You can use Cloud Build to automate builds and deployments to Cloud Run by using Cloud Build trigger to automatically build and deploy your code whenever new commits are pushed to a given branch of a Git repository. For an example, see the quickstart for creating a template repository and deploying continuously from git.
When you use a Cloud Build trigger to build containers, the source repository information is displayed in the Google Cloud console for your service after you deploy to Cloud Run.
Alternatively, you can use Cloud Deploy to set up a continuous-delivery pipeline to deploy Cloud Run services to multiple environments.
Before you begin
- You either have a git repository with a
Dockerfileor your codebase is written in one of the languages supported by Google Cloud's buildpacks. -
Enable the Cloud Build API.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission. Learn how to grant roles.
Required roles
To get the permissions that you need to deploy Cloud Run services from Git using Cloud Build, ask your administrator to grant you the following IAM roles on your project:
-
Artifact Registry Administrator (
roles/artifactregistry.admin) -
Cloud Build Editor (
roles/cloudbuild.builds.editor) -
Cloud Run Developer (
roles/run.developer) -
Service Account User (
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser) -
Service Usage Admin (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin)
The service account running the build must have the following roles:
- Cloud Build Service Account (
roles/cloudbuild.builds.builder) - Cloud Run Admin (
roles/run.admin) - Service Account User (
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser)
For a list of IAM roles and permissions that are associated with Cloud Run, see Cloud Run IAM roles and Cloud Run IAM permissions. If your Cloud Run service interfaces with Google Cloud APIs, such as Cloud Client Libraries, see the service identity configuration guide. For more information about granting roles, see deployment permissions and manage access.
Set up continuous deployment from the Cloud Run user interface
The setup procedure varies slightly depending on whether you are setting up continuous deployment on a new service or on an existing service. Click the appropriate tab to learn more.
New service
Create a new service as described in Deploy a new service, making sure you select Continuously deploy new revisions from a source repository in the Service settings page.
In the Service settings page, click Set up with Cloud Build.
GitHub is the default repository provider. If you are not yet authenticated, click Authenticate and follow the instructions. Connecting a repository is done using the Cloud Build GitHub app.
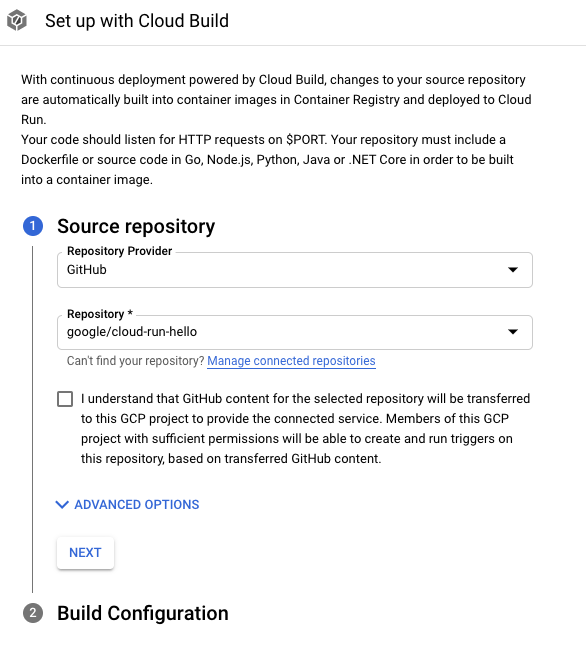
Click Next.
Fill the options in Build Configuration step:
- Branch - indicates what source should be used when running the trigger. You can put the regex here. Matched branches are automatically verified: you can see them below the input. Note that if exactly one branch is matched, the trigger will be automatically executed after the creation.
Build Type
If your repository should be built using Docker and it contains a Dockerfile, select Dockerfile. Source location indicates the location and name of the Dockerfile. This directory will be used as the Docker build context. All paths should be relative to the current directory.
Otherwise, select Google Cloud Buildpacks. Use Buildpack context to specify the directory and Entrypoint (optional) to provide the command to start the server. Example:
gunicorn -p :8080 main:appfor Python,java -jar target/myjar.jarfor Java. Leave it blank to use default behavior.
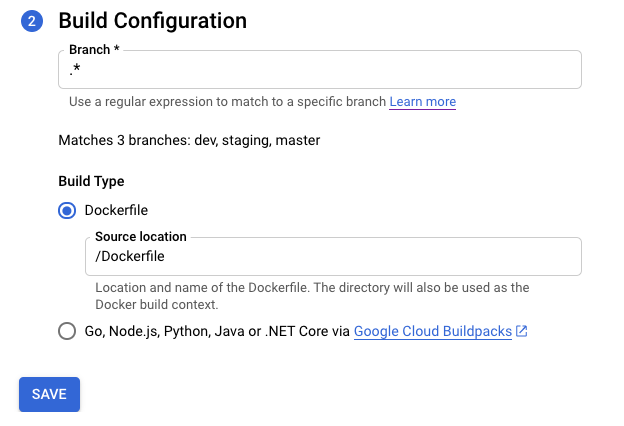
Click Save.
Verify the selected settings.
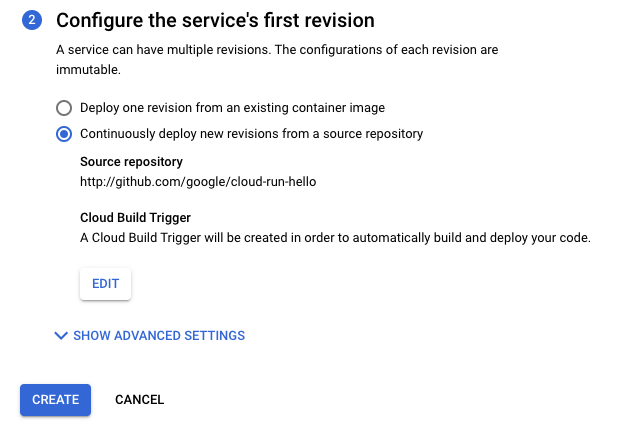
Click Create.
Note that you are redirected to the Service Details page, where you can track the progress of your Continuous Deployment set up.
Once all steps are completed, note additional options:
- Edit Continuous Deployment.
- Build History.
- Source details in the Revision Details section.
Existing service
Locate the service in the services list, and click it.
Click Set up Continuous Deployment.
GitHub is the default repository provider. If you are not yet authenticated, click Authenticate and follow the instructions. Connecting a repository is done using the Cloud Build GitHub app.

Click Next.
Fill the options in Build Configuration step:
- Branch - indicates what source should be used when running the trigger. You can put the regex here. Matched branches are automatically verified: you can see them below the input. Note that if exactly one branch is matched, the trigger will be automatically executed after the creation.
Build Type
If your repository should be built using Docker and it contains a Dockerfile, select Dockerfile. Source location indicates the location and name of the Dockerfile. This directory will be used as the Docker build context. All paths should be relative to the current directory.
Otherwise, select Google Cloud Buildpacks. Use Buildpack context to specify the directory and Entrypoint (optional) to provide the command to start the server. Example:
gunicorn -p :8080 main:appfor Python,java -jar target/myjar.jarfor Java. Leave it blank to use default behavior.

Click Save.
The page reloads and displays the progress of the Continuous Deployment setup.
Once all steps are completed, note additional options:
- Edit Continuous Deployment.
- Build History.
- Source details in the Revision Details section.
Set up continuous deployment manually
Refer to Setting up continuous deployment manually if you need to use a manual procedure and not the UI.
Attach existing Cloud Build trigger to Cloud Run service.
If you already have an existing Cloud Build trigger, you can attach it to the service and take advantage of Google Cloud console features in the Service Details page: Edit Continuous Deployment button and Build History chart.
To do this, add a label with gcb-trigger-id as a key and the unique identifier of the Cloud Build trigger as value (not the trigger name). See Set or modify labels for setting up the label.
