함수 호출(도구 사용이라고도 함)은 LLM에 외부 도구(예: get_current_weather 함수)의 정의를 제공합니다. 프롬프트를 처리할 때 모델은 도구가 필요한지 지능적으로 판단하고, 필요한 경우 호출할 도구와 파라미터(예: get_current_weather(location='Boston'))를 지정하는 구조화된 데이터를 출력합니다. 그러면 애플리케이션이 이 도구를 실행하고 결과를 모델에 다시 제공하여 모델이 동적이고 실제 정보 또는 작업 결과를 사용하여 응답을 완료할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 LLM과 시스템이 효과적으로 연결되고 기능이 확장됩니다.
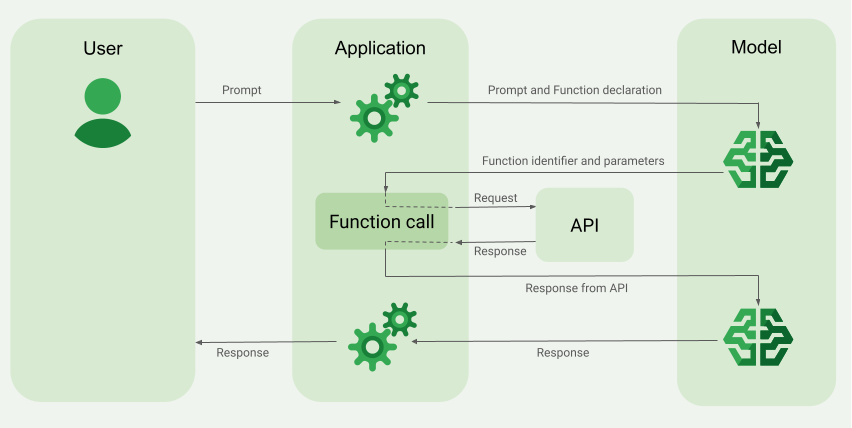
함수 호출은 다음 두 가지 주요 사용 사례를 지원합니다.
데이터 가져오기: 현재 날씨, 통화 변환, 기술 자료 및 API의 특정 데이터와 같은 모델 응답에 대한 최신 정보를 가져옵니다(RAG).
작업 수행: 양식 제출, 애플리케이션 상태 업데이트, 에이전트 워크플로 오케스트레이션(예: 대화 핸드오프)과 같은 외부 작업을 실행합니다.
함수 호출을 기반으로 하는 사용 사례와 예시를 더 보려면 사용 사례를 참조하세요.
기능 및 제한사항
다음 모델은 함수 호출을 지원합니다.
FunctionDeclarations를 최대 512개까지 지정할 수 있습니다.OpenAPI 스키마 형식으로 함수를 정의합니다.
이름 및 설명 관련 도움말을 포함하여 함수 선언과 관련된 권장사항은 권장사항을 참조하세요.
개방형 모델의 경우 이 사용자 가이드를 따르세요.
함수 호출 애플리케이션을 만드는 방법
함수 호출을 사용하려면 다음 작업을 실행하세요.
1단계: 프롬프트 및 함수 선언을 모델에 제출
OpenAPI 스키마와 호환되는 스키마 형식으로 Tool를 선언합니다. 자세한 내용은 스키마 예시를 참조하세요.
다음 예에서는 프롬프트와 함수 선언을 Gemini 모델에 제출합니다.
REST
PROJECT_ID=myproject
LOCATION=us-central1
MODEL_ID=gemini-2.0-flash-001
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
https://${LOCATION}-aiplatform.googleapis.com/v1/projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${LOCATION}/publishers/google/models/${MODEL_ID}:generateContent \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "What is the weather in Boston?"
}]
}],
"tools": [{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name of the location for which to get the weather.",
"default": {
"string_value": "Boston, MA"
}
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}]
}'
Python
Python 딕셔너리를 사용하여 수동으로 또는 from_func 도우미 함수를 사용하여 자동으로 스키마를 지정할 수 있습니다. 다음 예시에서는 함수를 수동으로 선언하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
import vertexai
from vertexai.generative_models import (
Content,
FunctionDeclaration,
GenerationConfig,
GenerativeModel,
Part,
Tool,
ToolConfig
)
# Initialize Vertex AI
# TODO(developer): Update the project
vertexai.init(project="PROJECT_ID", location="us-central1")
# Initialize Gemini model
model = GenerativeModel(model_name="gemini-2.0-flash")
# Manual function declaration
get_current_weather_func = FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_current_weather",
description="Get the current weather in a given location",
# Function parameters are specified in JSON schema format
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name of the location for which to get the weather.",
"default": {
"string_value": "Boston, MA"
}
}
},
},
)
response = model.generate_content(
contents = [
Content(
role="user",
parts=[
Part.from_text("What is the weather like in Boston?"),
],
)
],
generation_config = GenerationConfig(temperature=0),
tools = [
Tool(
function_declarations=[get_current_weather_func],
)
]
)
또는 다음 예시와 같이 from_func 도우미 함수를 사용하여 함수를 자동으로 선언할 수 있습니다.
def get_current_weather(location: str = "Boston, MA"):
"""
Get the current weather in a given location
Args:
location: The city name of the location for which to get the weather.
"""
# This example uses a mock implementation.
# You can define a local function or import the requests library to call an API
return {
"location": "Boston, MA",
"temperature": 38,
"description": "Partly Cloudy",
"icon": "partly-cloudy",
"humidity": 65,
"wind": {
"speed": 10,
"direction": "NW"
}
}
get_current_weather_func = FunctionDeclaration.from_func(get_current_weather)
Node.js
이 예시에서는 함수 하나와 프롬프트 하나가 포함된 텍스트 시나리오를 보여줍니다.
Node.js
이 샘플을 사용해 보기 전에 Vertex AI 빠른 시작: 클라이언트 라이브러리 사용의 Node.js 설정 안내를 따르세요. 자세한 내용은 Vertex AI Node.js API 참고 문서를 참조하세요.
Vertex AI에 인증하려면 애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보를 설정합니다. 자세한 내용은 로컬 개발 환경의 인증 설정을 참조하세요.
Go
이 예시에서는 함수 하나와 프롬프트 하나가 포함된 텍스트 시나리오를 보여줍니다.
Go를 설치하거나 업데이트하는 방법을 알아보세요.
자세한 내용은 SDK 참고 문서를 참조하세요.
Vertex AI에서 Gen AI SDK를 사용하도록 환경 변수를 설정합니다.
# Replace the `GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT` and `GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION` values # with appropriate values for your project. export GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT export GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION=global export GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI=True
C#
이 예시에서는 함수 하나와 프롬프트 하나가 포함된 텍스트 시나리오를 보여줍니다.
C#
이 샘플을 사용해 보기 전에 Vertex AI 빠른 시작: 클라이언트 라이브러리 사용의 C# 설정 안내를 따르세요. 자세한 내용은 Vertex AI C# API 참고 문서를 참조하세요.
Vertex AI에 인증하려면 애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보를 설정합니다. 자세한 내용은 로컬 개발 환경의 인증 설정을 참조하세요.
Java
Java
이 샘플을 사용해 보기 전에 Vertex AI 빠른 시작: 클라이언트 라이브러리 사용의 Java 설정 안내를 따르세요. 자세한 내용은 Vertex AI Java API 참고 문서를 참조하세요.
Vertex AI에 인증하려면 애플리케이션 기본 사용자 인증 정보를 설정합니다. 자세한 내용은 로컬 개발 환경의 인증 설정을 참조하세요.
모델에서 특정 함수 출력이 필요하다고 판단하면 애플리케이션이 모델에서 수신하는 응답에는 함수 이름과 함수를 호출해야 하는 파라미터 값이 포함됩니다.
다음은 "보스턴 날씨는 어때?"와 같은 사용자 프롬프트에 대한 모델 응답의 예시입니다. 모델은 Boston, MA 파라미터를 사용하여 get_current_weather 함수를 호출하도록 제안합니다.
candidates {
content {
role: "model"
parts {
function_call {
name: "get_current_weather"
args {
fields {
key: "location"
value {
string_value: "Boston, MA"
}
}
}
}
}
}
...
}
2단계: 모델에 API 출력 제공
외부 API를 호출하고 API 출력을 모델에 다시 전달합니다.
다음 예시에서는 합성 데이터를 사용하여 외부 API의 응답 페이로드를 시뮬레이션하고 출력을 모델에 다시 제출합니다.
REST
PROJECT_ID=myproject
MODEL_ID=gemini-2.0-flash
LOCATION="us-central1"
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
https://${LOCATION}-aiplatform.googleapis.com/v1/projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${LOCATION}/publishers/google/models/${MODEL_ID}:generateContent \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": {
"text": "What is the weather in Boston?"
}
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"args": {
"location": "Boston, MA"
}
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"response": {
"temperature": 20,
"unit": "C"
}
}
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"function_declarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a specific location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name of the location for which to get the weather."
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
Python
function_response_contents = []
function_response_parts = []
# Iterates through the function calls in the response in case there are parallel function call requests
for function_call in response.candidates[0].function_calls:
print(f"Function call: {function_call.name}")
# In this example, we'll use synthetic data to simulate a response payload from an external API
if (function_call.args['location'] == "Boston, MA"):
api_response = { "location": "Boston, MA", "temperature": 38, "description": "Partly Cloudy" }
if (function_call.args['location'] == "San Francisco, CA"):
api_response = { "location": "San Francisco, CA", "temperature": 58, "description": "Sunny" }
function_response_parts.append(
Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response={"contents": api_response}
)
)
# Add the function call response to the contents
function_response_contents = Content(role="user", parts=function_response_parts)
# Submit the User's prompt, model's response, and API output back to the model
response = model.generate_content(
[
Content( # User prompt
role="user",
parts=[
Part.from_text("What is the weather like in Boston?"),
],
),
response.candidates[0].content, # Function call response
function_response_contents # API output
],
tools=[
Tool(
function_declarations=[get_current_weather_func],
)
],
)
# Get the model summary response
print(response.text)
API 호출과 관련된 권장사항은 권장사항 - API 호출을 참조하세요.
모델이 여러 병렬 함수 호출을 제안했으면 애플리케이션이 모든 응답을 다시 모델에 제공해야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 병렬 함수 호출 예시를 참조하세요.
모델은 다른 함수의 출력이 프롬프트 응답에 필요한지 확인할 수 있습니다. 이 경우에 애플리케이션이 모델로부터 수신하는 응답에는 다른 함수 이름과 다른 파라미터 값 집합이 포함됩니다.
모델에서 API 응답이 사용자 프롬프트에 응답하기에 충분하다고 판단하면 자연어 응답을 만들어 애플리케이션에 반환합니다. 이 경우 애플리케이션에서 응답을 다시 사용자에게 전달해야 합니다. 다음은 자연어 응답의 예시입니다.
It is currently 38 degrees Fahrenheit in Boston, MA with partly cloudy skies.
생각이 포함된 함수 호출
thinking이 사용 설정된 상태에서 함수를 호출할 때는 모델 응답 객체에서 thought_signature를 가져와 함수의 실행 결과를 모델에 다시 보낼 때 반환해야 합니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
Python
# Call the model with function declarations
# ...Generation config, Configure the client, and Define user prompt (No changes)
# Send request with declarations (using a thinking model)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash", config=config, contents=contents)
# See thought signatures
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if not part.text:
continue
if part.thought and part.thought_signature:
print("Thought signature:")
print(part.thought_signature)
사고 서명을 볼 필요는 없지만 함수 실행 결과와 함께 반환하도록 2단계를 조정하여 최종 대답에 사고를 통합할 수 있도록 해야 합니다.
Python
# Create user friendly response with function result and call the model again
# ...Create a function response part (No change)
# Append thought signatures, function call and result of the function execution to contents
function_call_content = response.candidates[0].content
# Append the model's function call message, which includes thought signatures
contents.append(function_call_content)
contents.append(types.Content(role="user", parts=[function_response_part])) # Append the function response
final_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
config=config,
contents=contents,
)
print(final_response.text)
생각 서명을 반환할 때는 다음 가이드라인을 따르세요.
- 모델은 응답의 다른 부분(예: 함수 호출 또는 텍스트, 텍스트 또는 생각 요약 부분) 내에서 서명을 반환합니다. 후속 턴에서 모든 파트가 포함된 전체 대답을 모델에 반환합니다.
- 서명이 포함된 파트를 서명이 포함된 다른 파트와 병합하지 마세요. 서명은 함께 연결할 수 없습니다.
- 서명이 있는 부분을 서명이 없는 부분과 병합하지 마세요. 이렇게 하면 서명으로 표현된 생각의 올바른 위치가 깨집니다.
생각 페이지에서 생각 서명의 제한사항 및 사용법과 일반적인 생각 모델에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
병렬 함수 호출
"보스턴과 샌프란시스코 날씨 정보를 알려줘"와 같은 프롬프트의 경우에는 모델이 몇 가지 병렬 함수 호출을 제안할 수 있습니다. 병렬 함수 호출을 지원하는 모델 목록은 지원되는 모델을 참조하세요.
REST
이 예시에서는 get_current_weather 함수가 하나 있는 시나리오를 보여줍니다.
사용자 프롬프트는 '보스턴과 샌프란시스코의 날씨 정보를 알려줘'입니다. 모델은 두 가지 병렬 get_current_weather 함수 호출을 제안합니다. 하나는 Boston 파라미터를 사용하고 다른 하나는 San Francisco 파라미터를 사용합니다.
요청 파라미터에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 Gemini API를 참조하세요.
{
"candidates": [
{
"content": {
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"args": {
"location": "Boston"
}
}
},
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"args": {
"location": "San Francisco"
}
}
}
]
},
...
}
],
...
}
다음 명령어는 모델에 함수 출력을 제공하는 방법을 보여줍니다. my-project를 Google Cloud 프로젝트 이름으로 바꿉니다.
모델 요청
PROJECT_ID=my-project
MODEL_ID=gemini-2.0-flash
LOCATION="us-central1"
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
https://${LOCATION}-aiplatform.googleapis.com/v1/projects/${PROJECT_ID}/locations/${LOCATION}/publishers/google/models/${MODEL_ID}:generateContent \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": {
"text": "What is difference in temperature in Boston and San Francisco?"
}
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"args": {
"location": "Boston"
}
}
},
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"args": {
"location": "San Francisco"
}
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"response": {
"temperature": 30.5,
"unit": "C"
}
}
},
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"response": {
"temperature": 20,
"unit": "C"
}
}
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"function_declarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a specific location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name of the location for which to get the weather."
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
모델에서 생성된 자연어 응답은 다음과 비슷합니다.
모델 응답
[
{
"candidates": [
{
"content": {
"parts": [
{
"text": "The temperature in Boston is 30.5C and the temperature in San Francisco is 20C. The difference is 10.5C. \n"
}
]
},
"finishReason": "STOP",
...
}
]
...
}
]
Python
이 예시에서는 get_current_weather 함수가 하나 있는 시나리오를 보여줍니다.
사용자 프롬프트는 '보스턴과 샌프란시스코의 날씨는 어때?'입니다.
my-project를 Google Cloud 프로젝트 이름으로 바꿉니다.
import vertexai
from vertexai.generative_models import (
Content,
FunctionDeclaration,
GenerationConfig,
GenerativeModel,
Part,
Tool,
ToolConfig
)
# Initialize Vertex AI
# TODO(developer): Update the project
vertexai.init(project="my-project", location="us-central1")
# Initialize Gemini model
model = GenerativeModel(model_name="gemini-2.0-flash")
# Manual function declaration
get_current_weather_func = FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_current_weather",
description="Get the current weather in a given location",
# Function parameters are specified in JSON schema format
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name of the location for which to get the weather.",
"default": {
"string_value": "Boston, MA"
}
}
},
},
)
response = model.generate_content(
contents = [
Content(
role="user",
parts=[
Part.from_text("What is the weather like in Boston and San Francisco?"),
],
)
],
generation_config = GenerationConfig(temperature=0),
tools = [
Tool(
function_declarations=[get_current_weather_func],
)
]
)
다음 명령어는 모델에 함수 출력을 제공하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
function_response_contents = []
function_response_parts = []
# You can have parallel function call requests for the same function type.
# For example, 'location_to_lat_long("London")' and 'location_to_lat_long("Paris")'
# In that case, collect API responses in parts and send them back to the model
for function_call in response.candidates[0].function_calls:
print(f"Function call: {function_call.name}")
# In this example, we'll use synthetic data to simulate a response payload from an external API
if (function_call.args['location'] == "Boston, MA"):
api_response = { "location": "Boston, MA", "temperature": 38, "description": "Partly Cloudy" }
if (function_call.args['location'] == "San Francisco, CA"):
api_response = { "location": "San Francisco, CA", "temperature": 58, "description": "Sunny" }
function_response_parts.append(
Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response={"contents": api_response}
)
)
# Add the function call response to the contents
function_response_contents = Content(role="user", parts=function_response_parts)
function_response_contents
response = model.generate_content(
contents = [
Content(
role="user",
parts=[
Part.from_text("What is the weather like in Boston and San Francisco?"),
],
), # User prompt
response.candidates[0].content, # Function call response
function_response_contents, # Function response
],
tools = [
Tool(
function_declarations=[get_current_weather_func],
)
]
)
# Get the model summary response
print(response.text)
Go
함수 호출 모드
function_calling_config 내에서 모드를 설정하여 모델이 제공된 도구(함수 선언)를 사용하는 방식을 제어할 수 있습니다.
| 모드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
AUTO |
기본 모델 동작입니다. 모델은 컨텍스트에 따라 함수 호출을 예측할지 아니면 자연어로 응답할지 결정합니다. 이 모드는 가장 유연한 모드이며 대부분의 시나리오에 권장됩니다. |
VALIDATED(미리보기) |
모델이 함수 호출 또는 자연어를 예측하도록 제한되며 함수 스키마 준수를 보장합니다. allowed_function_names가 제공되지 않았으면 모델이 사용 가능한 모든 함수 선언 중에서 선택합니다. allowed_function_names가 제공되었으면 모델이 허용된 함수 집합 중에서 선택합니다. |
ANY |
모델이 항상 하나 이상의 함수 호출을 예측하도록 제한되며 함수 스키마 준수를 보장합니다. allowed_function_names가 제공되지 않았으면 모델이 사용 가능한 모든 함수 선언 중에서 선택합니다. allowed_function_names가 제공되었으면 모델이 허용된 함수 집합 중에서 선택합니다. 모든 프롬프트에 함수 호출 응답이 필요한 경우 이 모드를 사용하세요(해당하는 경우). |
NONE |
모델이 함수 호출을 실행하는 것이 금지됩니다. 이는 함수 선언 없이 요청을 전송하는 것과 동일합니다. 이 모드를 사용하면 도구 정의를 삭제하지 않고 함수 호출을 일시적으로 사용 중지할 수 있습니다. |
강제 함수 호출
예를 들어 모델이 자연어 응답과 함수 호출 중에서 선택하도록 허용하는 대신 함수 호출만 예측하도록 할 수 있습니다. 이를 강제 함수 호출이라고 합니다. 모델에 전체 함수 선언 집합을 제공할 수도 있지만 이러한 함수의 하위 집합으로 응답을 제한할 수도 있습니다.
다음 예에서는 get_weather 함수 호출만 예측하도록 강제합니다.
Python
response = model.generate_content(
contents = [
Content(
role="user",
parts=[
Part.from_text("What is the weather like in Boston?"),
],
)
],
generation_config = GenerationConfig(temperature=0),
tools = [
Tool(
function_declarations=[get_weather_func, some_other_function],
)
],
tool_config=ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=ToolConfig.FunctionCallingConfig(
# ANY mode forces the model to predict only function calls
mode=ToolConfig.FunctionCallingConfig.Mode.ANY,
# Allowed function calls to predict when the mode is ANY. If empty, any of
# the provided function calls will be predicted.
allowed_function_names=["get_weather"],
)
)
)
함수 스키마 예시
함수 선언은 OpenAPI 스키마와 호환됩니다. type, nullable, required, format, description, properties, items, enum, anyOf, $ref, $defs 속성이 지원됩니다. 나머지 속성은 지원되지 않습니다.
객체 및 배열 파라미터가 있는 함수
다음 예에서는 Python 사전을 사용하여 객체 및 배열 파라미터를 모두 사용하는 함수를 선언합니다.
extract_sale_records_func = FunctionDeclaration( name="extract_sale_records", description="Extract sale records from a document.", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "records": { "type": "array", "description": "A list of sale records", "items": { "description": "Data for a sale record", "type": "object", "properties": { "id": {"type": "integer", "description": "The unique id of the sale."}, "date": {"type": "string", "description": "Date of the sale, in the format of MMDDYY, e.g., 031023"}, "total_amount": {"type": "number", "description": "The total amount of the sale."}, "customer_name": {"type": "string", "description": "The name of the customer, including first name and last name."}, "customer_contact": {"type": "string", "description": "The phone number of the customer, e.g., 650-123-4567."}, }, "required": ["id", "date", "total_amount"], }, }, }, "required": ["records"], }, )
열거형 파라미터가 있는 함수
다음 예에서는 Python 사전을 사용하여 정수 enum 파라미터를 사용하는 함수를 선언합니다.
set_status_func = FunctionDeclaration( name="set_status", description="set a ticket's status field", # Function parameters are specified in JSON schema format parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "status": { "type": "integer", "enum": [ "10", "20", "30" ], # Provide integer (or any other type) values as strings. } }, }, )
ref 및 def가 있는 함수
다음 JSON 함수 선언에서는 ref 및 defs 속성을 사용합니다.
{ "contents": ..., "tools": [ { "function_declarations": [ { "name": "get_customer", "description": "Search for a customer by name", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "first_name": { "ref": "#/defs/name" }, "last_name": { "ref": "#/defs/name" } }, "defs": { "name": { "type": "string" } } } } ] } ] }
사용 참고사항:
- OpenAPI 스키마와 달리
$기호 없이ref및defs를 지정합니다. ref는defs의 직계 하위를 참조해야 합니다. 외부 참조는 허용되지 않습니다.- 중첩된 스키마의 최대 깊이는 32입니다.
defs(자기 참조)의 재귀 깊이는 2로 제한됩니다.
배열 파라미터가 포함된 from_func
다음 코드 샘플은 숫자 배열을 곱하고 from_func를 사용하여 FunctionDeclaration 스키마를 생성하는 함수를 선언합니다.
from typing import List # Define a function. Could be a local function or you can import the requests library to call an API def multiply_numbers(numbers: List[int] = [1, 1]) -> int: """ Calculates the product of all numbers in an array. Args: numbers: An array of numbers to be multiplied. Returns: The product of all the numbers. If the array is empty, returns 1. """ if not numbers: # Handle empty array return 1 product = 1 for num in numbers: product *= num return product multiply_number_func = FunctionDeclaration.from_func(multiply_numbers) """ multiply_number_func contains the following schema: {'name': 'multiply_numbers', 'description': 'Calculates the product of all numbers in an array.', 'parameters': {'properties': {'numbers': {'items': {'type': 'INTEGER'}, 'description': 'list of numbers', 'default': [1.0, 1.0], 'title': 'Numbers', 'type': 'ARRAY'}}, 'description': 'Calculates the product of all numbers in an array.', 'title': 'multiply_numbers', 'property_ordering': ['numbers'], 'type': 'OBJECT'}} """
함수 호출 권장사항
명확하고 자세한 함수 이름, 파라미터 설명, 명령어 작성
함수 이름은 문자 또는 밑줄로 시작해야 하며 최대 64자의 a-z, A-Z, 0-9, 밑줄, 마침표, 대시만 포함해야 합니다.
함수 및 파라미터 설명을 매우 명확하고 구체적으로 작성하세요. 모델은 이를 기반으로 올바른 함수를 선택하고 적절한 인수를 제공합니다. 예를 들어
book_flight_ticket함수에는book flight tickets after confirming users' specific requirements, such as time, departure, destination, party size and preferred airline설명이 있을 수 있습니다.
강력한 유형의 파라미터 사용
파라미터 값이 유한한 집합에서 파생된 경우 값 집합을 설명에 포함하는 대신 enum 필드를 추가합니다. 파라미터 값이 항상 정수이면 유형을 number 대신 integer로 설정합니다.
도구 선택
모델은 임의의 수의 도구를 사용할 수 있지만 너무 많은 도구를 제공하면 잘못되거나 최적화되지 않은 도구를 선택할 위험이 커집니다. 최상의 결과를 얻으려면 컨텍스트 또는 작업과 관련된 도구만 제공하는 것이 좋습니다. 활성 도구 세트는 최대 10~20개로 유지하는 것이 좋습니다. 총 도구 수가 많은 경우 대화 컨텍스트에 기반한 동적 도구 선택을 고려하세요.
일반적인 하위 수준 도구(예: bash)를 제공하면 모델이 도구를 더 자주 사용하지만 정확성은 떨어질 수 있습니다. get_weather과 같은 구체적인 상위 수준 도구를 제공하면 모델이 도구를 더 정확하게 사용할 수 있지만 도구가 자주 사용되지 않을 수 있습니다.
시스템 안내 사용
날짜, 시간, 위치 파라미터와 함께 함수를 사용할 때는 시스템 안내에 따라 현재 날짜, 시간, 관련 위치 정보(예: 도시 및 국가)를 포함합니다. 이렇게 하면 사용자 프롬프트에 세부정보가 부족하더라도 요청을 정확하게 처리하는 데 필요한 컨텍스트가 모델에 포함됩니다.
프롬프트 엔지니어링
최상의 결과를 얻으려면 사용자 프롬프트 앞에 다음 세부정보를 추가합니다.
- 모델의 추가 컨텍스트(예:
You are a flight API assistant to help with searching flights based on user preferences.) - 함수 사용 방법과 시기에 대한 세부정보나 안내(예:
Don't make assumptions on the departure or destination airports. Always use a future date for the departure or destination time.) - 사용자 쿼리가 모호한 경우 명확하게 질문하기 위한 안내(예:
Ask clarifying questions if not enough information is available.)
생성 구성 사용
강도 파라미터에는 0 또는 다른 낮은 값을 사용합니다. 이렇게 하면 모델이 보다 신뢰할 수 있는 결과를 생성하도록 할 수 있고 할루시네이션을 줄일 수 있습니다.
API 호출 유효성 검사
모델이 주문을 전송하거나, 데이터베이스를 업데이트하거나, 그 밖의 이유로 중대한 결과가 발생할 수 있는 함수의 호출을 제안하는 경우에는 이를 실행하기 전에 사용자와 함께 함수 호출 유효성을 검사합니다.
생각 서명 사용
최상의 결과를 얻으려면 항상 함수 호출과 함께 사고 서명을 사용해야 합니다.
가격 책정
함수 호출 가격은 텍스트 입력과 출력에 포함된 문자 수를 기준으로 책정됩니다. 자세한 내용은 Vertex AI 가격 책정을 참조하세요.
여기서 텍스트 입력(프롬프트)은 현재 대화 차례의 사용자 프롬프트, 현재 대화 차례의 함수 선언, 대화 기록을 나타냅니다. 대화 기록에는 쿼리, 함수 호출, 이전 대화 차례의 함수 응답이 포함됩니다. Vertex AI는 대화 기록을 32,000자(영문 기준)로 자릅니다.
텍스트 출력(응답)은 현재 대화 차례의 함수 호출 및 텍스트 응답을 나타냅니다.
함수 호출 사용 사례
다음 태스크에 함수 호출을 사용할 수 있습니다.
| 사용 사례 | 예시 설명 | 예시 링크 |
|---|---|---|
| 외부 API와 통합 | 기상 API를 사용하여 날씨 정보 가져오기 | 노트북 튜토리얼 |
| 주소를 위도/경도 좌표로 변환 | 노트북 튜토리얼 | |
| 환율 API를 사용하여 통화 변환 | Codelab | |
| 고급 챗봇 빌드 | 제품 및 서비스에 대한 고객 질문 답변 | 노트북 튜토리얼 |
| 회사에 대한 재무 및 소식 질문에 답변하는 어시스턴트 만들기 | 노트북 튜토리얼 | |
| 함수 호출 구성 및 제어 | 원시 로그 데이터에서 구조화된 항목 추출 | 노트북 튜토리얼 |
| 사용자 입력에서 단일 또는 여러 파라미터 추출 | 노트북 튜토리얼 | |
| 함수 호출에서 목록 및 중첩된 데이터 구조 처리 | 노트북 튜토리얼 | |
| 함수 호출 동작 처리 | 병렬 함수 호출 및 응답 처리 | 노트북 튜토리얼 |
| 모델이 호출할 수 있는 함수 및 시기 관리 | 노트북 튜토리얼 | |
| 자연어를 이용한 데이터베이스 쿼리 | 자연어 질문을 BigQuery용 SQL 쿼리로 변환 | 샘플 앱 |
| 멀티모달 함수 호출 | 이미지, 동영상, 오디오, PDF를 입력으로 사용하여 함수 호출 트리거 | 노트북 튜토리얼 |
다음은 몇 가지 사용 사례를 보여줍니다.
음성 명령 해석: 차내 태스크에 해당하는 함수를 만듭니다. 예를 들어 라디오를 켜거나 에어컨을 활성화하는 함수를 만들 수 있습니다. 사용자 음성 명령 오디오 파일을 모델에 전송하고 오디오를 텍스트로 변환하고 사용자가 호출하려는 함수를 식별하도록 모델에 요청합니다.
환경 트리거를 기준으로 워크플로 자동화: 자동화할 수 있는 프로세스를 나타내는 함수를 만듭니다. 모델에 환경 센서의 데이터를 제공하고 데이터를 파싱 및 처리하여 워크플로 하나 이상이 활성화되어야 하는지 여부를 결정하도록 요청합니다. 예를 들어 모델이 창고에서 온도 데이터를 처리하고 스프링클러 함수를 활성화할 수 있습니다.
지원 티켓 할당 자동화: 모델에 지원 티켓, 로그, 컨텍스트 인식 규칙을 제공합니다. 모델에 이 모든 정보를 모두 처리하여 티켓이 할당되어야 하는 대상을 결정하도록 요청합니다. 함수를 호출하여 모델이 추천한 사람에게 티켓을 할당합니다.
기술 자료에서 정보 검색: 특정 주제에 대한 학술 자료를 검색하고 요약하는 함수를 만듭니다. 모델이 학술 주제에 대한 질문에 답하고 답변에 대한 인용을 제공할 수 있도록 사용 설정합니다.
