This page describes how you can connect an Agent Development Kit (ADK) agent with Vertex AI Agent Engine Sessions and use managed sessions in the local and production environment.
Before you begin
Make sure your environment is set up by following the Get the required roles and Authentication steps in Set up your environment.
Create a Vertex AI Agent Engine instance
To access Vertex AI Agent Engine Sessions, you first need to create an Vertex AI Agent Engine instance. You don't need to deploy any code to start using Sessions. Without code deployment, creating an Vertex AI Agent Engine instance only takes a few seconds.
import vertexai
client = vertexai.Client(
project="PROJECT_ID",
location="LOCATION"
)
# If you don't have an Agent Engine instance already, create an instance.
agent_engine = client.agent_engines.create()
# Print the agent engine ID, you will need it in the later steps to initialize
# the ADK `VertexAiSessionService`.
print(agent_engine.api_resource.name.split("/")[-1])
Replace the following:
PROJECT_ID: Your project ID.
LOCATION: Your region. See the supported regions for Sessions.
Develop your ADK agent
To create your ADK agent, follow the instructions in Agent Development Kit, or use the following code to create an agent that greets a user with fixed greetings:
from google import adk
def greetings(query: str):
"""Tool to greet user."""
if 'hello' in query.lower():
return {"greeting": "Hello, world"}
else:
return {"greeting": "Goodbye, world"}
# Define an ADK agent
root_agent = adk.Agent(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
name='my_agent',
instruction="You are an Agent that greet users, always use greetings tool to respond.",
tools=[greetings]
)
Set up the ADK runner
The ADK Runtime orchestrates the execution of your agents, tools, and callbacks, and orchestrates calls to read and write sessions. Initialize the Runner with VertexAiSessionService, which connects with Vertex AI Agent Engine Sessions.
from google.adk.sessions import VertexAiSessionService
from google.genai import types
app_name="APP_NAME"
user_id="USER_ID"
# Create the ADK runner with VertexAiSessionService
session_service = VertexAiSessionService(
"PROJECT_ID",
"LOCATION",
"AGENT_ENGINE_ID"
)
runner = adk.Runner(
agent=root_agent,
app_name=app_name,
session_service=session_service)
# Helper method to send query to the runner
def call_agent(query, session_id, user_id):
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
events = runner.run(
user_id=user_id, session_id=session_id, new_message=content)
for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
Replace the following:
APP_NAME: The name of your agent application.
USER_ID: Choose your own user ID with a character limit of 128. For example,
user-123.AGENT_ENGINE_ID: The resource ID of a Vertex AI Agent Engine instance.
For deployed agents, the resource ID is listed as the
GOOGLE_CLOUD_AGENT_ENGINE_IDenvironment variableFor local agents, you can retrieve the resource ID using
agent_engine.api_resource.name.split("/")[-1].
Interact with your agent
After defining your agent and setting up Vertex AI Agent Engine Sessions, you can interact with your agent to check that the session history and states persist.
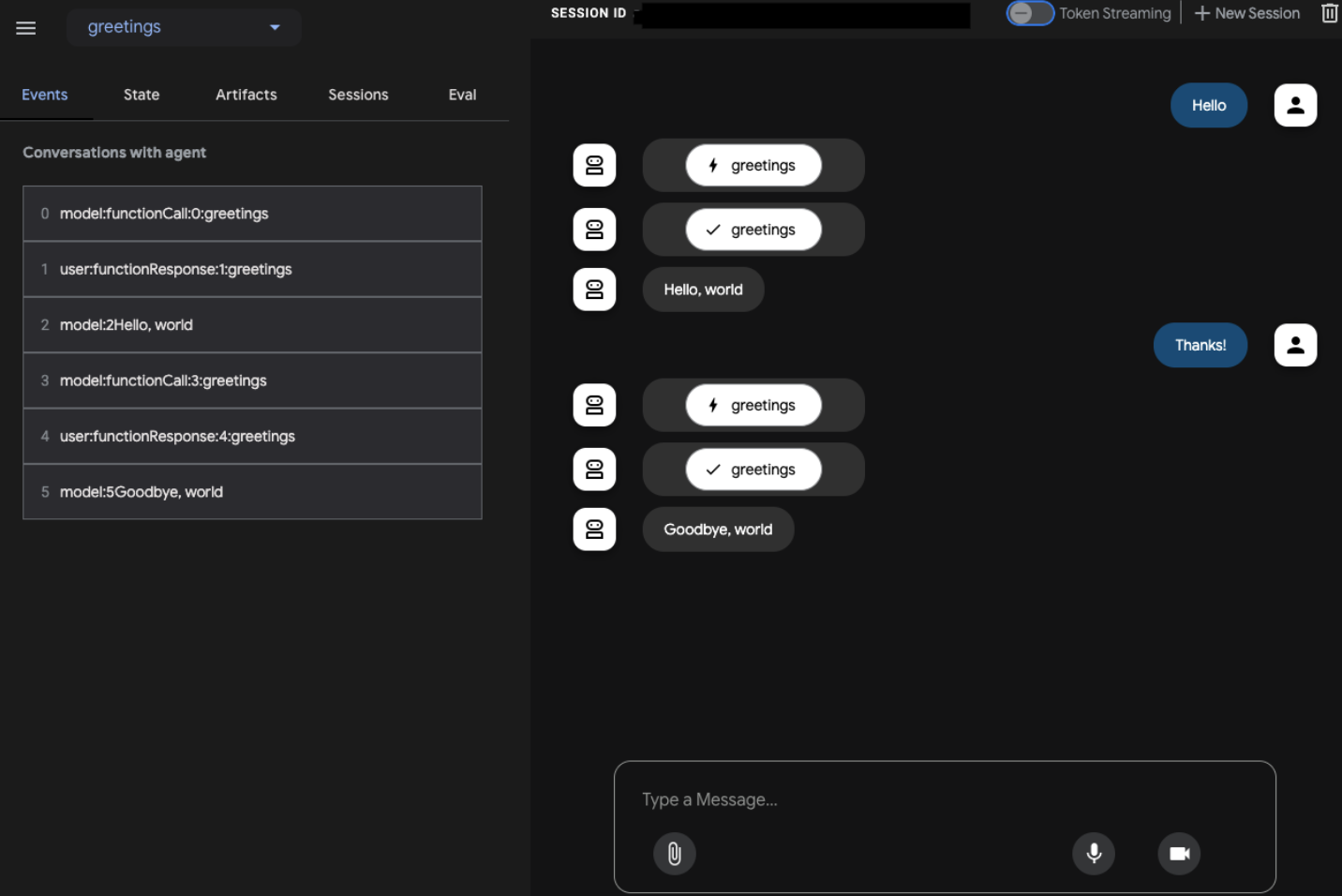
ADK UI
Test your agent with the ADK user interface and connect to Vertex AI Agent Engine Session using the session_service_uri command line option:
agent_engine_id="AGENT_ENGINE_ID"
adk web --session_service_uri=agentengine://${agent_engine_id}
# Sample output
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ADK Web Server started |
| |
| For local testing, access at http://localhost:8000. |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Python
Use ADK Python code to manage sessions and states.
Create a session and query the agent
Use the following code to create a session and send a query to your agent:
# Create a session
session = await session_service.create_session(
app_name=app_name,
user_id=user_id)
call_agent("Hello!", session.id, user_id)
# Agent response: "Hello, world"
call_agent("Thanks!", session.id, user_id)
# Agent response: "Goodbye, world"
After the session is created and passed to the runner, ADK uses the session to store events from the current interaction. You can also resume a previous session by providing the ID for that session.
List existing sessions
List all existing sessions associated with a given user ID.
# List sessions
await session_service.list_sessions(app_name=app_name,user_id=user_id)
# ListSessionsResponse(session_ids=['1122334455', '9988776655'])
Manage session states
States hold information that the agent needs for a conversation. You can provide an initial state as a dictionary when you create a session:
# Create a session with state
session = await session_service.create_session(
app_name=app_name,
user_id=user_id,
state={'key': 'value'})
print(session.state['key'])
# value
To update the session state outside the runner, append a new event to the session using state_delta:
from google.adk.events import Event, EventActions
import time
# Define state changes
state_changes = {'key': 'new_value'}
# Create event with actions
actions_with_update = EventActions(state_delta=state_changes)
system_event = Event(
invocation_id="invocation_id",
author="system", # Or 'agent', 'tool' etc.
actions=actions_with_update,
timestamp=time.time()
)
# Append the event
await session_service.append_event(session, system_event)
# Check updated state
updated_session = await session_service.get_session(
app_name=app_name,
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session.id)
# State is updated to new value
print(updated_session.state['key'])
# new_value
Delete a session
Delete a specific session associated with a user ID:
await session_service.delete_session(app_name=app_name, user_id=user_id, session_id=session.id)
Deploy your agent to Vertex AI Agent Engine
After you test your agent locally, you can deploy the agent to production by updating the Vertex AI Agent Engine instance with parameters:
client.agent_engines.update(
resource_name=agent_engine.api_resource.name,
agent=AGENT,
config={
"display_name": DISPLAY_NAME, # Optional.
"requirements": REQUIREMENTS, # Optional.
"staging_bucket": STAGING_BUCKET, # Required.
},
)
Replace the following:
AGENT: The application that implements the
query / stream_querymethod (for example,AdkAppfor an ADK agent). For more information, see Deployment considerations.DISPLAY_NAME: A user-friendly name for your agent.
REQUIREMENTS: A list of pip packages required by your agent. For example,
["google-cloud-storage", "google-cloud-aiplatform[agent_engines,adk]"].STAGING_BUCKET: A Cloud Storage bucket prefixed by
gs://.
Clean up
To clean up all resources used in this project, you can delete the Vertex AI Agent Engine instance along with its child resources:
agent_engine.delete(force=True)
