In diesem Leitfaden erfahren Sie, wie Sie einen webhook verwenden, damit Ihr Agent dynamischer sein kann. Cloud Functions werden aufgrund ihrer Einfachheit zum Hosten des Webhooks verwendet. Es gibt jedoch viele andere Möglichkeiten, einen Webhook-Dienst zu hosten. Im Beispiel wird auch die Programmiersprache Go verwendet. Sie können jedoch jede von Cloud Functions unterstützte Sprache verwenden. Sie müssen den Code für diesen Leitfaden nicht bearbeiten.
Der Beispiel-Webhook-Code führt Folgendes aus:
- Liest Parameterwerte aus der Webhook-Anfrage.
- Schreibt einen Parameterwert in die Webhook-Antwort.
- Stellt eine Textantwort in der Webhook-Antwort bereit.
Hinweise
Wenn Sie keine Webhooks verwenden möchten, können Sie diesen Schnellstart überspringen.
Bevor Sie diese Anleitung lesen, sollten Sie mit Folgendem vertraut sein:
- Grundlagen von Abläufen
- Einrichtungsschritte ausführen
- Führen Sie die Schritte in der Kurzanleitung Agent mithilfe von Flows erstellen aus. In den folgenden Schritten wird derselbe Agent weiterverwendet. Wenn Sie diesen Agent nicht mehr haben, können Sie ihn herunterladen und wiederherstellen.
Cloud Functions-Funktion erstellen
Cloud Functions können mit der Google Cloud Console erstellt werden (Dokumentation ansehen, Console öffnen). So erstellen Sie eine Funktion für diesen Leitfaden:
- Es ist wichtig, dass sich der Konversations-Agent (Dialogflow CX) und die Funktion im selben Projekt befinden. So erhalten Konversations-Agents (Dialogflow CX) am einfachsten sicheren Zugriff auf Ihre Funktion. Rufen Sie die Projektauswahl auf, um Ihr Projekt auszuwählen.
- Zur Übersichtsseite zu Cloud Functions
- Klicken Sie auf Funktion erstellen und legen Sie die folgenden Felder fest:
- Umgebung: 1. Generation
- Funktionsname: shirts-agent-webhook
- Region: Wenn Sie für Ihren Kundenservicemitarbeiter eine Region angegeben haben, verwenden Sie dieselbe Region.
- HTTP-Triggertyp: HTTP
- URL: Klicken Sie hier auf die Schaltfläche „Kopieren“ und speichern Sie den Wert. Sie benötigen diese URL, wenn Sie den Webhook konfigurieren.
- Authentifizierung: Authentifizierung verlangen
- HTTPS erforderlich: angeklickt
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
- Klicken Sie auf Weiter. Sie benötigen keine speziellen Laufzeit-, Build-, Verbindungs- oder Sicherheitseinstellungen.
- Legen Sie die Werte für die folgenden Felder fest:
- Laufzeit: Wählen Sie die neueste Go-Laufzeit aus.
- Quellcode: Inline-Editor
- Einstiegspunkt: HandleWebhookRequest
Ersetzen Sie den Code durch Folgendes:
// Package cxwh contains an example Dialogflow CX webhook package cxwh import ( "encoding/json" "fmt" "log" "net/http" ) type fulfillmentInfo struct { Tag string `json:"tag"` } type sessionInfo struct { Session string `json:"session"` Parameters map[string]interface{} `json:"parameters"` } type text struct { Text []string `json:"text"` } type responseMessage struct { Text text `json:"text"` } type fulfillmentResponse struct { Messages []responseMessage `json:"messages"` } // webhookRequest is used to unmarshal a WebhookRequest JSON object. Note that // not all members need to be defined--just those that you need to process. // As an alternative, you could use the types provided by the Dialogflow protocol buffers: // https://pkg.go.dev/google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/cloud/dialogflow/cx/v3#WebhookRequest type webhookRequest struct { FulfillmentInfo fulfillmentInfo `json:"fulfillmentInfo"` SessionInfo sessionInfo `json:"sessionInfo"` } // webhookResponse is used to marshal a WebhookResponse JSON object. Note that // not all members need to be defined--just those that you need to process. // As an alternative, you could use the types provided by the Dialogflow protocol buffers: // https://pkg.go.dev/google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/cloud/dialogflow/cx/v3#WebhookResponse type webhookResponse struct { FulfillmentResponse fulfillmentResponse `json:"fulfillmentResponse"` SessionInfo sessionInfo `json:"sessionInfo"` } // confirm handles webhook calls using the "confirm" tag. func confirm(request webhookRequest) (webhookResponse, error) { // Create a text message that utilizes the "size" and "color" // parameters provided by the end-user. // This text message is used in the response below. t := fmt.Sprintf("You can pick up your order for a %s %s shirt in 5 days.", request.SessionInfo.Parameters["size"], request.SessionInfo.Parameters["color"]) // Create session parameters that are populated in the response. // The "cancel-period" parameter is referenced by the agent. // This example hard codes the value 2, but a real system // might look up this value in a database. p := map[string]interface{}{"cancel-period": "2"} // Build and return the response. response := webhookResponse{ FulfillmentResponse: fulfillmentResponse{ Messages: []responseMessage{ { Text: text{ Text: []string{t}, }, }, }, }, SessionInfo: sessionInfo{ Parameters: p, }, } return response, nil } // handleError handles internal errors. func handleError(w http.ResponseWriter, err error) { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError) fmt.Fprintf(w, "ERROR: %v", err) } // HandleWebhookRequest handles WebhookRequest and sends the WebhookResponse. func HandleWebhookRequest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { var request webhookRequest var response webhookResponse var err error // Read input JSON if err = json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&request); err != nil { handleError(w, err) return } log.Printf("Request: %+v", request) // Get the tag from the request, and call the corresponding // function that handles that tag. // This example only has one possible tag, // but most agents would have many. switch tag := request.FulfillmentInfo.Tag; tag { case "confirm": response, err = confirm(request) default: err = fmt.Errorf("Unknown tag: %s", tag) } if err != nil { handleError(w, err) return } log.Printf("Response: %+v", response) // Send response if err = json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(&response); err != nil { handleError(w, err) return } }
Klicken Sie auf Bereitstellen.
Warten Sie, bis die Statusanzeige anzeigt, dass die Funktion erfolgreich bereitgestellt wurde. Sehen Sie sich in der Zwischenzeit den Code an, den Sie gerade bereitgestellt haben. Codekommentare beschreiben wichtige Details.
Webhook erstellen
Nachdem der Webhook als Cloud-Funktion vorhanden ist, verknüpfen Sie ihn mit Ihrem Agenten. So erstellst du den Webhook für deinen Agenten:
- Öffnen Sie die Dialogflow CX Console.
- Wählen Sie Ihr Google Cloud-Projekt aus.
- Wählen Sie den Agent aus.
- Wählen Sie den Tab Verwalten.
- Klicken Sie auf Webhooks.
- Klicken Sie auf Erstellen.
- Füllen Sie die folgenden Felder aus:
- Anzeigename: shirts-agent-webhook
- Webhook-URL: Geben Sie die Webhook-URL an, die Sie beim Erstellen der Funktion gespeichert haben.
- Untertyp: Standard.
- Für alle anderen Felder werden Standardwerte verwendet.
- Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
Webhook verwenden
Nachdem der Webhook für den Kundenservicemitarbeiter verfügbar ist, kannst du ihn bei der Auftragsausführung verwenden. Die Seite Bestellbestätigung enthält eine Eingabeauftragsausführung, die derzeit eine statische Textantwort hat. So aktualisierst du die Auftragsausführung, damit dein Webhook verwendet wird:
- Wählen Sie den Tab Erstellen aus.
- Klicken Sie auf die Seite Bestellbestätigung, um sie in der Agent Builder-Grafik zu maximieren.
- Klicken Sie auf der Seite auf das Feld Entry Fulfillment (Eintragsausführung), um den Bereich für die Auftragsausführung zu öffnen.
- Löschen Sie die vorhandene Textantwort unter der Überschrift Kundenservicemitarbeiter sagt. Wenn Sie den Mauszeiger auf den Text bewegen, wird die Schaltfläche „Löschen“ delete angezeigt.
- Klicken Sie auf Webhook aktivieren.
- Wählen Sie im Drop-down-Menü Webhook die Option
shirts-agent-webhookaus. - Geben Sie im Feld Tag den Wert
confirmein. - Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
- Schließen Sie den Bereich für die Auftragsausführung.
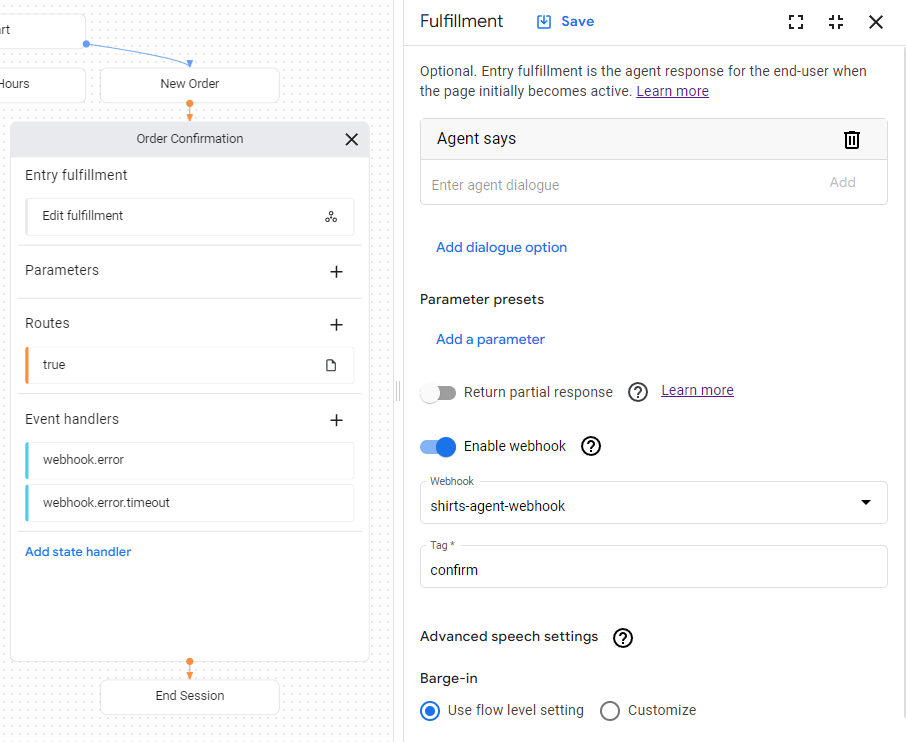
Der bereitgestellte Webhook-Code sendet eine Antwort, durch die ein Parameter namens cancel-period erstellt wird.
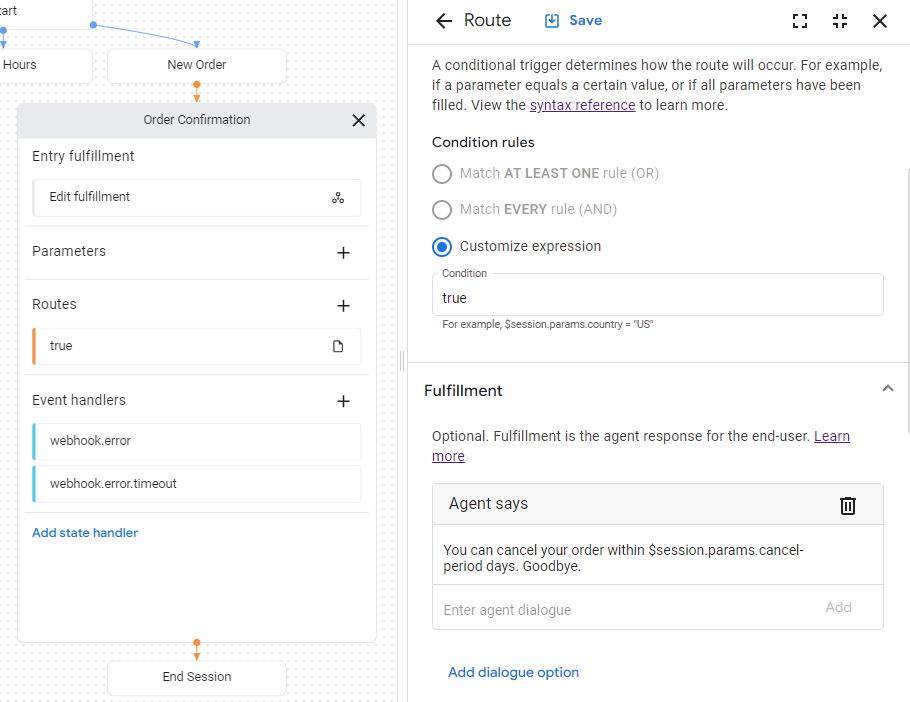
Aktualisieren Sie den Agenten, damit er in der endgültigen Antwort des Kundenservicemitarbeiters für dieselbe Seite Bestellbestätigung auf diesen Parameter verweist:
- Klicken Sie auf die Bedingung route, die mit einer
truegekennzeichnet ist, um das Steuerfeld „Route“ zu öffnen. - Scrollen Sie im Steuerfeld für die Route nach unten zum Abschnitt Ausführung und fügen Sie unter der Überschrift Kundenservicemitarbeiter sagt die folgende Textantwort hinzu:
You can cancel your order within $session.params.cancel-period days. Goodbye. - Klicken Sie auf Speichern.
- Schließen Sie den Bereich „Route“.
Agent im Simulator testen
Ihr Agent und Webhook können jetzt mit dem Simulator getestet werden:
- Klicken Sie auf Test-Kundenservicemitarbeiter.
- Geben Sie
I want to buy a large red shirtein und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste.
Da Sie sowohl eine Größe als auch eine Farbe angegeben haben, hat der Kundenservicemitarbeiter alles, was er zum Erstellen einer T-Shirt-Bestellung benötigt. Daher wird direkt zur Seite Bestellbestätigung weitergeleitet.
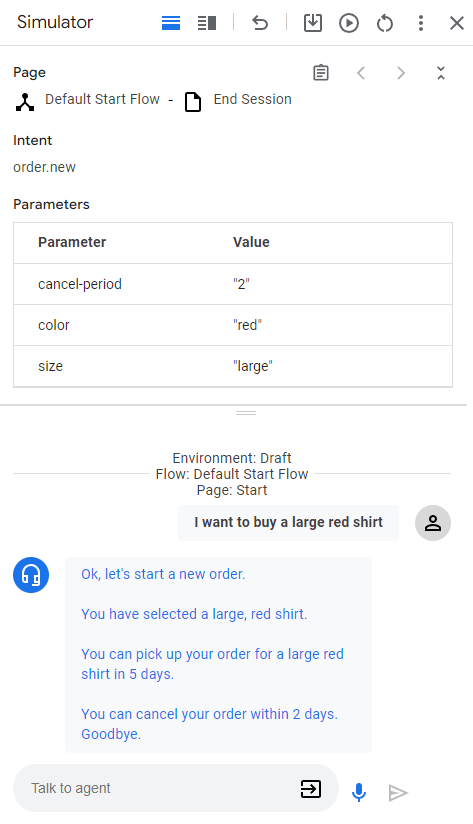
Im Folgenden werden die Antworten des Kundenservicemitarbeiters beschrieben:
| Antwort | Erklärung |
|---|---|
| Okay, starten wir einen neuen Auftrag. | Als die Seite Neue Bestellung aktiv wurde, wurde die Auftragsausführung aufgerufen. Die Antwort wurde von dieser Auftragsausführung ausgelöst. |
| Sie haben ein großes rotes Hemd ausgewählt. | Wenn alle Formularparameter für die Seite Neue Bestellung angegeben wurden, wird die Bedingungsroute aufgerufen, die das Ausfüllen des Formulars prüft. Die Antwort wurde von der Auftragsausführung für diese Route ausgelöst. Diese Route führt ebenfalls zur Seite Bestellbestätigung. |
| Sie können Ihre Bestellung für ein rotes Hemd in Größe L in 5 Tagen abholen. | Die Auftragsausführung für die Seite Bestellbestätigung ruft den Webhook auf. Siehe Funktion confirm im Webhook-Code. Diese Funktion erstellt diese Textantwort und verwendet die in der Webhook-Anfrage angegebenen Parameter. |
| Sie können Ihre Bestellung innerhalb von zwei Tagen stornieren. Auf Wiedersehen. | Die Seite Bestellbestätigung enthält eine Bedingungsroute mit einer Bedingung, die immer wahr ist. Diese Antwort wird durch die Auftragsausführung für diese Route ausgelöst. Hinweis: In der Antwort wird der Parameter verwendet, der vom Webhook in der Webhook-Antwort festgelegt wurde. |

