Ce document explique comment configurer et interroger une base de données Spanner Graph pour modéliser, stocker et analyser des relations de données complexes à l'aide de la console Google Cloud et des bibliothèques clientes.
Les rubriques suivantes vous aideront à comprendre comment :
Pour en savoir plus sur les tarifs de Spanner, consultez la page Tarifs de Spanner.
Pour essayer un atelier de programmation, consultez Premiers pas avec Spanner Graph.
Avant de commencer
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
-
Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator
(
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission. Learn how to grant roles.
-
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
-
Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator
(
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission. Learn how to grant roles.
-
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
- Activez l'API Spanner :
Accéder à Activer l'API Spanner -
Pour obtenir les autorisations nécessaires pour créer des instances et des bases de données, demandez à votre administrateur de vous accorder le rôle IAM Administrateur Cloud Spanner (
roles/spanner.admin) sur votre projet. -
Pour obtenir les autorisations nécessaires pour interroger les graphiques Spanner si vous n'avez pas le rôle Administrateur Cloud Spanner, demandez à votre administrateur de vous accorder le rôle IAM Lecteur de bases de données Cloud Spanner (
roles/spanner.databaseReader) sur votre projet. Dans la console Google Cloud , accédez à la page Spanner.
Sélectionnez ou créez un projet Google Cloud si vous ne l'avez pas encore fait.
Effectuez l'une des opérations suivantes :
Si vous n'avez jamais créé d'instance Spanner, sur la page Bienvenue dans Spanner, cliquez sur Créer une instance provisionnée.
Si vous avez créé une instance Spanner, sur la page Instances, cliquez sur Créer une instance.
Sur la page Sélectionner une édition, sélectionnez Enterprise Plus ou Enterprise.
Spanner Graph n'est disponible que dans les éditions Enterprise ou Enterprise Plus. Pour comparer les différentes éditions, cliquez sur Comparer les éditions. Pour en savoir plus, consultez la présentation des éditions Spanner.
Cliquez sur Continuer.
Dans Nom de l'instance, saisissez un nom d'instance (par exemple,
test-instance).Dans ID d'instance, conservez ou modifiez l'ID d'instance. L'ID de votre instance est défini par défaut sur le nom de votre instance, mais vous pouvez le modifier. Le nom et l'ID de votre instance peuvent être identiques ou différents.
Cliquez sur Continuer.
Dans Choisir une configuration, procédez comme suit :
Laissez l'option Régional sélectionnée.
Dans Sélectionner une configuration, sélectionnez une région. Spanner stocke et réplique vos instances dans la région que vous sélectionnez.
Cliquez sur Continuer.
Dans Configurer la capacité de calcul, procédez comme suit :
Dans Sélectionner une unité, sélectionnez Unités de traitement (PU).
Dans Choisir un mode de scaling, conservez l'option Allocation manuelle sélectionnée et, dans Quantité, conservez 1 000 unités de traitement.
Cliquez sur Créer. La console Google Cloud affiche la page Présentation de l'instance que vous avez créée.
Dans la console Google Cloud , accédez à la page Instances Spanner.
Cliquez sur l'instance que vous avez créée, par exemple
Test Instance.Dans Vue d'ensemble, sous le nom de votre instance, cliquez sur Créer une base de données.
Dans Nom de la base de données, saisissez le nom d'une base de données. Exemple :
example-dbDans Sélectionner le dialecte de la base de données, choisissez "SQL standard Google". Spanner Graph n'est pas disponible dans le dialecte PostgreSQL.
Saisissez le schéma suivant dans l'onglet de l'éditeur Modèles LDD. Le schéma contient deux définitions de tables de nœuds,
PersonetAccount, et deux définitions de tables d'arêtes,PersonOwnAccountetAccountTransferAccount. Spanner Graph utilise des tables relationnelles pour définir des graphiques. Vous verrez donc à la fois des tables relationnelles et des instructions de graphique dans le schéma. Pour en savoir plus sur le schéma Spanner Graph, consultez la présentation du schéma Spanner Graph :CREATE TABLE Person ( id INT64 NOT NULL, name STRING(MAX), birthday TIMESTAMP, country STRING(MAX), city STRING(MAX), ) PRIMARY KEY (id); CREATE TABLE Account ( id INT64 NOT NULL, create_time TIMESTAMP, is_blocked BOOL, nick_name STRING(MAX), ) PRIMARY KEY (id); CREATE TABLE PersonOwnAccount ( id INT64 NOT NULL, account_id INT64 NOT NULL, create_time TIMESTAMP, FOREIGN KEY (account_id) REFERENCES Account (id) ) PRIMARY KEY (id, account_id), INTERLEAVE IN PARENT Person ON DELETE CASCADE; CREATE TABLE AccountTransferAccount ( id INT64 NOT NULL, to_id INT64 NOT NULL, amount FLOAT64, create_time TIMESTAMP NOT NULL, order_number STRING(MAX), FOREIGN KEY (to_id) REFERENCES Account (id) ) PRIMARY KEY (id, to_id, create_time), INTERLEAVE IN PARENT Account ON DELETE CASCADE; CREATE OR REPLACE PROPERTY GRAPH FinGraph NODE TABLES (Account, Person) EDGE TABLES ( PersonOwnAccount SOURCE KEY (id) REFERENCES Person (id) DESTINATION KEY (account_id) REFERENCES Account (id) LABEL Owns, AccountTransferAccount SOURCE KEY (id) REFERENCES Account (id) DESTINATION KEY (to_id) REFERENCES Account (id) LABEL Transfers );Conservez les paramètres par défaut dans Afficher les options de chiffrement.
Cliquez sur Créer. Google Cloud console affiche la page Présentation de la base de données que vous avez créée.
Sur la page Spanner Studio, cliquez sur Nouvel onglet ou utilisez l'onglet de l'éditeur.
Copiez et collez les instructions d'insertion de données de graphique suivantes dans les nœuds et les arêtes.
INSERT INTO Account (id, create_time, is_blocked, nick_name) VALUES (7,"2020-01-10 06:22:20.222",false,"Vacation Fund"), (16,"2020-01-27 17:55:09.206",true,"Vacation Fund"), (20,"2020-02-18 05:44:20.655",false,"Rainy Day Fund"); INSERT INTO Person (id, name, birthday, country, city) VALUES (1,"Alex","1991-12-21 00:00:00","Australia","Adelaide"), (2,"Dana","1980-10-31 00:00:00","Czech_Republic","Moravia"), (3,"Lee","1986-12-07 00:00:00","India","Kollam"); INSERT INTO AccountTransferAccount (id, to_id, amount, create_time, order_number) VALUES (7,16,300,"2020-08-29 15:28:58.647","304330008004315"), (7,16,100,"2020-10-04 16:55:05.342","304120005529714"), (16,20,300,"2020-09-25 02:36:14.926","103650009791820"), (20,7,500,"2020-10-04 16:55:05.342","304120005529714"), (20,16,200,"2020-10-17 03:59:40.247","302290001255747"); INSERT INTO PersonOwnAccount (id, account_id, create_time) VALUES (1,7,"2020-01-10 06:22:20.222"), (2,20,"2020-01-27 17:55:09.206"), (3,16,"2020-02-18 05:44:20.655");Cliquez sur Exécuter. Une fois l'exécution terminée, l'onglet Résultats indique que trois lignes ont été insérées.
Sur la page Présentation de la base de données, cliquez sur Spanner Studio dans le menu de navigation.
Sur la page Spanner Studio, cliquez sur Nouvel onglet ou utilisez l'onglet de l'éditeur.
Saisissez la requête suivante dans l'éditeur de requête. La requête permet de trouver toutes les personnes à qui Dana a transféré de l'argent, ainsi que le montant de ces transferts.
GRAPH FinGraph MATCH (from_person:Person {name: "Dana"})-[:Owns]-> (from_account:Account)-[transfer:Transfers]-> (to_account:Account)<-[:Owns]-(to_person:Person) RETURN from_person.name AS from_account_owner, from_account.id AS from_account_id, to_person.name AS to_account_owner, to_account.id AS to_account_id, transfer.amount AS amountCliquez sur Exécuter.
L'onglet Résultats affiche les chemins suivants de Dana, qui possède le compte 20 :
- À
Account {id:7}appartenant à Alex. À
Account {id:16}appartenant à Lee.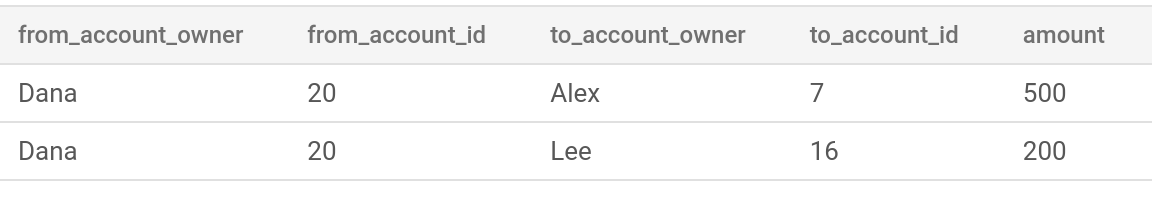
- À
Dans la console Google Cloud , accédez à Instances Spanner.
Cliquez sur le nom de l'instance, par exemple Test Instance.
Cliquez sur le nom de la base de données, par exemple example-db.
Sur la page Détails de la base de données, cliquez sur Supprimer la base de données.
Confirmez que vous souhaitez supprimer la base de données en saisissant son nom et en cliquant sur Supprimer.
Dans la console Google Cloud , accédez à la page Instances Spanner.
Cliquez sur le nom de l'instance que vous souhaitez supprimer, par exemple Instance de test.
Cliquez sur Supprimer l'instance.
Confirmez que vous souhaitez supprimer l'instance en saisissant son nom et en cliquant sur Supprimer.
- En savoir plus sur Spanner Graph grâce à un atelier de programmation
- En savoir plus sur le schéma Spanner Graph
- Créer, mettre à jour ou supprimer un schéma Spanner Graph.
- Insérer, mettre à jour ou supprimer des données Spanner Graph
- Présentation des requêtes Spanner Graph
- Migrez vers Spanner Graph.
Créer une instance Spanner
Lorsque vous utilisez Spanner pour la première fois, vous devez créer une instance qui alloue des ressources pour les bases de données Spanner. Cette section vous explique comment créer une instance à l'aide de la console Google Cloud .
Créer une base de données de graphiques à l'aide d'un schéma
Cette section explique comment créer une base de données Spanner Graph à l'aide d'un schéma Spanner Graph. Vous pouvez utiliser la console Google Cloud ou les bibliothèques clientes.
Console
Bibliothèques clientes
Python
Java
Go
C++
Insérer des données de graphique
Une fois votre base de données créée, vous pouvez y ajouter des données. Cette section explique comment insérer des données dans votre graphique à l'aide de la console Google Cloud pour une interface graphique ou à l'aide des bibliothèques clientes de manière programmatique.
Console
Bibliothèques clientes
Python
Java
Go
C++
Le graphique suivant montre les personnes, les comptes, la propriété des comptes et les transferts de comptes à partir des encarts :
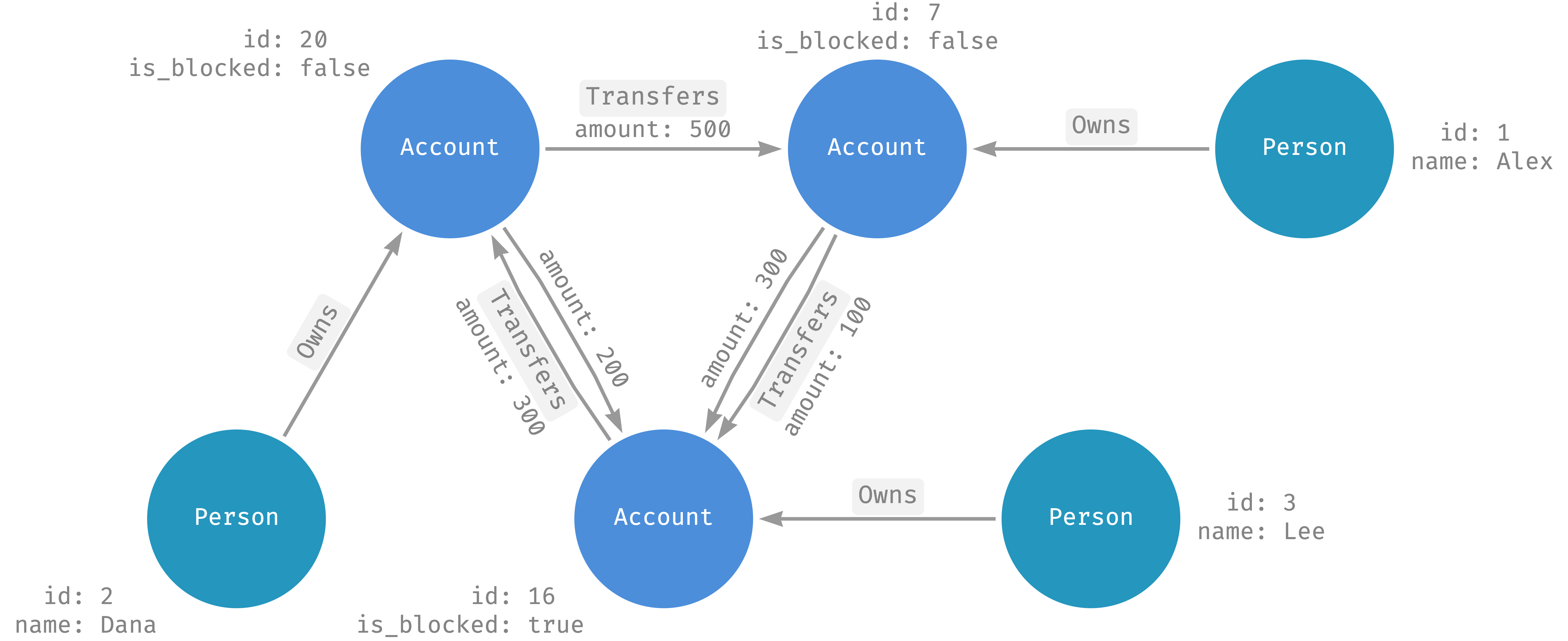
Exécuter une requête de graphique
Après avoir inséré des données dans votre graphique, vous pouvez les interroger pour trouver des tendances et des relations. Cette section vous explique comment exécuter des requêtes à l'aide de la consoleGoogle Cloud pour une interface graphique, ou de manière programmatique avec des bibliothèques clientes.
Console
Bibliothèques clientes
Python
Java
Go
C++
Effectuer un nettoyage
Cette section vous explique comment nettoyer les ressources que vous avez créées pour éviter que des frais ne soient facturés sur votre compte de facturation Cloud. Si vous prévoyez d'explorer d'autres exemples de graphiques Spanner dans la section Étapes suivantes, n'effectuez pas encore ces étapes. La suppression d'une instance Spanner supprime également toutes les bases de données qu'elle contient.

