Auf dieser Seite wird erläutert, wie Sie Vorhersagen aus Ihrem Bildklassifizierungsmodell bereitstellen und in einer Webanwendung aufrufen.
Diese Anleitung umfasst mehrere Seiten:Vorhersagen aus einem benutzerdefinierten Bildklassifizierungsmodell bereitstellen
Auf jeder Seite wird davon ausgegangen, dass Sie die Anleitung auf den vorherigen Seiten des Leitfadens bereits ausgeführt haben.
Im weiteren Verlauf dieses Dokuments wird davon ausgegangen, dass Sie dieselbe Cloud Shell-Umgebung verwenden, die Sie erstellt haben, wenn Sie der ersten Seite dieser Anleitung gefolgt sind. Wenn Ihre ursprüngliche Cloud Shell-Sitzung nicht mehr geöffnet ist, können Sie mit folgenden Schritten zur Umgebung zurückkehren:-
In the Google Cloud console, activate Cloud Shell.
-
Führen Sie in der Cloud Shell-Sitzung den folgenden Befehl aus:
cd hello-custom-sample
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console im Bereich „Vertex AI“ die Seite Modelle auf.
Suchen Sie die Zeile des Modells,
hello_custom, das Sie im vorherigen Schritt dieser Anleitung trainiert haben, und klicken Sie auf den Namen des Modells, um die Detailseite des Modells zu öffnen.Klicken Sie auf dem Tab Bereitstellen und testen auf Auf Endpunkt bereitstellen, um den Bereich Auf Endpunkt bereitstellen zu öffnen.
Fügen Sie im Schritt Endpunkt definieren einige grundlegende Informationen für den Endpunkt hinzu:
Wählen Sie Neuen Endpunkt erstellen aus.
Geben Sie im Feld Endpunktname
hello_customein.Prüfen Sie im Abschnitt Modelleinstellungen, ob der Name Ihres Modells mit dem Namen
hello_customangezeigt wird. Geben Sie die folgenden Modelleinstellungen an:Geben Sie im Feld Trafficaufteilung den Wert
100ein. Vertex AI unterstützt das Aufteilen des Traffics für einen Endpunkt in mehrere Modelle. In dieser Anleitung wird diese Funktion jedoch nicht verwendet.Geben Sie im Feld Mindestanzahl von Knoten den Wert
1ein.Wählen Sie in der Drop-down-Liste Maschinentyp die Option n1-standard-2 aus dem Abschnitt Standard aus.
Klicken Sie auf Fertig.
Prüfen Sie im Abschnitt Logging, ob beide Arten von Vorhersage-Logging aktiviert sind.
Klicken Sie auf Weiter.
Bestätigen Sie im Schritt Endpunktdetails, dass der Endpunkt in
us-central1 (Iowa)bereitgestellt wird.Klicken Sie nicht das Kästchen Vom Kunden verwalteten Verschlüsselungsschlüssel verwenden an. In dieser Anleitung wird CMEK nicht verwendet.
Klicken Sie auf Bereitstellen, um den Endpunkt zu erstellen und Ihr Modell auf dem Endpunkt bereitzustellen.
Sie können eine Cloud Run Functions-Funktion so konfigurieren, dass sie nicht authentifizierte Anfragen empfängt. Außerdem werden Funktionen mit einem Dienstkonto mit der Rolle "Bearbeiter" ausgeführt. Dieses Feature enthält die Berechtigung
aiplatform.endpoints.predict, die erforderlich ist, um Vorhersagen von Ihrem Vertex AI-Endpunkt abzurufen.Diese Funktion führt auch eine sinnvolle Vorverarbeitung von Anfragen durch. Der Vertex AI-Endpunkt erwartet Vorhersageanfragen im Format der ersten Schicht der TensorFlow Keras-Grafik: einen Tensor der normalisierten floats mit festen Abmessungen. Die Funktion nimmt die URL eines Bildes als Eingabe an und verarbeitet das Bild in dieses Format, bevor eine Vorhersage vom Vertex AI-Endpunkt angefordert wird.
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console im Abschnitt „Vertex AI“ die Seite Endpunkte auf.
Suchen Sie die Zeile des Endpunkts, die Sie im vorherigen Abschnitt erstellt haben und den Namen
hello_customerhalten. Klicken Sie in dieser Zeile auf Beispielanfrage, um den Bereich Beispielanfrage zu öffnen.Suchen Sie im Bereich Beispielanfrage nach der Zeile des Shell-Codes, der dem folgenden Muster entspricht:
ENDPOINT_ID="ENDPOINT_ID"
ENDPOINT_ID ist eine Zahl, die diesen Endpunkt identifiziert.
Kopieren Sie diese Codezeile und führen Sie sie in Ihrer Cloud Shell-Sitzung aus, um die Variable
ENDPOINT_IDfestzulegen.Führen Sie in Ihrer Cloud Shell-Sitzung den folgenden Befehl aus, um die Cloud Run Functions-Funktion bereitzustellen:
gcloud functions deploy classify_flower \ --region=us-central1 \ --source=function \ --runtime=python37 \ --memory=2048MB \ --trigger-http \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --set-env-vars=ENDPOINT_ID=${ENDPOINT_ID}Legen Sie einige Shell-Variablen für Befehle in den folgenden Schritten fest:
PROJECT_ID=PROJECT_ID BUCKET_NAME=BUCKET_NAMEErsetzen Sie Folgendes:
- PROJECT_ID: Ihre Google Cloud Projekt-ID.
- BUCKET_NAME: Der Name des Cloud Storage-Buckets, den Sie erstellt haben, wenn Sie der ersten Seite dieser Anleitung gefolgt sind.
Bearbeiten Sie die Anwendung so, dass sie die Trigger-URL Ihrer Cloud Run Functions-Funktion enthält:
echo "export const CLOUD_FUNCTION_URL = 'https://us-central1-${PROJECT_ID}.cloudfunctions.net/classify_flower';" \ > webapp/function-url.jsLaden Sie das Verzeichnis
webappin Ihren Cloud Storage-Bucket hoch:gcloud storage cp webapp gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/ --recursiveMachen Sie die Webanwendungsdateien, die Sie gerade hochgeladen haben, öffentlich lesbar:
gcloud storage objects update gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/webapp/** --add-acl-grant=entity=allUsers,role=READERSie können jetzt die folgende URL aufrufen, um eine Webanwendung zu öffnen und Vorhersagen abzurufen:
https://storage.googleapis.com/BUCKET_NAME/webapp/index.html
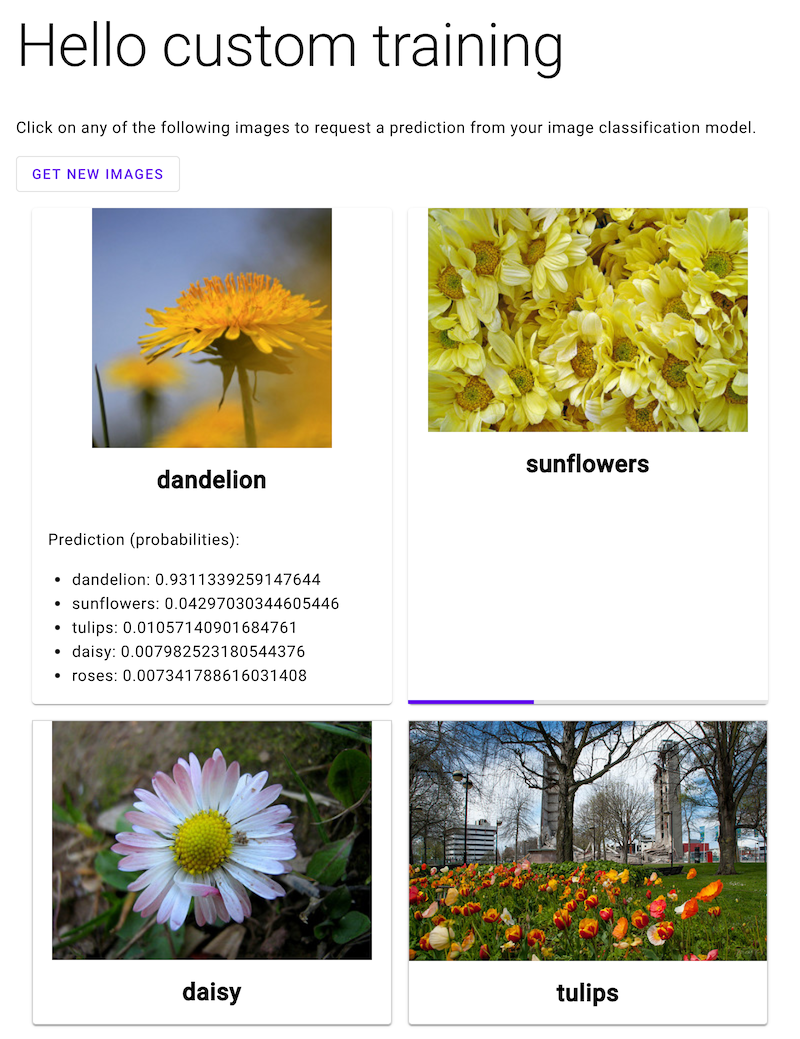
Öffnen Sie die Webanwendung und klicken Sie auf ein Bild einer Blume, um die Klassifizierung des ML-Modells anzusehen. Die Webanwendung stellt die Vorhersage als Liste der Blumentypen und die Wahrscheinlichkeit dar, dass das Bild jede Art von Blumen enthält.
Endpunkt erstellen
Erstellen Sie einen Vertex AI-Endpunkt, um Onlinevorhersagen aus dem ML-Modell abzurufen, das Sie zuvor auf der vorherigen Seite dieser Anleitung trainiert haben. Endpoints stellt Onlinevorhersagen aus einem oder mehreren Modellen bereit.
Nach einigen Minuten wird in der Tabelle Endpoints neben dem neuen Endpunkt angezeigt. Gleichzeitig erhalten Sie eine E-Mail, in der Sie darüber informiert werden, dass Sie den Endpunkt erstellt und Ihr Modell auf dem Endpunkt bereitgestellt haben.
Cloud Run-Funktion bereitstellen
Sie können Vorhersagen aus dem soeben erstellten Vertex AI-Endpunkt abrufen, indem Sie Anfragen an die REST-Schnittstelle der Vertex AI API senden. Allerdings können nur Hauptkonten mit der Berechtigung aiplatform.endpoints.predict Anfragen für Onlinevorhersagen senden. Sie können den Endpunkt nicht für jeden freigeben, der Anfragen senden kann, z. B. über eine Webanwendung.
In diesem Abschnitt stellen Sie Code für Cloud Run Functions bereit, um nicht authentifizierte Anfragen zu verarbeiten. Der Beispielcode, den Sie beim Lesen der ersten Seite dieser Anleitung heruntergeladen haben, enthält Code für diese Cloud Run Functions-Funktion im Verzeichnis function/. Führen Sie optional den folgenden Befehl aus, um sich den Cloud Run Functions-Code anzusehen:
less function/main.py
Die Bereitstellung der Funktion dient folgenden Zwecken:
So stellen Sie die Cloud Run Functions-Funktion bereit:
Eine Webanwendung zum Senden von Vorhersageanfragen bereitstellen
Hosten Sie schließlich eine statische Webanwendung in Cloud Storage, um Vorhersagen aus Ihrem trainierten ML-Modell zu erhalten. Die Webanwendung sendet Anfragen an Ihre Cloud Run Functions-Funktion, die sie vorverarbeitet und Vorhersagen vom Vertex AI-Endpunkt abruft.
Das Verzeichnis webapp des heruntergeladenen Beispielcodes enthält eine Beispiel-Webanwendung. Führen Sie in Ihrer Cloud Shell-Sitzung die folgenden Befehle aus, um die Webanwendung vorzubereiten und bereitzustellen:
Im folgenden Screenshot hat die Webanwendung bereits eine Vorhersage erhalten und wird eine weitere Vorhersageanfrage senden.
Nächste Schritte
Befolgen Sie die letzte Seite der Anleitung, um von Ihnen erstellte Ressourcen zu bereinigen.

