Nesta página, você verá como exibir previsões do modelo de classificação de imagens e visualizá-las em um app da Web.
Este tutorial tem várias páginas:Como treinar um modelo de classificação de imagens personalizado
Como exibir previsões de um modelo de classificação de imagens personalizado
Cada página pressupõe que você já tenha realizado as instruções das páginas anteriores do tutorial.
O restante deste documento pressupõe que você está usando o mesmo ambiente do Cloud Shell criado ao seguir a primeira página deste tutorial. Se a sessão original do Cloud Shell não estiver mais aberta, será possível retornar ao ambiente fazendo o seguinte:-
In the Google Cloud console, activate Cloud Shell.
-
Na sessão do Cloud Shell, execute o seguinte comando:
cd hello-custom-sample
No console Google Cloud , na seção "Vertex AI", acesse a página Modelos.
Encontre a linha do modelo que você treinou na etapa anterior deste tutorial,
hello_custom, e clique no nome do modelo para abrir a página de detalhes.Na guia Implantar e testar, clique em Implantar no endpoint para abrir o painel Implantar no endpoint.
Na etapa Definir seu endpoint, adicione algumas informações básicas para seu endpoint:
Selecione Criar novo endpoint.
No campo Nome do endpoint, digite
hello_custom.Na seção Configurações do modelo, verifique se você vê o nome do modelo, também chamado de
hello_custom. Especifique as seguintes configurações de modelo:No campo Divisão de tráfego, digite
100. A Vertex AI permite dividir o tráfego de um endpoint para vários modelos, mas este tutorial não usa esse recurso.No campo Número mínimo de nós de computação, digite
1.Na lista suspensa Tipo de máquina, selecione n1-standard-2 na seção Standard.
Clique em Concluído.
Na seção Geração de registros, verifique se os dois tipos de geração de registros de previsão estão ativados.
Clique em Continuar.
Na etapa Detalhes do endpoint, confirme se o endpoint será implantado em
us-central1 (Iowa).Não marque a caixa de seleção Usar uma chave de criptografia gerenciada pelo cliente (CMEK). Este tutorial não usa CMEK.
Clique em Implantar para criar o endpoint e implantar o modelo no endpoint.
É possível configurar uma função do Cloud Run para receber solicitações não autenticadas. Além disso, as funções são executadas usando uma conta de serviço com o papel "Editor" por padrão, que inclui a permissão
aiplatform.endpoints.predictnecessária para conseguir previsões do endpoint da Vertex AI.Esta função também realiza um pré-processamento útil das solicitações. O endpoint da Vertex AI espera solicitações de previsão no formato da primeira camada do gráfico treinado Keras do TensorFlow: um tensor de flutuantes normalizados com dimensões fixas. A função usa o URL de uma imagem como entrada e pré-processa a imagem nesse formato antes de solicitar uma previsão do endpoint da Vertex AI.
No console Google Cloud , na seção "Vertex AI", acesse a página Endpoints.
Encontre a linha do endpoint criado na seção anterior, chamada
hello_custom. Nessa linha, clique em Exemplo de solicitação para abrir o painel Exemplo de solicitação.No painel Exemplo de solicitação, localize a linha de código do shell que corresponde ao seguinte padrão:
ENDPOINT_ID="ENDPOINT_ID"
ENDPOINT_ID é um número que identifica esse endpoint específico.
Copie essa linha de código e execute-a na sessão do Cloud Shell para definir a variável
ENDPOINT_ID.Execute o seguinte comando na sessão do Cloud Shell para implantar a função do Cloud Run:
gcloud functions deploy classify_flower \ --region=us-central1 \ --source=function \ --runtime=python37 \ --memory=2048MB \ --trigger-http \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --set-env-vars=ENDPOINT_ID=${ENDPOINT_ID}Defina algumas variáveis do shell para que os comandos das próximas etapas usem:
PROJECT_ID=PROJECT_ID BUCKET_NAME=BUCKET_NAMESubstitua:
- PROJECT_ID: o ID do projeto Google Cloud .
- BUCKET_NAME: o nome do bucket do Cloud Storage criado ao seguir a primeira página deste tutorial.
Edite o app para fornecer o URL do gatilho da função do Cloud Run:
echo "export const CLOUD_FUNCTION_URL = 'https://us-central1-${PROJECT_ID}.cloudfunctions.net/classify_flower';" \ > webapp/function-url.jsFaça o upload do diretório
webapppara o bucket do Cloud Storage:gcloud storage cp webapp gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/ --recursiveTorne os arquivos do app da Web que você acabou de enviar publicamente acessíveis para leitura:
gcloud storage objects update gs://${BUCKET_NAME}/webapp/** --add-acl-grant=entity=allUsers,role=READERAgora navegue até o seguinte URL para abrir o app da Web e receber previsões:
https://storage.googleapis.com/BUCKET_NAME/webapp/index.html
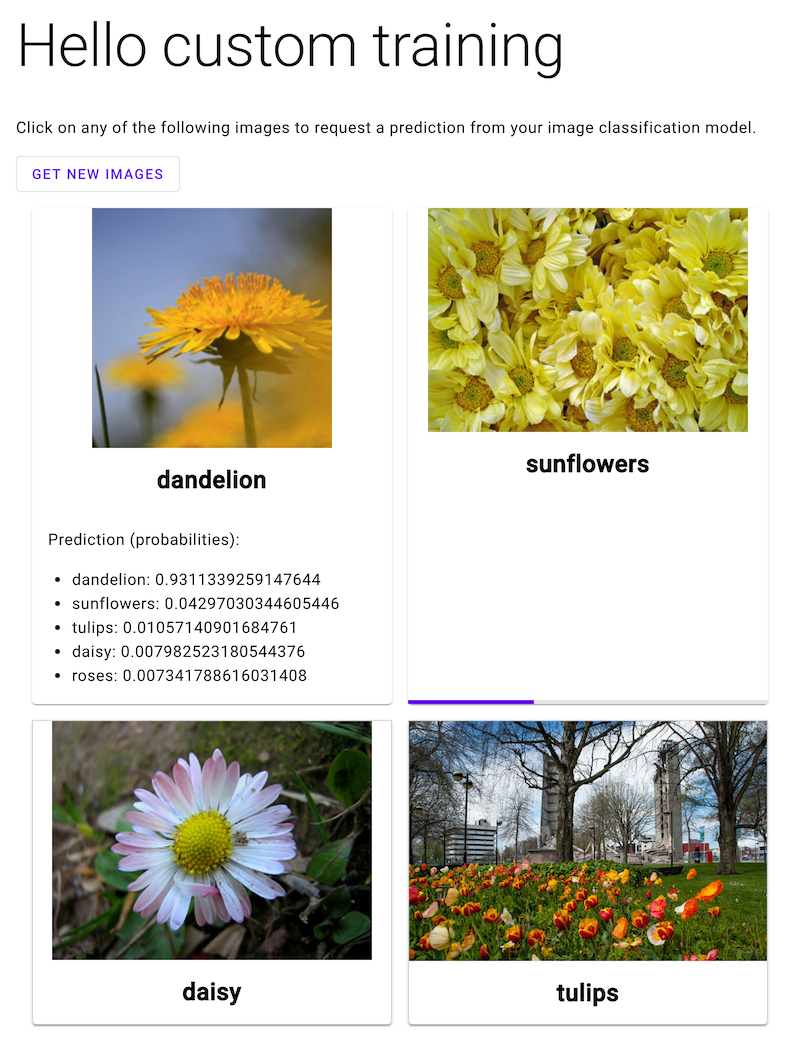
Abra o app da Web e clique na imagem de uma flor para ver a classificação do seu modelo de ML do tipo de flor. O app da Web apresenta a previsão como uma lista de tipos de flores e a probabilidade de que a imagem contenha cada tipo de flor.
Crie um endpoint
Para conseguir previsões on-line com base no modelo de ML que você treinou de acordo com a página anterior deste tutorial, crie um endpoint da Vertex AI. Os endpoints exibem previsões on-line de um ou mais modelos.
Após alguns minutos, aparecerá ao lado do novo endpoint na tabela Endpoints. Ao mesmo tempo, você também recebe um e-mail indicando que criou o endpoint e implantou o modelo no endpoint.
Implantar uma função do Cloud Run
É possível receber previsões do endpoint da Vertex AI que você acabou de
criar. Basta enviar solicitações para a interface REST da API Vertex AI. No entanto, somente
principals com a permissão
aiplatform.endpoints.predict podem enviar solicitações de previsão on-line. Não é
possível tornar o endpoint público para que qualquer pessoa envie solicitações, por exemplo,
por meio de um app da Web.
Nesta seção, implante o código nas funções do Cloud Run para lidar com
solicitações não autenticadas. O exemplo de código que você baixou ao ler a
primeira página deste tutorial contém o código dessa
função do Cloud Run no diretório function/. Se quiser, execute o
seguinte comando para explorar o código da função do Cloud Run:
less function/main.py
A implantação da função tem as seguintes finalidades:
Para implantar a função do Cloud Run, faça o seguinte:
Implantar um app da Web para enviar solicitações de previsão
Por fim, hospede um app da Web estático no Cloud Storage para receber previsões do modelo de ML treinado. O app da Web envia solicitações para a função do Cloud Run, que as pré-processa e recebe previsões do endpoint da Vertex AI.
O diretório webapp do exemplo de código que você baixou contém um
exemplo de app da Web. Na sessão do Cloud Shell, execute os seguintes
comandos para preparar e implantar o app da Web:
Na captura de tela a seguir, o app da Web já recebeu uma previsão e está enviando outra solicitação de previsão.
A seguir
Siga a última página do tutorial para limpar os recursos criados.

