Vertex AI Platform の一部である Vertex AI Agent Engine は、開発者が本番環境で AI エージェントをデプロイ、管理、スケーリングできるようにする一連のサービスです。本番環境でエージェントをスケーリングするためのインフラストラクチャの処理は Agent Engine が行うため、開発者はアプリケーションの作成に集中できます。Vertex AI Agent Engine で提供されるサービスは次のとおりです。これらは、個別に使用することも組み合わせて使用することもできます。
ランタイム:
- マネージド ランタイムとエンドツーエンドの管理機能を使用して、エージェントをデプロイしてスケーリングします。
- システム依存関係のビルド時のインストール スクリプトを使用して、エージェントのコンテナ イメージをカスタマイズします。
- VPC-SC コンプライアンスや認証と IAM の設定などのセキュリティ機能を使用します。
- 関数呼び出しなどのモデルやツールにアクセスします。
- さまざまな Python フレームワークと Agent2Agent オープン プロトコルを使用して構築されたエージェントをデプロイします。
- Google Cloud Trace(OpenTelemetry をサポート)、Cloud Monitoring、Cloud Logging を使用して、エージェントの動作を把握します。
品質と評価(プレビュー): 統合された Gen AI Evaluation Service でエージェントの品質を評価し、Gemini モデルのトレーニング実行でエージェントを最適化します。
Example Store(プレビュー): 少数ショットの例を保存して動的に取得し、エージェントのパフォーマンスを改善します。
Sessions(プレビュー): Agent Engine Sessions を使用すると、ユーザーとエージェントの間の個々のインタラクションを保存し、会話のコンテキストの明確なソースを提供できます。
Memory Bank(プレビュー): Agent Engine Memory Bank を使用すると、セッションから情報を保存して取得し、エージェントのインタラクションをパーソナライズできます。
Code Execution(プレビュー): Agent Engine Code Execution を使用すると、エージェントは隔離された安全なマネージド サンドボックス環境でコードを実行できます。
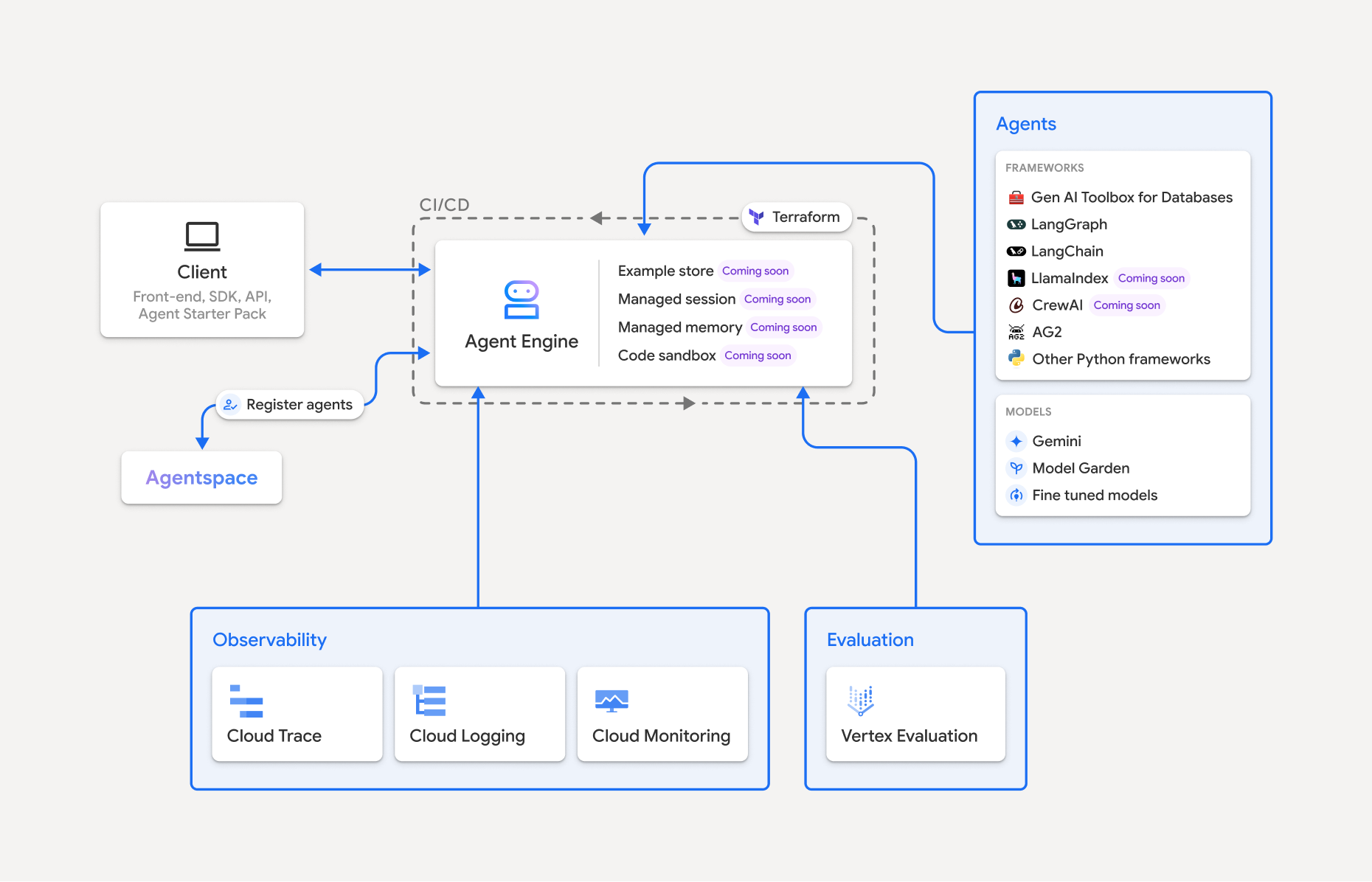
Vertex AI Agent Engine は、AI エージェントの検出、構築、デプロイを行うための機能スイートである Vertex AI Agent Builder の一部です。
Vertex AI Agent Engine で作成してデプロイする
注: Vertex AI Agent Engine での合理化された IDE ベースの開発とデプロイのエクスペリエンスについては、agent-starter-pack をご覧ください。すぐに使用できるテンプレートと試験運用のための組み込みの UI が用意されており、デプロイ、運用、評価、カスタマイズ、オブザーバビリティが簡素化されます。
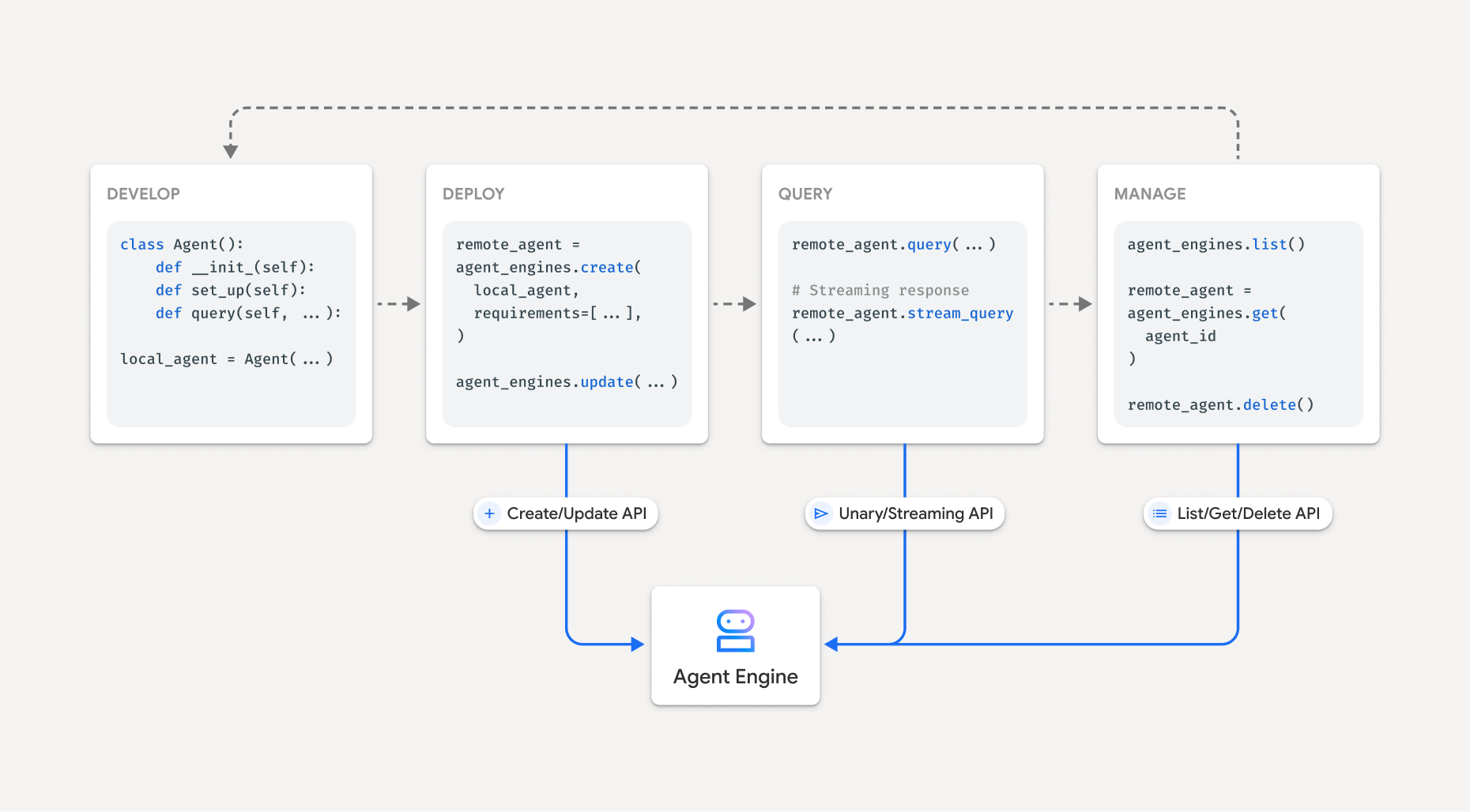
Vertex AI Agent Engine でエージェントを構築するワークフローは次のとおりです。
| ステップ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 1. 環境を設定する | Google プロジェクトを設定し、最新バージョンの Vertex AI SDK for Python をインストールします。 |
| 2. エージェントを開発する | Vertex AI Agent Engine にデプロイできるエージェントを開発します。 |
| 3. エージェントをデプロイする | エージェントを Vertex AI Agent Engine マネージド ランタイムにデプロイします。 |
| 4. エージェントを使用する | API リクエストを送信してエージェントをクエリします。 |
| 5. デプロイされたエージェントを管理する | Vertex AI Agent Engine にデプロイしたエージェントを管理、削除します。 |
次の図は、このプロセスを示しています。
サポートされているフレームワーク
次の表に、各種のエージェント フレームワークに対して Vertex AI Agent Engine が提供するサポートレベルを示します。
| サポートレベル | エージェント フレームワーク |
|---|---|
| カスタム テンプレート: カスタム テンプレートを適応させて、フレームワークから Vertex AI Agent Engine へのデプロイをサポートできます。 | CrewAI、カスタム フレームワーク |
| Vertex AI SDK の統合: Vertex AI Agent Engine は、Vertex AI SDK とドキュメントでフレームワークごとにマネージド テンプレートを提供します。 | AG2、LlamaIndex |
| 完全な統合: フレームワーク、Vertex AI Agent Engine、より広範な Google Cloud エコシステム全体で機能するように統合されています。 | Agent Development Kit(ADK)、LangChain、LangGraph |
Agent Starter Pack を使用して本番環境にデプロイする
Agent Starter Pack は、Vertex AI Agent Engine 用に構築された本番環境対応の生成 AI エージェント テンプレートのコレクションです。Agent Starter Pack には次のものが含まれています。
- 事前構築済みのエージェント テンプレート: ReAct、RAG、マルチエージェントなどのテンプレート。
- インタラクティブなプレイグラウンド: エージェントをテストして操作します。
- 自動化されたインフラストラクチャ: リソース管理の合理化のために Terraform を使用しています。
- CI / CD パイプライン: Cloud Build を活用した自動デプロイ ワークフロー。
- オブザーバビリティ: Cloud Trace と Cloud Logging の組み込みのサポート。
利用を開始するには、クイックスタートをご覧ください。
ユースケース
エンドツーエンドの例を使用して Vertex AI Agent Engine の詳細を確認するには、次のリソースをご覧ください。
エンタープライズ セキュリティ
Vertex AI Agent Engine は、企業のセキュリティ要件を満たし、組織のセキュリティ ポリシーを遵守し、セキュリティのベスト プラクティスに従うのに役立つ機能をいくつかサポートしています。次の機能がサポートされています。
顧客管理の暗号鍵(CMEK): Vertex AI Agent Engine は、独自の暗号鍵でデータを保護する CMEK をサポートしています。これにより、 Google Cloudで保存データを保護する鍵の所有権と完全な制御を保持できます。詳細については、Agent Engine CMEK をご覧ください。
VPC Service Controls: Vertex AI Agent Engine は、データ セキュリティを強化し、データの引き出しのリスクを軽減するために、VPC Service Controls をサポートしています。VPC Service Controls が構成されている場合、デプロイされたエージェントは、BigQuery API、Cloud SQL Admin API、Vertex AI API などの Google API とサービスへの安全なアクセスを維持し、定義された境界内でのシームレスなオペレーションを確認します。VPC Service Controls は、すべての公共のインターネット アクセスを効果的にブロックし、データ移動を承認済みネットワーク境界内に制限することで、企業のセキュリティ ポスチャーを大幅に強化します。
データ所在地(DRZ): Vertex AI Agent Engine は、すべての保存データが指定されたリージョン内に保存されるように、データ所在地(DRZ)をサポートしています。
Private Service Connect インターフェース: PSC-I を使用すると、エージェントはユーザーの VPC でプライベートにホストされているサービスとやり取りできます。詳細については、Vertex AI Agent Engine で Private Service Connect インターフェースを使用するをご覧ください。
HIPAA: Vertex AI Platform の一部として、Vertex AI Agent Engine は HIPAA ワークロードをサポートしています。
サポートされるリージョン
Vertex AI Agent Engine と Agent Engine Sessions は、次のリージョンでサポートされています。
| リージョン | ロケーション | サポート対象のバージョン |
|---|---|---|
us-central1 |
アイオワ | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
us-east4 |
北バージニア | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
us-west1 |
オレゴン | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
europe-west1 |
ベルギー | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
europe-west2 |
ロンドン | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
europe-west3 |
フランクフルト | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
europe-west4 |
オランダ | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
europe-southwest1 |
マドリッド | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
asia-east1 |
台湾 | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
asia-northeast1 |
東京 | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
asia-south1 |
ムンバイ | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
asia-southeast1 |
シンガポール | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
australia-southeast2 |
メルボルン | v1 が一般提供機能としてサポートされています。v1beta1 はプレビュー機能としてサポートされています。 |
Agent Engine Memory Bank(プレビュー)は、次のリージョンでサポートされています。
| リージョン | ロケーション | サポート対象のバージョン |
|---|---|---|
us-central1 |
アイオワ | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
us-east4 |
北バージニア | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
us-west1 |
オレゴン | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
europe-west1 |
ベルギー | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
europe-west4 |
オランダ | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
europe-southwest1 |
マドリッド | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
Agent Engine Code Execution(プレビュー)は、次のリージョンでサポートされています。
| リージョン | ロケーション | サポート対象のバージョン |
|---|---|---|
us-central1 |
アイオワ | v1beta1 バージョンがサポートされています。 |
割り当て
各リージョンの特定のプロジェクトの Vertex AI Agent Engine には、次の上限が適用されます。| 説明 | 上限 |
|---|---|
| 1 分あたりの Vertex AI Agent Engine の作成、削除、更新回数 | 10 |
| 1 分あたりの Vertex AI Agent Engine セッションの作成、削除、更新回数 | 100 |
1 分あたりの Vertex AI Agent Engine のクエリ回数(Query または StreamQuery) |
90 |
| 1 分あたりの Vertex AI Agent Engine セッションへのイベントの追加回数 | 300 |
| Vertex AI Agent Engine リソースの最大数 | 100 |
| 1 分あたりの Vertex AI Agent Engine メモリリソースの作成、削除、更新回数 | 100 |
| 1 分あたりの Vertex AI Agent Engine Memory Bank からの取得、一覧表示、取得回数 | 300 |
| 1 分あたりのサンドボックス環境(Code Execution)の実行リクエスト数 | 1000 |
| リージョンあたりのサンドボックス環境(Code Execution)のエンティティ数 | 1000 |
1 分あたりの A2A エージェントの POST リクエスト数(sendMessage や cancelTask など) |
60 |
1 分あたりの A2A エージェントの GET リクエスト数(getTask や getCard など) |
600 |
料金
Agent Engine ランタイムの料金は、エージェントがリクエストの処理に使用するコンピューティング(vCPU 時間)とメモリ(GiB 時間)に基づいています。デプロイされたエージェントがアイドル状態になっている時間に対しては課金されません。
| プロダクト | SKU ID | 価格 |
|---|---|---|
| ReasoningEngine vCPU | 8A55-0B95-B7DC | $0.0994/vCPU-Hr |
| ReasoningEngine Memory | 0B45-6103-6EC1 | $0.0105/GiB-Hr |
詳細は、料金をご覧ください。
クライアント ベースの SDK への移行
Vertex AI SDK for Python 内の agent_engines モジュールは、主に次の理由から、クライアント ベースの設計にリファクタリングされています。
- Google ADK と Google Gen AI SDK の標準の型表現に合わせるため。これにより、さまざまな SDK で一貫性のある標準化された方法でデータ型が表現されるため、相互運用が簡単になり、変換のオーバーヘッドが軽減されます。
- マルチプロジェクト、マルチロケーションのアプリケーションで Google Cloud パラメータのスコープをクライアント レベルで設定するため。これにより、各クライアント インスタンスを特定のプロジェクトとロケーションの設定で構成することで、異なる Google Cloud プロジェクトや地理的位置にわたるリソースとのインタラクションをアプリケーションで管理できます。
- Vertex AI Agent Engine サービスの見つけやすさとまとまりを向上させるため。
