Wenn Sie einen Job ausführen, verwendet Model Monitoring v2 Daten aus Ihren Ziel- und Baseline-Datasets, berechnet Messwerte und generiert möglicherweise Benachrichtigungen. Model Monitoring v2 bietet On-Demand-Jobs für Ad-hoc-Monitoring oder geplante Jobs für kontinuierliches Monitoring. Unabhängig davon, welche Option Sie auswählen, ist jeder Job eine einzelne Batchausführung.
Weitere Informationen zu Monitoringzielen und unterstützten Modellen finden Sie unter Model Monitoring v2 – Übersicht und Modell-Monitoring einrichten.
Job on demand ausführen
Einmaligen Monitoring-Job ausführen Legen Sie die Ziel- und Baseline-Datasets sowie die Monitoring-Spezifikationen für die zu beobachtenden Zielvorhaben fest. Ihre Konfiguration überschreibt alle Standardwerte, sofern festgelegt, die vom Modellmonitor definiert werden.
Konsole
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Seite Monitoring auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Modellmonitor, für den Sie einen Monitoring-Job ausführen möchten.
Klicken Sie auf der Detailseite des Modellmonitors auf Jetzt ausführen, um den Monitoring-Job zu konfigurieren.
Konfigurieren Sie den Job oder verwenden Sie die im Modellmonitor definierten Standardeinstellungen.
Klicken Sie auf Ausführen.
Python SDK
from vertexai.resources.preview import ml_monitoring FEATURE_THRESHOLDS = { "culmen_length_mm": 0.001, "body_mass_g": 0.002, } FEATURE_DRIFT_SPEC=ml_monitoring.spec.DataDriftSpec( categorical_metric_type="l_infinity", numeric_metric_type="jensen_shannon_divergence", default_categorical_alert_threshold=0.001, default_numeric_alert_threshold=0.002, feature_alert_thresholds=FEATURE_THRESHOLDS, ) PREDICTION_OUTPUT_DRIFT_SPEC=ml_monitoring.spec.DataDriftSpec( categorical_metric_type="l_infinity", numeric_metric_type="jensen_shannon_divergence", default_categorical_alert_threshold=0.001, default_numeric_alert_threshold=0.001, ) FEATURE_ATTRIBUTION_SPEC=ml_monitoring.spec.FeatureAttributionSpec( default_alert_threshold=0.0003, feature_alert_thresholds={"cnt_ad_reward":0.0001}, ) EXPLANATION_SPEC=ExplanationSpec( parameters=ExplanationParameters( {"sampled_shapley_attribution": {"path_count": 2}} ), metadata=ExplanationMetadata( inputs={ "cnt_ad_reward": ExplanationMetadata.InputMetadata({ "input_tensor_name": "cnt_ad_reward", "encoding": "IDENTITY", "modality": "numeric" }), ... }, ... ) ) TRAINING_DATASET=ml_monitoring.spec.MonitoringInput( gcs_uri=TRAINING_URI, data_format="csv" ) TARGET_DATASET=ml_monitoring.spec.MonitoringInput( table_uri=BIGQUERY_URI ) model_monitoring_job=my_model_monitor.run( display_name=JOB_DISPLAY_NAME, baseline_dataset=TRAINING_DATASET, target_dataset=TARGET_DATASET, tabular_objective_spec=ml_monitoring.spec.TabularObjective( # Optional: set to monitor input feature drift. feature_drift_spec=FEATURE_DRIFT_SPEC, # Optional: set to monitor prediction output drift. prediction_output_drift_spec=PREDICTION_OUTPUT_DRIFT_SPEC, # Optional: set to monitor feature attribution drift. feature_attribution_spec=FEATURE_ATTRIBUTION_SPEC ), # Optional: additional configurations to override default values. explanation_config=EXPLANATION_SPEC, notification_spec=NOTIFICATION_SPEC, output_spec=OUTPUT_SPEC )
Kontinuierliche Ausführungen planen
Sie können einen oder mehrere geplante Ausführungen für einen Modellmonitor festlegen. Wenn Sie das kontinuierliche Monitoring mit Zeitangaben verwenden möchten, muss Ihr Dataset eine Zeitstempelspalte enthalten, damit Model Monitoring v2 die Daten aus dem angegebenen Zeitraum abrufen kann.
Konsole
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Seite Monitoring auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Modellmonitor, für den Sie das kontinuierliche Monitoring konfigurieren möchten.
Klicken Sie auf Wiederkehrende Ausführung planen.
Legen Sie die Ziel- und Baseline-Datasets fest und klicken Sie dann auf Weiter.
Legen Sie die zu überwachenden Zielvorhaben, ihre Grenzwerte sowie die Benachrichtigungseinstellungen fest, wenn eine Benachrichtigung generiert wird.
Klicken Sie auf Weiter.
Zeitplan für wiederkehrende Jobs konfigurieren:
- Geben Sie einen Namen für den Scheduler an.
- Geben Sie unter Startzeit an, wann der erste Job gestartet werden soll.
- Verwenden Sie für Häufigkeit einen Cron-Ausdruck, um die Häufigkeit zu bestimmen, und legen Sie dann die Zeitzone fest.
- Geben Sie unter Ende an, wann der Scheduler endet.
Klicken Sie auf Erstellen.
Python SDK
Verwenden Sie einen Cron-Ausdruck, um die Häufigkeit von Monitoring-Jobs festzulegen.
my_model_monitoring_schedule=my_model_monitor.create_schedule( display_name=SCHEDULE_DISPLAY_NAME, # Every day at 0:00(midnight) cron='"0 * * * *"', baseline_dataset=ml_monitoring.spec.MonitoringInput( endpoints=[ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_NAME], offset="24h", window="24h", ), target_dataset=ml_monitoring.spec.MonitoringInput( endpoints=[ENDPOINT_RESOURCE_NAME], window="24h" ), tabular_objective_spec=ml_monitoring.spec.TabularObjective( # Optional: set to monitor input feature drift. feature_drift_spec=FEATURE_DRIFT_SPEC, # Optional: set to monitor prediction output drift. prediction_output_drift_spec=PREDICTION_OUTPUT_DRIFT_SPEC, # Optional: set to monitor feature attribution drift. feature_attribution_spec=FEATURE_ATTRIBUTION_SPEC ), # Optional: additional configurations to override default values. explanation_config=EXPLANATION_SPEC, output_spec=OUTPUT_SPEC, notification_spec=NOTIFICATION_SPEC, )
Zeitplan pausieren oder fortsetzen
Sie können einen Zeitplan pausieren und fortsetzen, um die Ausführung von Monitoringjobs zu überspringen oder vorübergehend anzuhalten.
Konsole
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Seite Monitoring auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Modellmonitor, der den zu ändernden Zeitplan enthält.
Rufen Sie auf der Detailseite den Tab Zeitpläne auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Zeitplan, den Sie ändern möchten.
Klicken Sie auf Pausieren oder Fortsetzen, um den Zeitplan zu pausieren oder fortzusetzen.
Python SDK
# Pause schedule my_model_monitor.pause_schedule(my_monitoring_schedule.name) # Resume schedule my_model_monitor.resume_schedule(my_monitoring_schedule.name)
Zeitplan löschen
Löschen Sie einen Zeitplan, wenn Sie ihn nicht mehr verwenden. Ihre vorhandenen Daten und alle zuvor erstellten Jobs bleiben erhalten.
Konsole
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Seite Monitoring auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Modellmonitor, der den zu ändernden Zeitplan enthält.
Rufen Sie auf der Detailseite den Tab Zeitpläne auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Zeitplan, den Sie ändern möchten.
Klicken Sie auf Löschen und dann noch einmal auf Löschen, um den Löschvorgang zu bestätigen.
Python SDK
my_model_monitor.delete_schedule(my_monitoring_schedule.name)
Ergebnisse von Monitoringjobs analysieren
Sie können die Google Cloud Console verwenden, um die Datenverteilungen für jedes Monitoring-Ziel zu visualisieren und zu ermitteln, welche Änderungen im Zeitverlauf zu Abweichungen geführt haben.
Die Visualisierungen zeigen ein Histogramm, in dem die Datenverteilung zwischen den Ziel- und den Baseline-Daten verglichen wird. Je nach Toleranz können Sie beispielsweise die Pipeline zur Featuregenerierung anpassen oder das Modell neu trainieren.
Auftragsdetails aufrufen
Sie können sich Details zu einem Monitoring-Joblauf ansehen, z. B. eine Liste der überwachten Features und welche Features eine Benachrichtigung ausgelöst haben.
Konsole
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Seite Monitoring auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Modellmonitor, der den zu analysierenden Job enthält.
Klicken Sie auf der Seite Monitordetails auf den Tab Ausführungen.
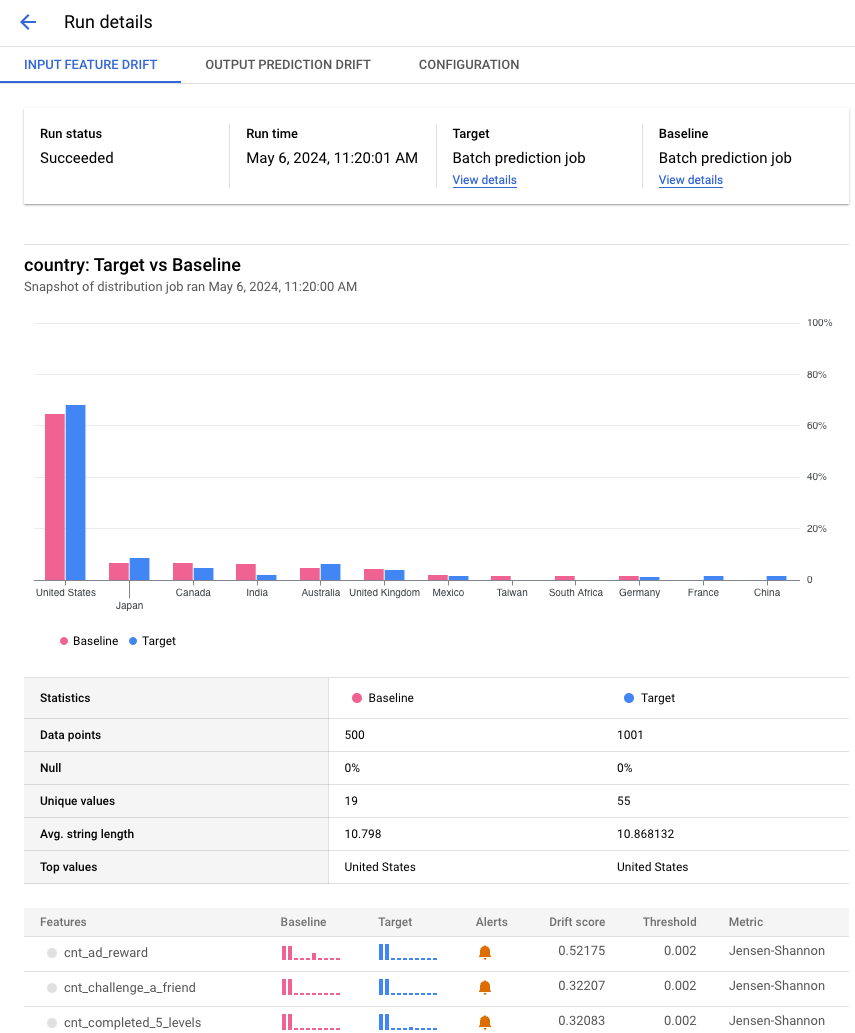
Klicken Sie in der Liste der Ausführungen auf eine Ausführung, um Details wie alle in einer Ausführung enthaltenen Features aufzurufen.
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt einen Verteilungsvergleich für das Attribut Land aus Jobs für die Batch-Vorhersage. In der Google Cloud Konsole finden Sie je nach Messwert auch Details zum Vergleich, z. B. die Anzahl der eindeutigen Werte, den Mittelwert und die Standardabweichung.
Featuredetails ansehen
Informationen zu einem Feature und eine Liste der Monitoringjobs, die das Feature enthalten, ansehen
Konsole
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Seite Monitoring auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Modellmonitor, der die zu analysierenden Jobs enthält.
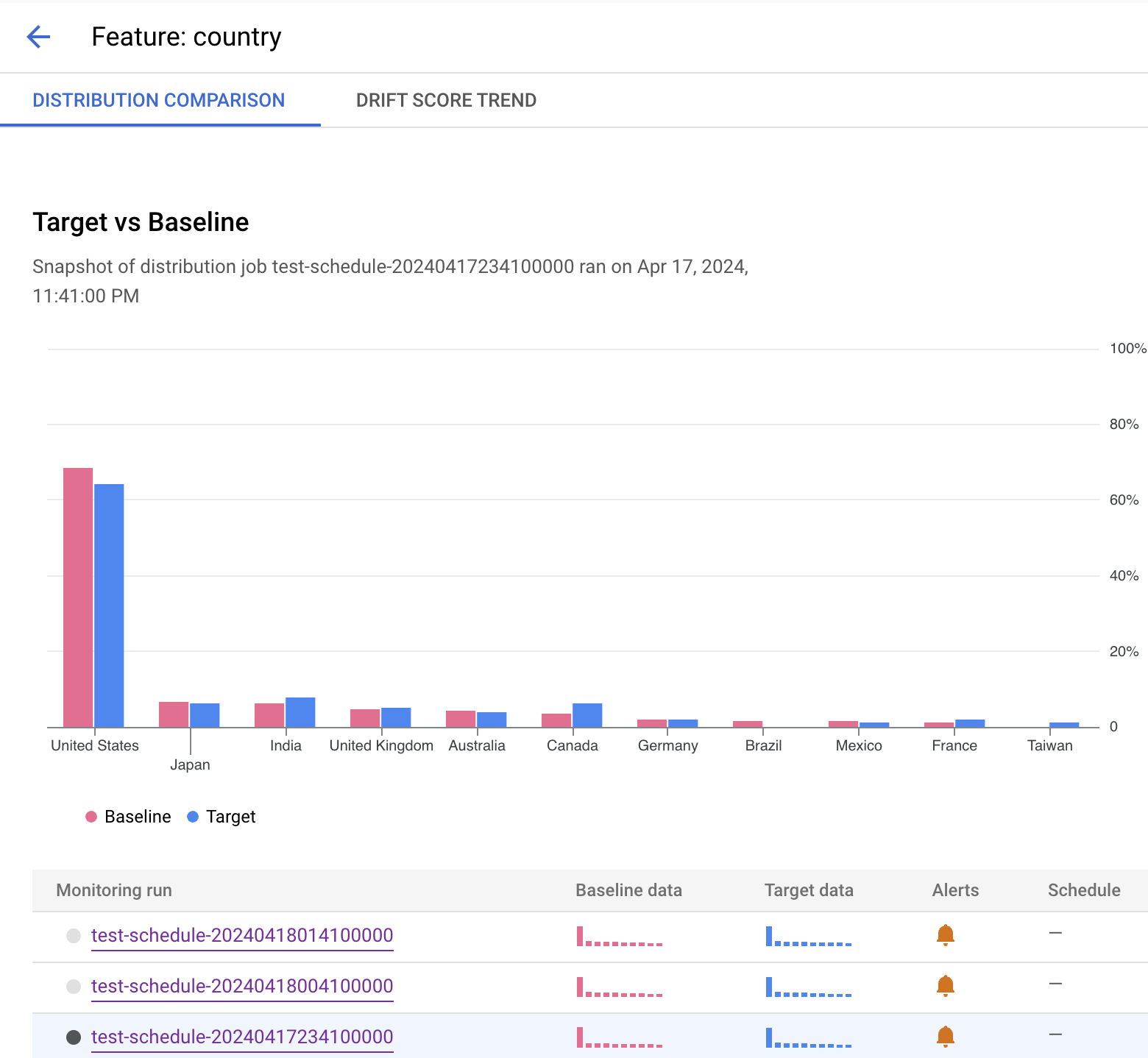
Im Tab Übersicht sehen Sie eine Zusammenfassung mit den Abweichungstrends aller beobachteten Zielvorhaben, sofern Sie das kontinuierliche Monitoring eingerichtet haben. Sie können sich auch bestimmte Zielvorhaben genauer ansehen, um Details wie die Namen der überwachten Funktionen und eine Liste der Monitoringausführungen zu sehen.
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt einen Verteilungsvergleich für das Attribut Land. Nach dem Histogramm sehen Sie, für welche Ausführungen eine Benachrichtigung generiert wurde, oder Sie können einen anderen Monitoring-Job auswählen, der Monitoring-Daten für dieses Feature enthält.