You can create a custom metric to raise alerts or provide information to troubleshoot problems with scheduled snapshots.
For example, to set up an alert for scheduled snapshot failures, use the following procedure:
- Create a log filter to capture scheduled snapshot events.
- Create a metric based off of the log filter that counts scheduled snapshot failures.
- Create an alert policy to send an alert when there is a scheduled snapshot failure.
Before you begin
-
If you haven't already, set up authentication.
Authentication verifies your identity for access to Google Cloud services and APIs. To run
code or samples from a local development environment, you can authenticate to
Compute Engine by selecting one of the following options:
Select the tab for how you plan to use the samples on this page:
Console
When you use the Google Cloud console to access Google Cloud services and APIs, you don't need to set up authentication.
gcloud
-
Install the Google Cloud CLI. After installation, initialize the Google Cloud CLI by running the following command:
gcloud initIf you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
- Set a default region and zone.
REST
To use the REST API samples on this page in a local development environment, you use the credentials you provide to the gcloud CLI.
Install the Google Cloud CLI. After installation, initialize the Google Cloud CLI by running the following command:
gcloud initIf you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
For more information, see Authenticate for using REST in the Google Cloud authentication documentation.
-
Required roles and permissions
To get the permissions that you need to create a snapshot schedule, ask your administrator to grant you the following IAM roles on the project:
-
Compute Instance Admin (v1) (
roles/compute.instanceAdmin.v1) -
To connect to a VM that can run as a service account:
Service Account User (v1) (
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser)
For more information about granting roles, see Manage access to projects, folders, and organizations.
You might also be able to get the required permissions through custom roles or other predefined roles.
Create a log filter
Create a log filter to capture scheduled snapshot events.
Console
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Logging > Logs Explorer page.
In the Filter by label or text search list, select Convert to advanced filter.
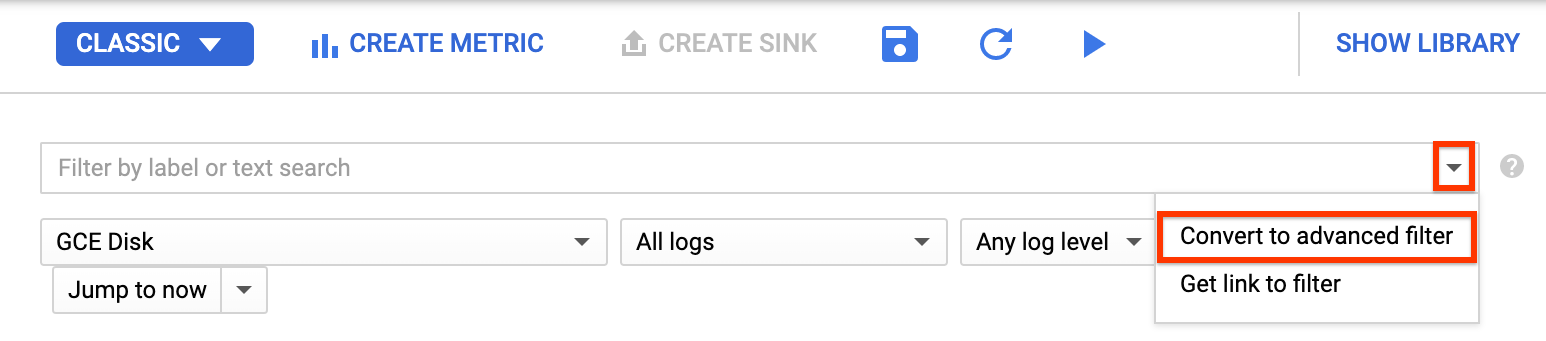
Replace the filter field by entering the following text, replacing
PROJECT_IDwith your project ID:resource.type="gce_disk" logName="projects/PROJECT_ID/logs/cloudaudit.googleapis.com%2Fsystem_event" protoPayload.methodName="ScheduledSnapshots" severity>"INFO"Click Submit Filter.
Create a metric
After you create the log filter, create a metric that counts scheduled snapshot failures.
Console
On the Logs Explorer page, click Create metric.
In the Metric Editor, enter the following:
- Name:
scheduled_snapshot_failure_count. - Description:
count of scheduled snapshot failures. - Type:
Counter
- Name:
Under Labels, click Add item and enter the following:
- Name:
status - Description:
status of scheduled snapshot request - Label type:
String - Field name:
protoPayload.response.status
- Name:
Click Done.
Click Create Metric.
Create an alert policy
After you create the metric, create an alert policy to send an alert when there is a scheduled snapshot failure.
Console
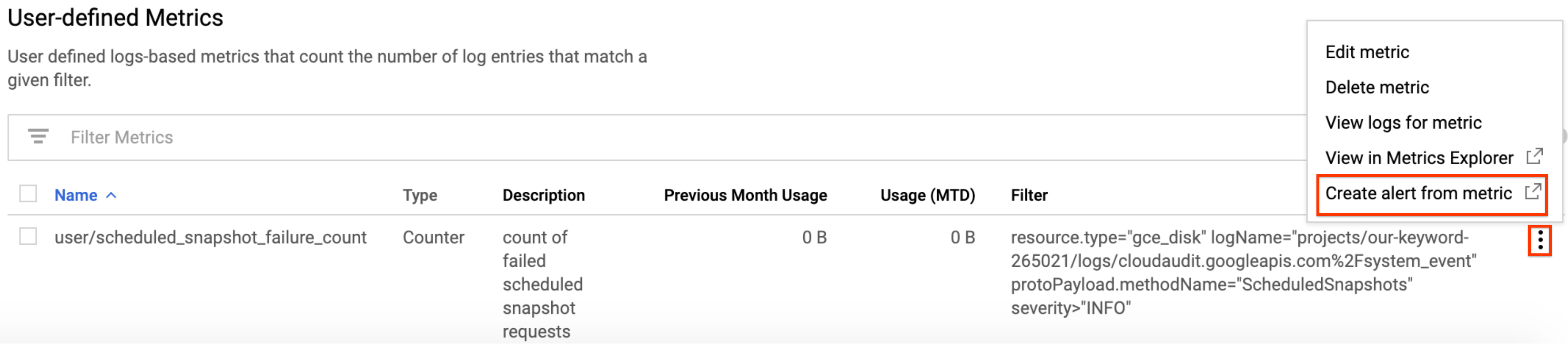
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Cloud Logging > Logs-based metrics page.
Under User-defined Metrics, find your new metric named
user/scheduled_snapshot_failure_count.Click the More menu button in this row and select Create alert from metric. The alert policy condition creation page opens.
In the Target panel, under Aggregator, select none.
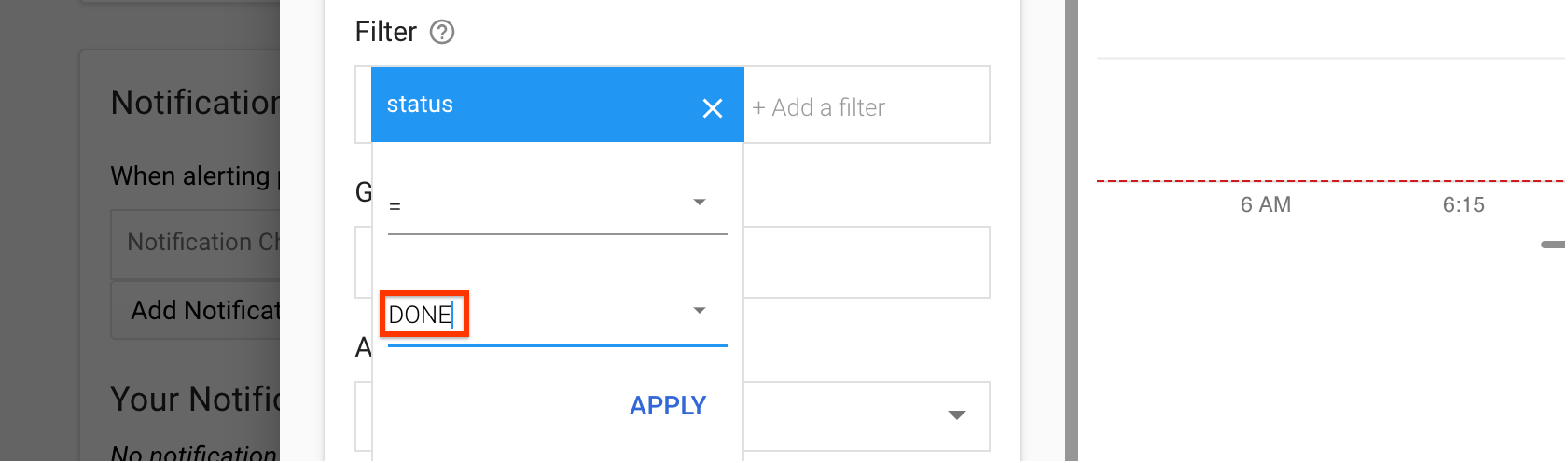
Under Filter:
- Click Add a filter.
- Select status from the list.
- In the Value field, type DONE.
- Click Apply.
Click Show advanced options.
In the Advanced aggregation pane, click the Aligner list and select sum.
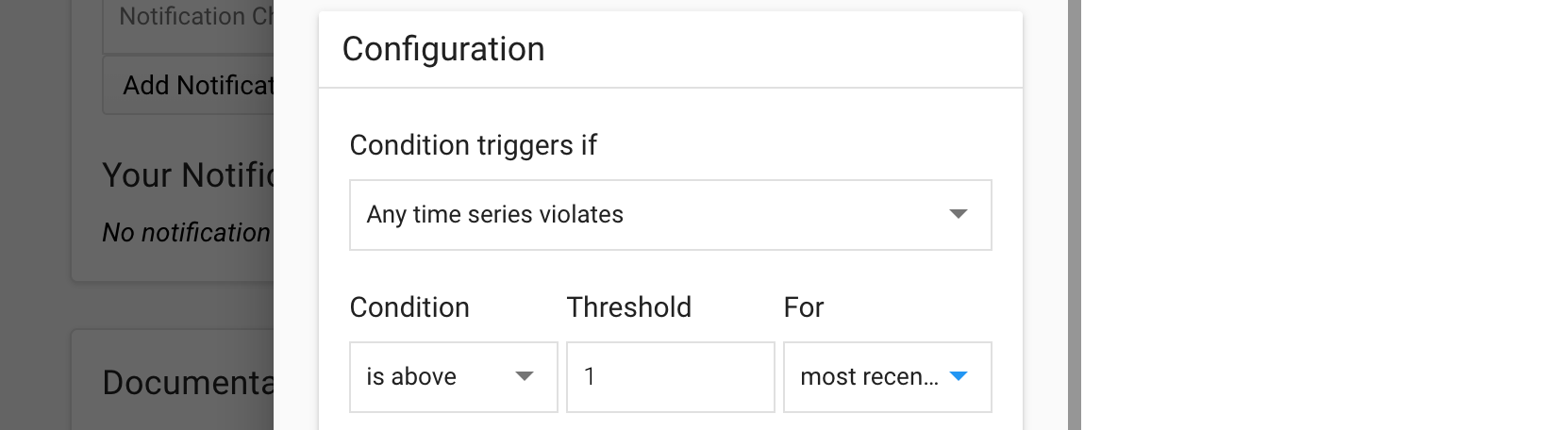
In the Configuration panel, select the following values:
- Condition triggers if:
Any time series violates - Condition:
is above - Threshold:
1 - For:
most recent value
- Condition triggers if:
Click Save.
On the Create new alerting policy page, enter a policy name. Optionally, you can add notification channels and documentation for this policy.
Click Save.
What's next
- Learn about snapshot schedule frequencies, retention policies, and naming rules in About snapshot schedules for disks.
- Learn about disk snapshots.
- Learn how to create scheduled snapshots for disks.
- Learn how to view logs.
