之间的通信,我们使用 VPC 网络对等互连。网络对等互连允许跨两个 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) 网络的内部 IP 地址连接(无论它们是否属于同一个项目或 Google Cloud 组织)。在网络对等互连步骤完成后,两个 VPC 可以进行通信。请参阅图 2。
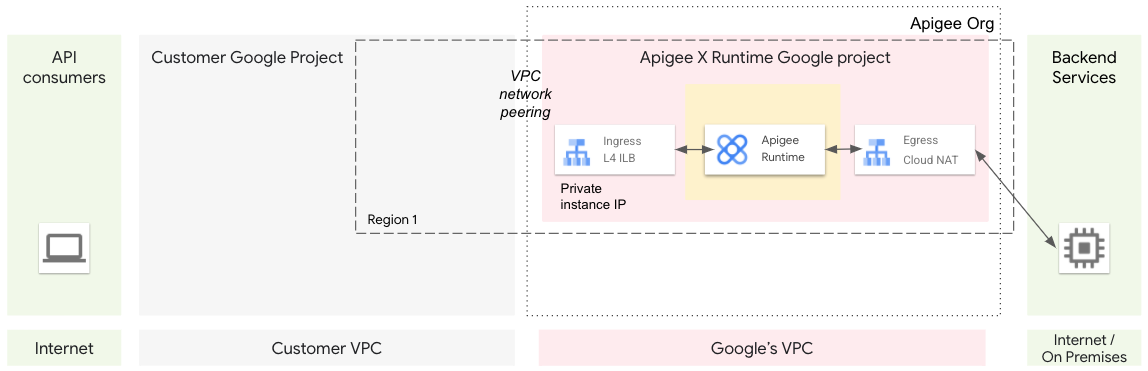
为了将流量从互联网上的客户端应用路由到 Apigee,我们使用全球外部 HTTPS 负载均衡器 (XLB)。XLB 可以使用跨项目服务引用,跨 Google Cloud 项目(例如在客户 Google Cloud 项目和 Apigee Google Cloud 项目之间)进行通信。
您还可以预配充当网络网桥的虚拟机的托管式实例组 (MIG)。MIG 虚拟机能够跨对等互连的网络进行双向通信。预配完成后,互联网上的应用与 XLB 通信,XLB 与网桥虚拟机通信,而网桥虚拟机与 Apigee 网络通信。请参见图 3 和图 4。

在此配置中,流量从 Apigee(例如,从 MessageLogging 政策)路由到内部 VPC 中运行的工作负载。在这种情况下,与内部 VPC 的通信不会通过出站流量的 NAT IP。您可以通过其中一个 Apigee 实例 IP 路由流量。
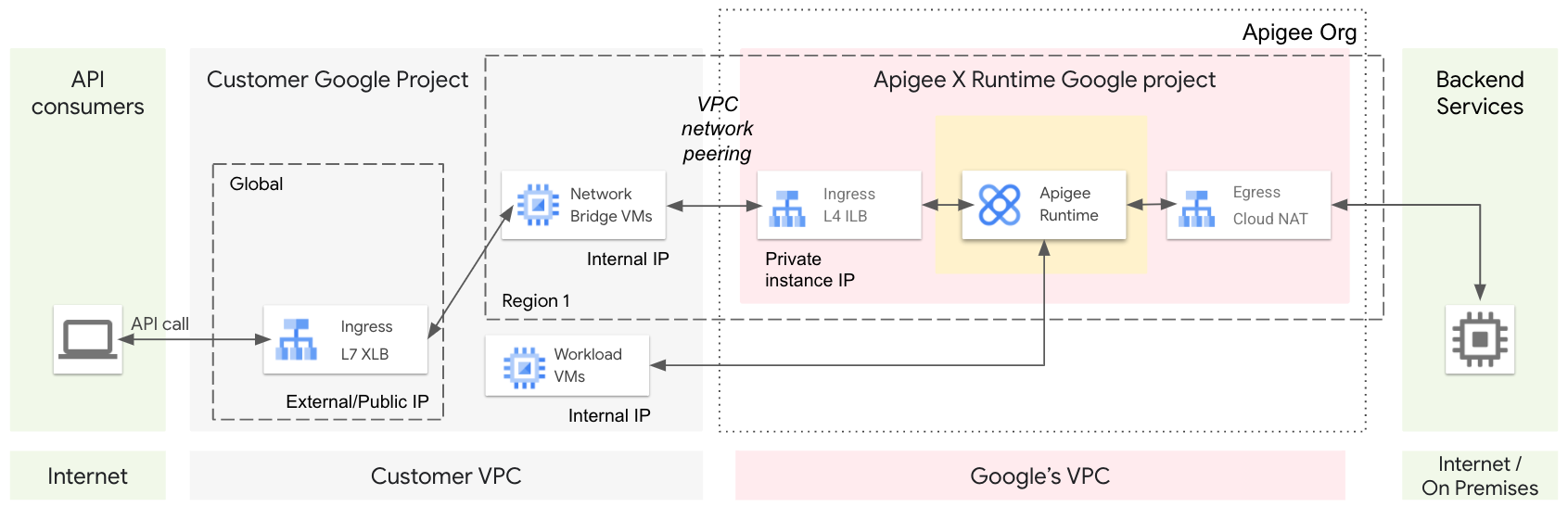
API 代理调用生命周期
下图显示了 API 代理调用通过预配 Apigee 系统组件的生命周期(图 5):
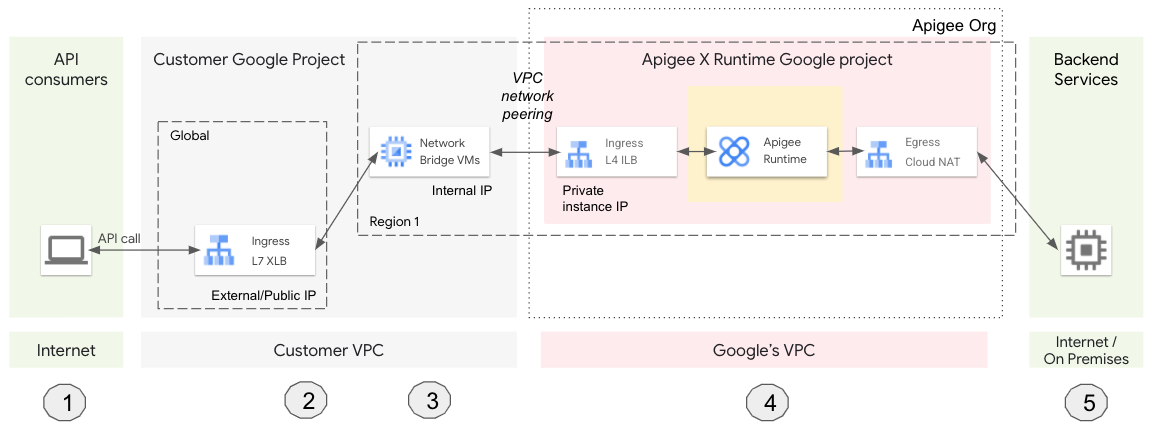
- 客户端应用调用 Apigee API 代理。
- 该请求发送到全球 L7 外部 HTTPS 负载均衡器 (XLB)。XLB 是使用外部/公共 IP 地址和 TLS 证书配置的。
- XLB 将请求发送到虚拟机。虚拟机充当您的 VPC 与 Google 的 VPC(由 Apigee 管理)之间的网桥。
- 虚拟机会向处理 API 代理请求的 Apigee 发送请求。
- Apigee 将请求发送到后端服务,而响应将发送回客户端。
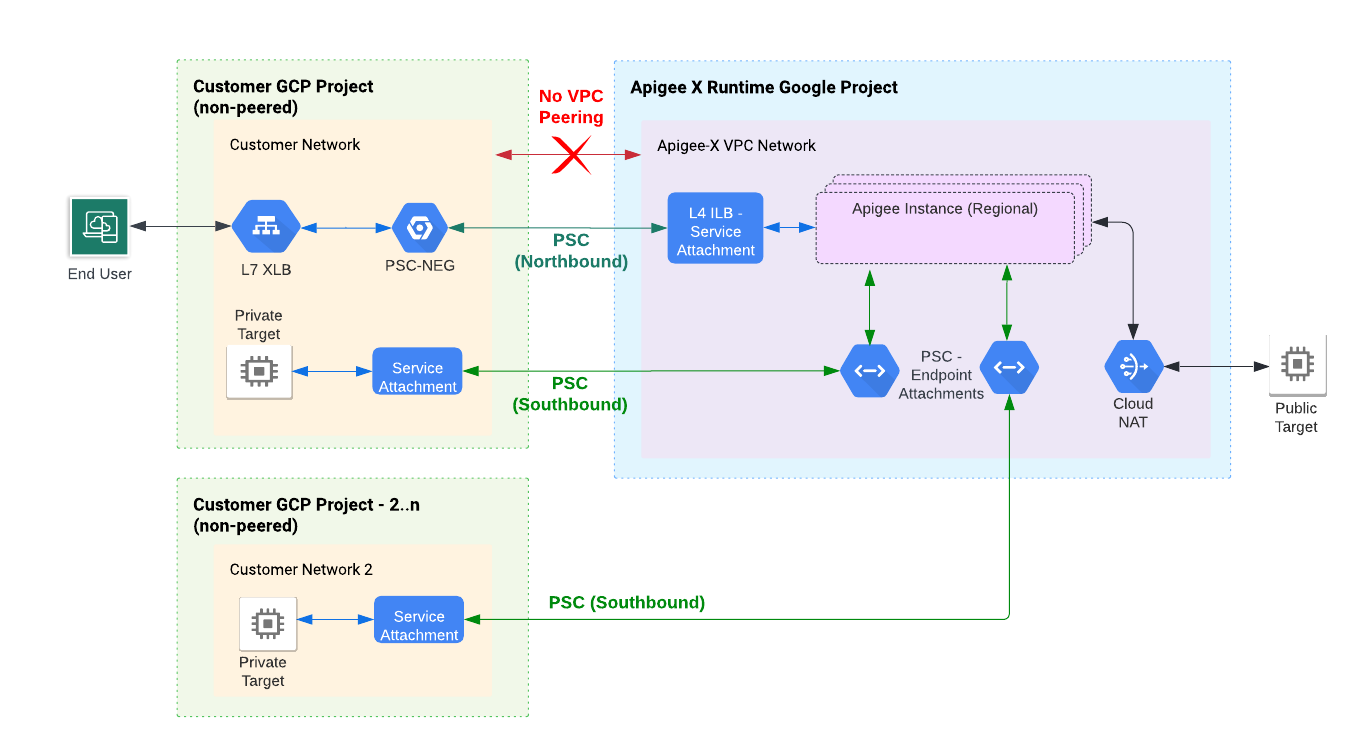
停用了 VPC 对等互连的架构
本部分介绍当 Apigee 未预配 VPC 对等互连选项时的 Apigee 系统架构。
在预配期间,将配置和创建组件,以允许您管理的虚拟专用云网络 (VPC) 与 Apigee 管理的 VPC 网络之间进行双向通信。完成前几个预配步骤后,两个 VPC 已存在,但仍无法来回通信。需要进一步的配置以允许双向通信。请参阅图 6。
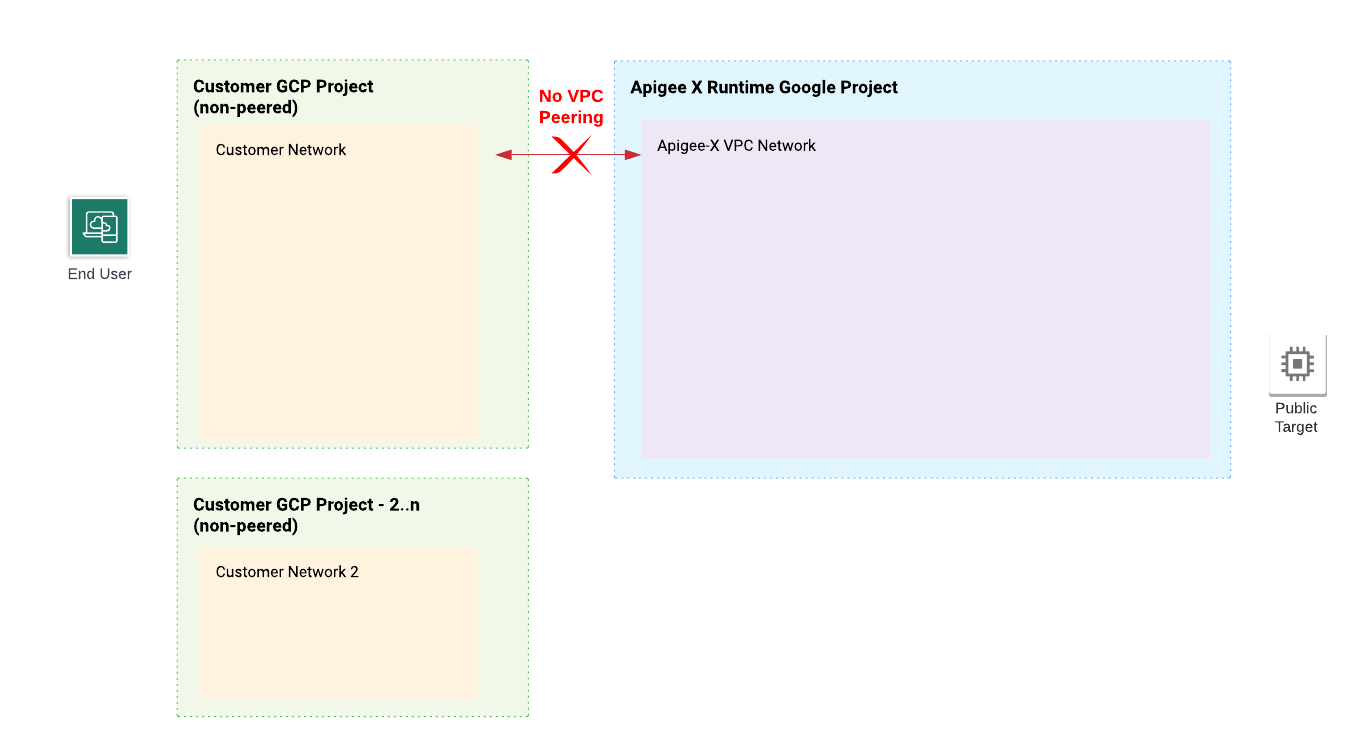
为了实现 VPC 之间的通信,我们使用 Private Service Connect (PSC) 将北向流量路由到 Apigee,将南向流量路由到在 Google Cloud 项目中运行的目标服务。
PSC 可在服务提供方 (Apigee) 和服务使用方(由您控制的一个或多个其他 Cloud 项目)之间启用专用连接。借助这种方法(图 7),请求会通过全球外部负载均衡器或区域外部负载均衡器传递到单连接点(称为服务连接)。
如需以非公开方式将 Apigee 连接到后端目标,您必须创建两个实体:在部署目标的 VPC 网络中创建一个服务连接,在 Apigee VPC 中创建一个端点连接。有了这两个实体,便可以将 Apigee 连接到目标服务。请参阅南向网络模式。
不使用 VPC 对等互连进行命令行预配中介绍了使用 PSC(不使用 VPC 对等互连)预配 Apigee 的步骤。