Anda dapat menggunakan Cloud Build untuk mengotomatiskan build dan deployment ke Cloud Run dengan menggunakan pemicu Cloud Build untuk mem-build dan men-deploy kode secara otomatis setiap kali commit baru didorong ke cabang tertentu dari repositori Git. Sebagai contoh, lihat panduan memulai untuk membuat repositori template dan men-deploy secara berkelanjutan dari git.
Saat Anda menggunakan pemicu Cloud Build untuk membangun container, informasi repositori sumber akan ditampilkan di konsol Google Cloud untuk layanan Anda setelah Anda melakukan deployment ke Cloud Run.
Atau, Anda dapat menggunakan Cloud Deploy untuk menyiapkan pipeline continuous delivery guna men-deploy layanan Cloud Run ke beberapa lingkungan.
Sebelum memulai
- Anda memiliki repositori git dengan
Dockerfileatau codebase Anda ditulis dalam salah satu bahasa yang didukung oleh buildpack Google Cloud. -
Enable the Cloud Build API.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission. Learn how to grant roles.
Peran yang diperlukan
Untuk mendapatkan izin yang Anda perlukan untuk men-deploy layanan Cloud Run dari Git menggunakan Cloud Build, minta administrator untuk memberi Anda peran IAM berikut di project Anda:
-
Administrator Artifact Registry (
roles/artifactregistry.admin) -
Editor Cloud Build (
roles/cloudbuild.builds.editor) -
Cloud Run Developer (
roles/run.developer) -
Service Account User (
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser) -
Service Usage Admin (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin)
Akun layanan yang menjalankan build harus memiliki peran berikut:
- Akun Layanan Cloud Build (
roles/cloudbuild.builds.builder) - Cloud Run Admin (
roles/run.admin) - Service Account User (
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser)
Untuk mengetahui daftar peran dan izin IAM yang terkait dengan Cloud Run, lihat Peran IAM Cloud Run dan Izin IAM Cloud Run. Jika layanan Cloud Run Anda berinteraksi dengan Google Cloud API, seperti Library Klien Cloud, lihat panduan konfigurasi identitas layanan. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang cara memberikan peran, lihat izin deployment dan mengelola akses.
Menyiapkan deployment berkelanjutan dari antarmuka pengguna Cloud Run
Prosedur penyiapan sedikit berbeda bergantung pada apakah Anda menyiapkan deployment berkelanjutan pada layanan baru atau pada layanan yang sudah ada. Klik tab yang sesuai untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut.
Layanan baru
Buat layanan baru seperti yang dijelaskan dalam Men-deploy layanan baru, pastikan Anda memilih Terus-menerus men-deploy revisi baru dari repositori sumber di Service setelan.
Di halaman Service settings, klik Set up with Cloud Build.
GitHub adalah penyedia repositori default. Jika Anda belum diautentikasi, klik Authenticate dan ikuti petunjuknya. Repositori dihubungkan menggunakan aplikasi GitHub Cloud Build.
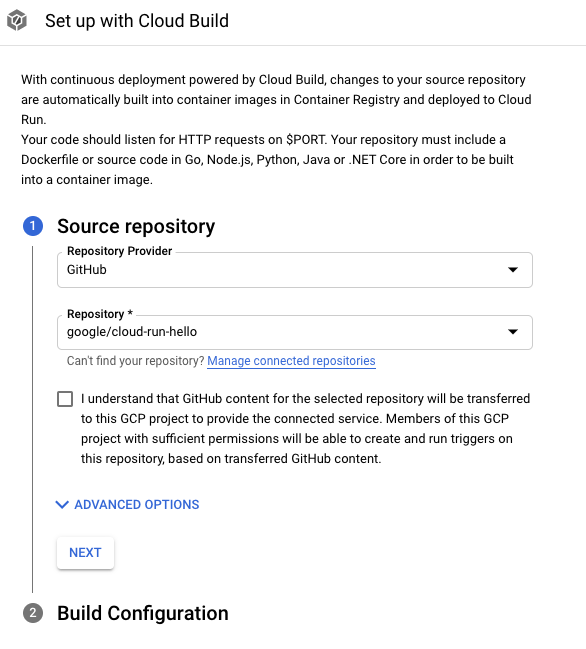
Klik Berikutnya.
Isi opsi pada langkah Konfigurasi Build:
- Branch - menunjukkan sumber yang harus digunakan saat menjalankan pemicu. Anda dapat memasukkan regex di sini. Cabang yang cocok akan otomatis diverifikasi: Anda dapat melihatnya di bawah input. Perhatikan bahwa jika hanya satu cabang yang cocok, pemicu akan otomatis dieksekusi setelah pembuatan.
Jenis Build
Jika repositori Anda harus di-build menggunakan Docker dan berisi Dockerfile, pilih Dockerfile. Source location menunjukkan lokasi dan nama Dockerfile. Direktori ini akan digunakan sebagai konteks build Docker. Semua jalur harus relatif terhadap direktori saat ini.
Jika tidak, pilih Google Cloud Buildpacks. Gunakan Konteks Buildpack untuk menentukan direktori dan Entrypoint (opsional) guna memberikan perintah untuk memulai server. Contoh:
gunicorn -p :8080 main:appuntuk Python,java -jar target/myjar.jaruntuk Java. Biarkan kosong untuk menggunakan perilaku default.
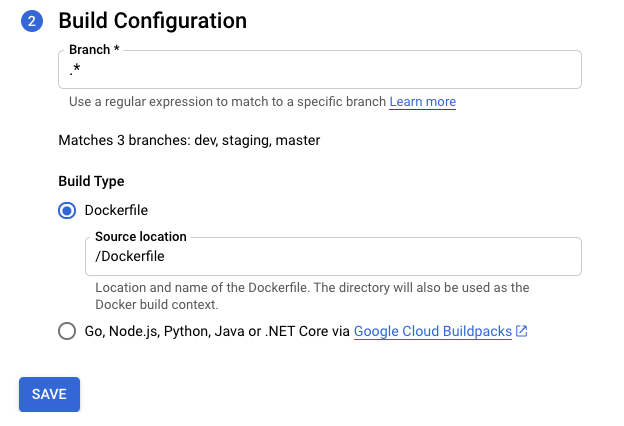
Klik Simpan.
Verifikasi setelan yang dipilih.
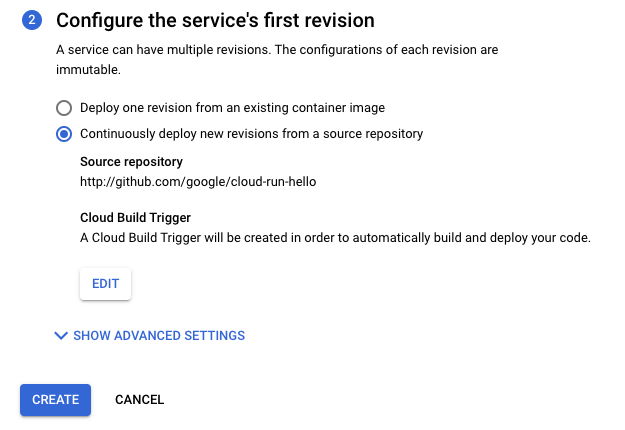
Klik Buat.
Perlu diperhatikan bahwa Anda akan dialihkan ke halaman Detail Layanan untuk melacak progres penyiapan Continuous Deployment.
Setelah semua langkah selesai, perhatikan opsi tambahan:
- Edit Continuous Deployment.
- Build History
- Detail sumber di bagian Detail Revisi.
Layanan yang ada
Temukan layanan dalam daftar layanan, lalu klik layanan tersebut.
Klik Set up Continuous Deployment.
GitHub adalah penyedia repositori default. Jika Anda belum diautentikasi, klik Authenticate dan ikuti petunjuknya. Repositori dihubungkan menggunakan aplikasi GitHub Cloud Build.

Klik Berikutnya.
Isi opsi pada langkah Konfigurasi Build:
- Branch - menunjukkan sumber yang harus digunakan saat menjalankan pemicu. Anda dapat memasukkan regex di sini. Cabang yang cocok akan otomatis diverifikasi: Anda dapat melihatnya di bawah input. Perhatikan bahwa jika hanya satu cabang yang cocok, pemicu akan otomatis dieksekusi setelah pembuatan.
Jenis Build
Jika repositori Anda harus di-build menggunakan Docker dan berisi Dockerfile, pilih Dockerfile. Source location menunjukkan lokasi dan nama Dockerfile. Direktori ini akan digunakan sebagai konteks build Docker. Semua jalur harus relatif terhadap direktori saat ini.
Jika tidak, pilih Google Cloud Buildpacks. Gunakan Konteks Buildpack untuk menentukan direktori dan Entrypoint (opsional) guna memberikan perintah untuk memulai server. Contoh:
gunicorn -p :8080 main:appuntuk Python,java -jar target/myjar.jaruntuk Java. Biarkan kosong untuk menggunakan perilaku default.

Klik Simpan.
Halaman akan dimuat ulang dan menampilkan progres penyiapan Continuous Deployment.
Setelah semua langkah selesai, perhatikan opsi tambahan:
- Edit Continuous Deployment.
- Build History
- Detail sumber di bagian Detail Revisi.
Menyiapkan deployment berkelanjutan secara manual
Lihat Menyiapkan deployment berkelanjutan secara manual jika Anda perlu menggunakan prosedur manual, bukan UI.
Memasang pemicu Cloud Build yang ada untuk layanan Cloud Run
Jika sudah memiliki pemicu Cloud Build, Anda dapat melampirkannya ke layanan dan memanfaatkan fitur konsol di halaman Service Details: tombol Edit Continuous Deployment dan diagram Build History. Google Cloud
Untuk melakukannya, tambahkan label dengan gcb-trigger-id sebagai kunci dan ID unik pemicu Cloud Build sebagai nilai (bukan nama pemicu). Lihat Menetapkan atau mengubah label untuk menyiapkan label.

