Der Job-Builder ist eine visuelle Benutzeroberfläche zum Erstellen und Ausführen von Dataflow-Pipelines in der Google Cloud -Konsole, ohne Code schreiben zu müssen.
Das folgende Bild zeigt einen Ausschnitt der Benutzeroberfläche des Job-Builders. In diesem Bild erstellt der Nutzer eine Pipeline, um Daten aus Pub/Sub in BigQuery zu lesen:
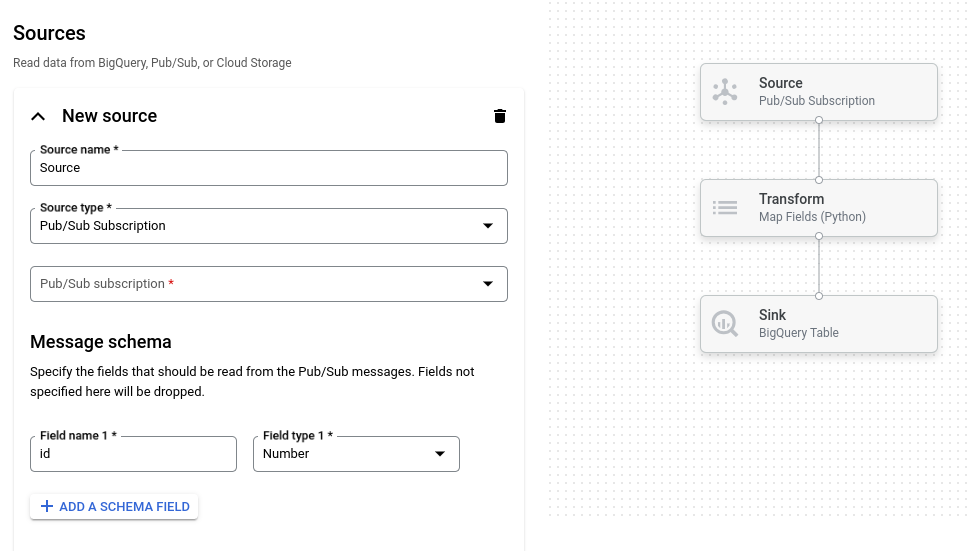
Übersicht
Der Job-Builder unterstützt das Lesen und Schreiben der folgenden Datentypen:
- Pub/Sub-Nachrichten
- BigQuery-Tabellendaten
- CSV‑, JSON‑ und Textdateien in Cloud Storage
- Tabellendaten aus PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle und SQL Server
Es unterstützt Pipeline-Transformationen wie Filter, Map, SQL, Group-by, Join und Explode (Array-Flatten).
Mit dem Job-Builder haben Sie folgende Möglichkeiten:
- Von Pub/Sub zu BigQuery mit Transformationen und aggregierten Fenstern streamen
- Daten aus Cloud Storage in BigQuery schreiben
- Fehlerbehandlung zum Filtern fehlerhafter Daten verwenden (Warteschlange für unzustellbare Nachrichten)
- Daten mit dem SQL-Transform mithilfe von SQL bearbeiten oder aggregieren
- Felder mit Mapping-Transformationen hinzufügen, ändern oder entfernen
- Wiederkehrende Batchjobs planen
Der Job-Builder kann auch Pipelines als Apache Beam-YAML-Dateien speichern und Pipeline-Definitionen aus Beam-YAML-Dateien laden. Mit diesem Feature können Sie Ihre Pipeline im Job-Builder entwerfen und die YAML-Datei dann zur Wiederverwendung in Cloud Storage oder einem Quellcode-Repository speichern. YAML-Jobdefinitionen können auch verwendet werden, um Jobs mit der gcloud CLI zu starten.
Betrachten Sie den Job-Builder für folgende Anwendungsfälle:
- Sie möchten schnell eine Pipeline erstellen, ohne Code zu schreiben.
- Sie möchten eine Pipeline zur Wiederverwendung in YAML speichern.
- Ihre Pipeline kann mit den unterstützten Quellen, Senken und Transformationen ausgedrückt werden.
- Es gibt keine von Google bereitgestellte Vorlage, die zu Ihrem Anwendungsfall passt.
Beispieljob ausführen
Das Beispiel „Word Count“ ist eine Batch-Pipeline, die Text aus Cloud Storage liest, die Textzeilen durch Tokenisierung in ihre einzelnen Wörter zerlegt und für jedes Wort eine Häufigkeitszählung durchführt.
Wenn sich der Cloud Storage-Bucket außerhalb des Dienstperimeters befindet, erstellen Sie eine Regel für ausgehenden Traffic, die Zugriff auf den Bucket ermöglicht.
So führen Sie die Pipeline „Word Count“ aus:
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud -Console die Seite Jobs auf.
Klicken Sie auf Job aus Vorlage erstellen.
Klicken Sie in der Seitenleiste auf Job-Builder.
Klicken Sie auf Blaupausen laden.
Klicken Sie auf Wörter zählen. Der Job-Builder wird mit einer grafischen Darstellung der Pipeline gefüllt.
Für jeden Pipelineschritt wird im Job Builder eine Karte mit den Konfigurationsparametern für diesen Schritt angezeigt. Im ersten Schritt werden beispielsweise Textdateien aus Cloud Storage gelesen. Der Speicherort der Quelldaten ist im Feld Textspeicherort bereits eingetragen.
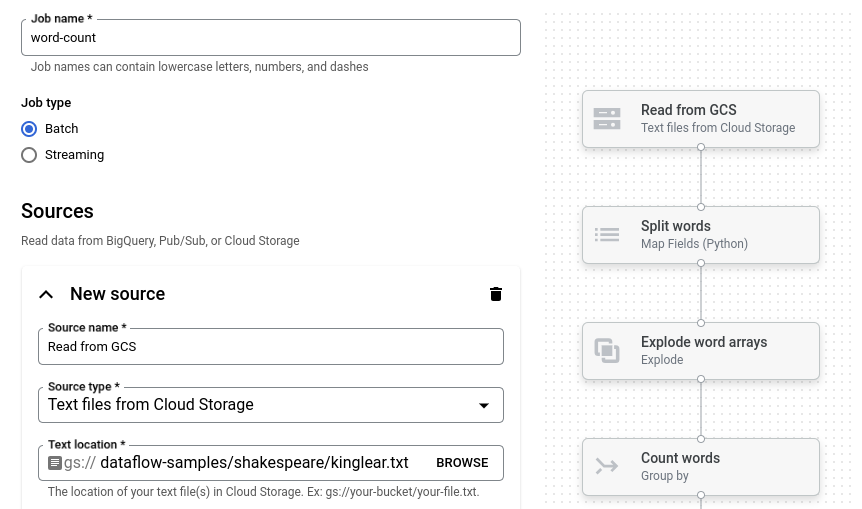
Suchen Sie die Karte mit dem Titel Neues Waschbecken. Eventuell müssen Sie scrollen.
Geben Sie im Feld Textspeicherort das Cloud Storage-Pfadpräfix für die Ausgabetextdateien ein.
Klicken Sie auf Job ausführen. Der Job-Builder erstellt einen Dataflow-Job und ruft dann das Job-Diagramm auf. Wenn der Job gestartet wird, zeigt die Jobgrafik eine grafische Darstellung der Pipeline. Diese grafische Darstellung ähnelt der im Job Builder. Während jeder Schritt der Pipeline ausgeführt wird, wird der Status im Job-Diagramm aktualisiert.
Im Bereich Jobinfo wird der Gesamtstatus des Jobs angezeigt. Wenn der Job erfolgreich abgeschlossen wird, wird das Feld Jobstatus auf Succeeded aktualisiert.
Nächste Schritte
- Dataflow-Job-Monitoring-Oberfläche verwenden
- Erstellen Sie einen benutzerdefinierten Job im Job-Builder.
- YAML-Jobdefinitionen im Job-Builder speichern und laden
- Weitere Informationen zu Beam YAML

