By default, Gemini Enterprise encrypts customer content at rest. Gemini Enterprise handles encryption for you without any additional actions on your part. This option is called Google default encryption.
If you want to control your encryption keys, then you can use customer-managed encryption keys (CMEKs) in Cloud KMS with CMEK-integrated services including Gemini Enterprise. Using Cloud KMS keys gives you control over their protection level, location, rotation schedule, usage and access permissions, and cryptographic boundaries. Using Cloud KMS also lets you track key usage, view audit logs, and control key lifecycles. Instead of Google owning and managing the symmetric key encryption keys (KEKs) that protect your data, you control and manage these keys in Cloud KMS.
After you set up your resources with CMEKs, the experience of accessing your Gemini Enterprise resources is similar to using Google default encryption. For more information about your encryption options, see Customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK).
Limitations of Cloud KMS in Gemini Enterprise
The following limitations apply to CMEK (Cloud KMS) keys in Gemini Enterprise:
- Keys that are already applied to a data store can't be changed.
- After a key has been registered, it can't be deregistered or removed from a data store.
- You must use US or EU multi-region data stores and apps (not global ones). For more information about multi-regions and data residency, including limits associated with using non-global locations, see locations.
If you need to register more than one key for a project, contact your Google account team to request a quota increase for CMEK configurations, providing a justification for why you need more than one key.
Using external key manager (EKM) with CMEK is in GA with allowlist. To use EKM with CMEK, contact your Google account team.
The following limitations apply to EKM or HSM with CMEK:
Your EKM and HSM quota for encrypt and decrypt calls should have at least 1,000 QPM of headroom. For how to check your quotas, see Check your Cloud KMS quotas.
If using EKM, the key must be reachable for more than 90% of any time window of longer than 30 seconds. If the key isn't reachable for this amount of time, it can negatively impact indexing and search freshness.
If there are billing issues, persistent out-of-quota issues, or persistent unreachability issues for more than 12 hours, the service automatically turns down the CmekConfig associated with the EKM or HSM key.
- Data stores created before a key is registered to the project can't be protected by the key.
For apps with multiple data stores, if one data store uses a CMEK configuration, all other data stores must also use the same CMEK configuration.
Key rotation is not supported for the single-region keys for the third-party connectors. If you disable or destroy a key version that protects a data store associated with a third-party connector, the connector stops working.
Key rotation is not compatible with analytics. If you rotate keys for a data store, apps that use that data store no longer display analytics.
- First-party connectors are not CMEK-compliant except for the "import-once" and "periodic" data stores for BigQuery and Cloud Storage.
- You can't use Terraform to configure CMEK for Gemini Enterprise.
Before you begin
Make sure you satisfy the following prerequisites:
Create a multi-region symmetric Cloud KMS key. See Create a key ring and Create a key in the Cloud KMS documentation.
Set the rotation period to Never (Manual rotation).
For Location, select Multi-region, and select europe or us from the drop-down.
If you use third-party connectors, create three single-region symmetric Cloud KMS keys. It is optional otherwise.
Set the rotation period to Never (Manual rotation).
For Location, select region.
Select the single-regions in the following table from the location drop-down. You need to have all three keys with you when you Register your Cloud KMS keys for third-party connectors.
us single-regionseurope single-regionsus-east1europe-west1us-central1europe-west4us-west1europe-north1
The CryptoKey Encrypter/Decrypter IAM role (
roles/cloudkms.cryptoKeyEncrypterDecrypter) on the key has been granted to the Discovery Engine service agent. The service agent account has an email address that uses the following format:service-PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-discoveryengine.iam.gserviceaccount.com. For general instructions on how to add a role to a service agent, see Grant or revoke a single role.The CryptoKey Encrypter/Decrypter IAM role (
roles/cloudkms.cryptoKeyEncrypterDecrypter) on the key has been granted to the Cloud Storage service agent. If this role is not granted, data import for CMEK-protected data stores will fail because Discovery Engine is not able to make the CMEK-protected, temporary bucket and directory that is required for importing.Don't create any data stores or apps that you want managed by your key until after you have completed the key registration instructions on this page.
Register your Cloud KMS key
To encrypt data using CMEK, you must register your multi-region key. Optionally, if your data needs single-region keys, for example, when using third-party connectors, you need to register your single-region keys.
Register your multi-region Cloud KMS key
Before you begin
Make sure of the following:
The region isn't already protected by a key. The procedure below fails if a key is already registered for the region through the REST command. To determine if there is an active key in Gemini Enterprise for a location, see View Cloud KMS keys.
You have the Discovery Engine Admin (
roles/discoveryengine.admin) role.
Procedure
REST
To register your own key for Gemini Enterprise, follow these steps:
Call the
UpdateCmekConfigmethod with the key that you want to register.curl -X PATCH \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"kmsKey":"projects/KMS_PROJECT_ID/locations/KMS_LOCATION/keyRings/KEY_RING/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME"}' \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/cmekConfigs/CMEK_CONFIG_ID?set_default=SET_DEFAULT"Replace the following:
KMS_PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the key. The project number won't work.KMS_LOCATION: the multi-region of your key:usoreurope.KEY_RING: the name of the key ring that holds the key.KEY_NAME: the name of the key.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data store.LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.CMEK_CONFIG_ID: set a unique ID for the CmekConfig resource, for example,default_cmek_config.SET_DEFAULT: set totrueto use the key as the default key for subsequent data stores created in the multi-region.
Optional: Record the
namevalue returned by the method and follow the instructions in Get details about a long-running operation to see when the operation is complete.It typically takes a few minutes to register a key.
After the operation completes, new data stores in that multi-region are protected by the key. For general information about creating data stores, see About apps and data stores.
Console
Procedure
To register your own key for Gemini Enterprise, follow these steps:
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Gemini Enterprise page.
Click Settings, and select the CMEK tab.
Click Add key for the us or eu location.
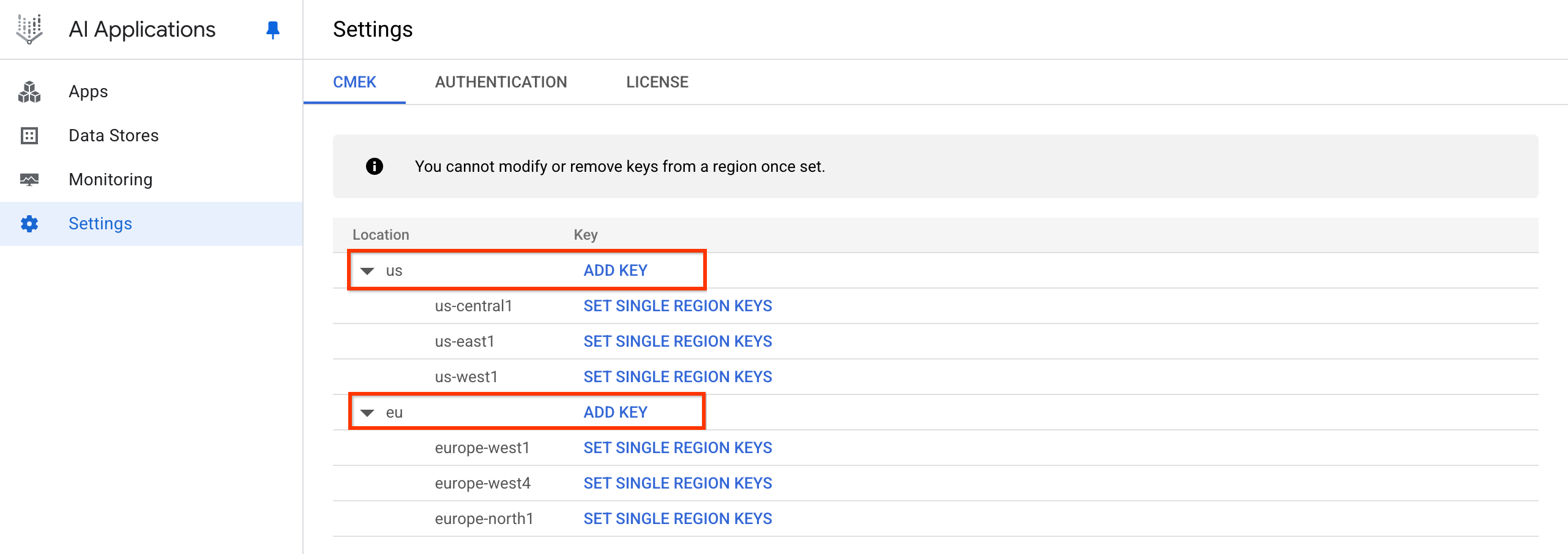
Click add key. Click the Select a Cloud KMS key drop-down, and select the key.
If the key is in a different project, click Switch project, click your project name, type the name of the key you created, and select the key.
If you know the resource name of the key, click Enter manually, paste the key resource name, and click Save.
Click OK > Save.
This registers your key, creating a CmekResource called default_cmek_config.
It can take several hours for the ingested data to show up in search results.
Register single-region Cloud KMS keys for third-party connectors
REST
To register your own key for Gemini Enterprise, follow these steps:
Call the
UpdateCmekConfigmethod with the key that you want to register.curl -X PATCH \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"kmsKey":"projects/KMS_PROJECT_ID/locations/KMS_LOCATION/keyRings/KEY_RING/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME"}' \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/cmekConfigs/CMEK_CONFIG_ID?set_default=SET_DEFAULT"Replace the following:
KMS_PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the key. The project number won't work.KMS_LOCATION: the multi-region of your key:usoreurope.KEY_RING: the name of the key ring that holds the key.KEY_NAME: the name of the key.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data store.LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.CMEK_CONFIG_ID: Set a unique ID for the CmekConfig resource, for example,default_cmek_config.SET_DEFAULT: set totrueto use the key as the default key for subsequent data stores created in the multi-region.
Optional: Record the
namevalue returned by the method and follow the instructions in Get details about a long-running operation to see when the operation is complete.It typically takes a few minutes to register a key.
After the operation completes, new data stores in that multi-region are protected by the key. For general information about creating data stores, see About apps and data stores.
If you use third-party connectors and want to protect your third-party data with your own key, then create three additional single-region keys as follows:
curl -X PATCH \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "kmsKey":"projects/KMS_PROJECT_ID/locations/KMS_LOCATION/keyRings/KEY_RING/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME", "singleRegionKeys": [ \ {"kmsKey": "projects/KMS_PROJECT_ID/locations/REGION_1/keyRings/KEY_RING_1/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME_1"}, \ {"kmsKey": "projects/KMS_PROJECT_ID/locations/REGION_2/keyRings/KEY_RING_2/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME_2"}, \ {"kmsKey": "projects/KMS_PROJECT_ID/locations/REGION_3/keyRings/KEY_RING_3/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME_3"} \ ] \ }' \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/cmekConfigs/CMEK_CONFIG_ID?set_default=SET_DEFAULT"Replace the following:
KMS_PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the key. The project number won't work.Set the
REGIONvalues:REGION_1: for theeulocation, set this toeurope-west1, and for theuslocation, set this tous-east1.REGION_2: for theeulocation, set this toeurope-west4, and for theuslocation, set this tous-central1.REGION_3: for theeulocation, set this toeurope-north1, and for theuslocation, set this tous-west1.
KEY_RING: the name of the key ring that holds the key.KEY_NAME: the name of the multi-region key.LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data store.CMEK_CONFIG_ID: Set to the ID for the CmekConfig resource. Use the same value as in Step 1, for example,default_cmek_config.SET_DEFAULT: set totrueto use the key as the default key for subsequent data stores created in the multi-region.
Console
Before you begin
Make sure that the regions aren't already protected by keys. The following procedure fails if a key is already registered for the region through the REST command.
To determine if there is an active key for a location, see View Cloud KMS keys.
Procedure
To register your own key when using Gemini Enterprise third-party connectors, follow these steps:
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Gemini Enterprise page.
Click Settings, and select the CMEK tab.
Click Add key for the us or eu location.

Click add key. Click the Select a cloud kms key drop-down, and select the key.
If the key is in a different project, click Switch project, click your project name, type the name of the key you created, and select the key.
If you know the resource name of the key, click Enter manually, paste the key resource name, and click Save.
Click Ok > Save.
This registers your key, creating a CmekResource called
default_cmek_config.
If you are connecting a third-party data source, click Set single region keys.
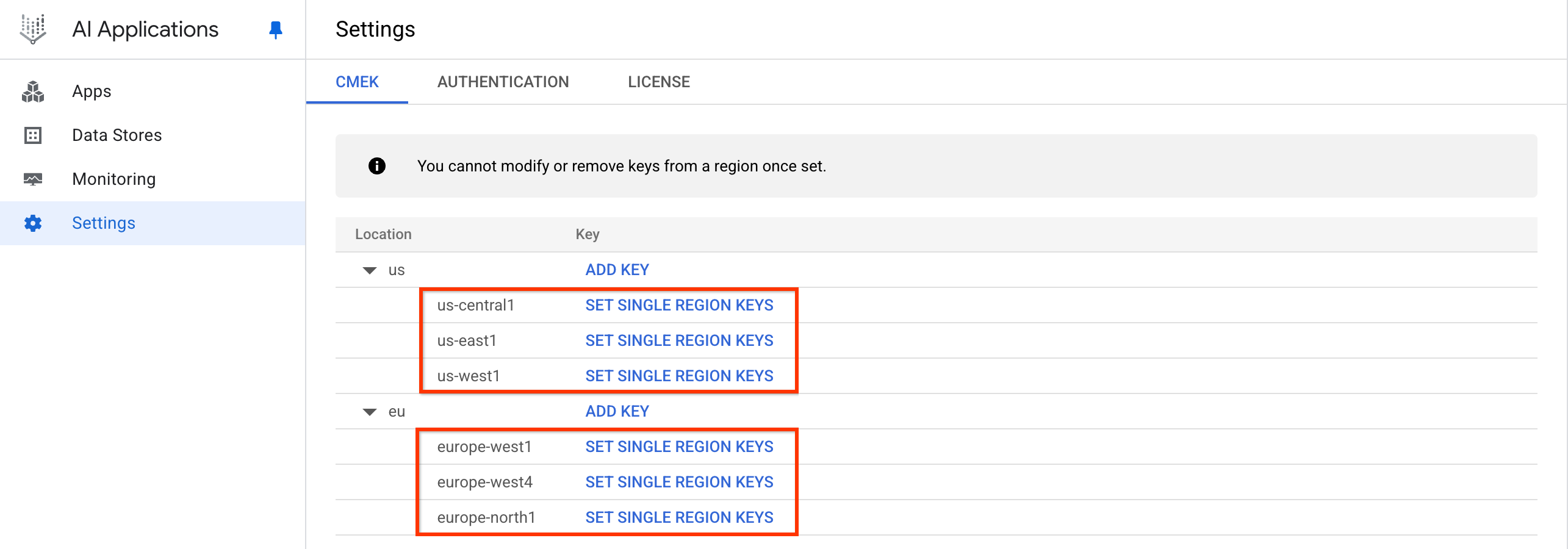
Click Set single region keys. Click the Select a cloud kms key drop-down, and select the key for each region.
If the key is in a different project, click Switch project, click your project name, type the name of the key you created, and select the key.
If you know the resource name of the key, click Enter manually, paste the key resource name, and click Save.
Click Save.
This registers your single-region keys in the CmekResource called
default_cmek_config.
It can take several hours for the ingested data to show up in search results.
View Cloud KMS keys
To view a registered key for Gemini Enterprise, do one of the following:
If you have the CmekConfig resource name, call the
GetCmekConfigmethod:curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/cmekConfigs/CMEK_CONFIG_ID"Replace the following:
LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data.CMEK_CONFIG_ID: the ID of the CmekConfig resource. If you registered your key using the console, the ID isdefault_cmek_config.
An example curl call and response looks like this:
$ curl -X GET -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" "https://us-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/cmekConfigs/default_cmek_config"
{ "name": "projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/cmekConfigs/default_cmek_config", "kmsKey": "projects/key-project-456/locations/us/keyRings/my-key-ring/cryptoKeys/my-key" "state": "ACTIVE" "isDefault": true }If you don't have the CmekConfig resource name, call the
ListCmekConfigsmethod:curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/cmekConfigs"Replace the following:
LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data.
An example curl call and response looks like this:
$ curl -X GET -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" "https://us-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/cmekConfigs"
{ "cmek_configs": [ { "name": "projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/cmekConfigs/default_cmek_config", "kmsKey": "projects/key-project-456/locations/us/keyRings/my-key-ring/cryptoKeys/my-key" "state": "ACTIVE" "isDefault": true } ] }
Unregister your Cloud KMS key
To unregister your key from Gemini Enterprise, follow these steps:
Call the
DeleteCmekConfigmethod with the CmekConfig resource name that you want to unregister.curl -X DELETE \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/cmekConfigs/CMEK_CONFIG_ID"Replace the following:
LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data store.CMEK_CONFIG_ID: the ID of the CmekConfig resource. If you registered your key using the console, the ID isdefault_cmek_config.
An example curl call and response looks like this:
$ curl -X DELETE -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" "https://us-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/cmekConfigs/default_cmek_config" { "name": "projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/operations/delete-cmek-config-56789", "metadata": { "@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.cloud.discoveryengine.v1.DeleteCmekConfigMetadata" } }Optional: Record the
namevalue returned by the method and follow the instructions in Get details about a long-running operation to see when the operation is complete.It typically takes a few minutes to delete a key.
Verify that a data store is protected by a key
Data stores that are created after your key is registered are protected by the key. If you want to confirm that a particular data store is protected by your key, follow these steps:
Run the following curl command on the data store:
curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -H "x-goog-user-project: PROJECT_ID" \ "https://LOCATION-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/LOCATION/collections/default_collection/dataStores/DATA_STORE_ID"Replace the following:
LOCATION: the multi-region of your data store:usoreu.PROJECT_ID: the ID of your project that contains the data store.DATA_STORE_ID: the ID of the data store.
An example curl call looks like this:
curl -X GET -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "x-goog-user-project: my-ai-app-project-123" "https://us-discoveryengine.googleapis.com/v1/projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/collections/default_collection/dataStores/my-data-store-1"
Review the output from the command: If the
cmekConfigfield is in the output and thekmsKeyfield shows the key that you registered, then the data store is protected by the key.An example response looks like this:
{ "name": "projects/969795412903/locations/us/collections/default_collection/dataStores/my-data-store-1", "displayName": "my-data-store-1", "industryVertical": "GENERIC", "createTime": "2023-09-05T21:20:21.520552Z", "solutionTypes": [ "SOLUTION_TYPE_SEARCH" ], "defaultSchemaId": "default_schema", "cmekConfig": { "name": "projects/969795412903/locations/us/collections/default_collection/dataStores/my-data-store-1/cmekConfigs/default_cmek_config", "kmsKey": "projects/my-ai-app-project-123/locations/us/keyRings/my-key-ring/cryptoKeys/my-key" } }
Other data protected by the Cloud KMS key
In addition to data in the data stores, your keys can protect other types of app-owned core information held by Gemini Enterprise, such as the session data generated during search with follow-ups. This kind of core information is CMEK-protected if the data stores associated with the app are CMEK-protected.
Although, you can't run a specific command to verify that sessions are protected, if you run the Verify that a data store is protected by a key command and see the key in the cmekConfig resource, then know that the session data is protected.
Rotate Cloud KMS keys
When you rotate keys, you are creating a new version of the key and setting the new version as the primary version. Leave the original version of the key enabled for a while before disabling it. This gives any long-running operations that might be using the older key time to complete.
The following procedure outlines the steps to rotate keys for a Gemini Enterprise data store. For general information about rotating keys, see Key rotation in the Cloud KMS guide.
Important: Do not rotate keys on data stores associated with recommendations apps or with any apps that need analytics, and don't rotate the single-region keys used for third-party connectors. See Limitations of Cloud KMS in Gemini Enterprise.
Reregister your key. Do this by repeating step 1 of Register your Cloud KMS key.
See the instructions in the Manage keys section of the Cloud KMS guide to do the following:
Create a new key version, enable it, and make it primary.
Leave the older key version enabled.
After a week or so, disable the older key version and make sure that everything is working as before.
At some later date, when you are certain that no problems were caused by disabling the older key version, you can destroy the older key version.
If a Cloud KMS key is disabled or revoked
If a key is disabled or permissions for the key are revoked, the data store stops ingesting data and stops serving data within 15 minutes. However, re-enabling a key or restoring permissions takes a long time. It can take up to 24 hours before the data store can resume serving data.
Therefore, don't disable a key unless necessary. Disabling and enabling a key on a data store is a time-consuming operation. For example, repeatedly switching a key between disabled and enabled means it will take a long time for the data store to reach a protected state. Disabling a key and re-enabling it immediately afterward could result in days of downtime because the key is first disabled from the data store and subsequently re-enabled.
