Consulte os conectores compatíveis com a integração de aplicativos.
Bordas e condições de borda
Edge
Uma borda é a conexão entre dois elementos em uma integração. A conexão indica a direção do fluxo de controle de um elemento (tarefa ou gatilho) para outro. A conexão pode estar entre um gatilho e uma tarefa ou entre duas tarefas. Ao usar uma borda com bifurcação e mesclagem, é possível implementar ramificações e condições complexas na sua integração. Para mais informações, consulte Bifurcações e mesclagens.
Por exemplo, se houver uma borda entre uma tarefa Enviar e-mail e uma tarefa Chamar integração, significa que, depois da tarefa Enviar e-mail ser executada, a próxima tarefa a ser executada é a Chamar integração. Uma borda também é compatível com verificações condicionais. Antes que o controle passe para a próxima tarefa, você pode verificar se há uma condição na borda e, com base no resultado, decidir executar ou não a tarefa. Para mais informações sobre as verificações condicionais compatíveis, consulte Condições de borda.
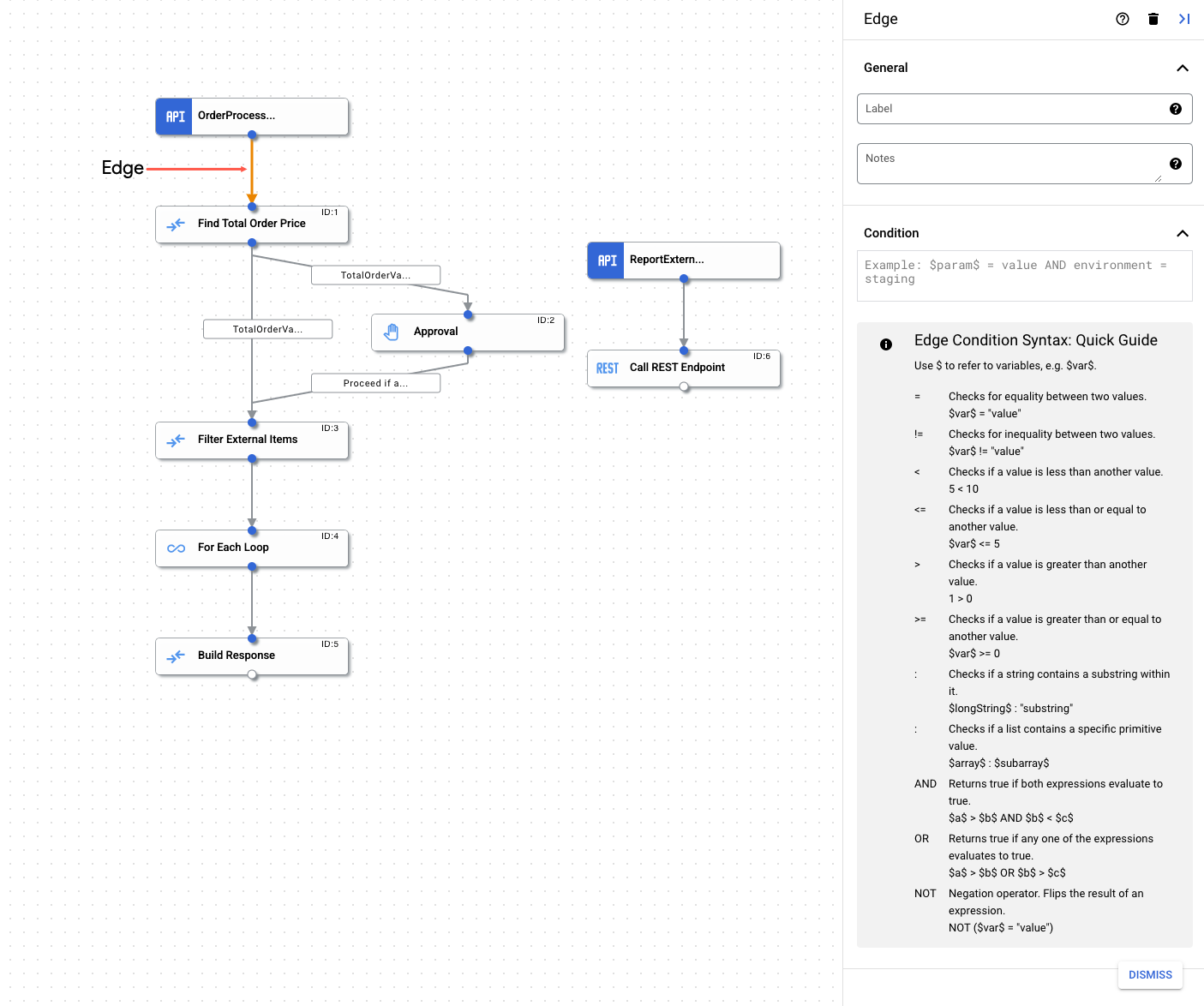

Condições de borda
As condições de borda permitem especificar as condições que precisam ser atendidas para controle de que uma integração seja transmitida para a tarefa conectada pela borda. A tarefa será executada somente se as condições especificadas forem atendidas. As condições de borda são úteis nos casos em que há várias bordas de entrada em uma tarefa, em que cada borda verifica condições específicas antes da tarefa.
Especifique as condições de borda usando as seguintes etapas:
- No console Google Cloud , acesse a página Integração de aplicativos.
- No menu de navegação, clique em Integrações.
A página Integrações aparece listando todas as integrações disponíveis no projeto do Google Cloud.
- Selecione uma integração ou clique em Criar integração para criar uma nova.
Caso você esteja criando uma nova integração, siga estas etapas:
- Insira um nome e uma descrição no painel Criar integração.
- Selecione uma região para a integração.
- Selecione uma conta de serviço para a integração. É possível mudar ou atualizar os detalhes da conta de serviço de uma integração a qualquer momento no painel Resumo da integração na barra de ferramentas de integração.
- Clique em Criar. A integração recém-criada é aberta no editor de integração.
- Na barra de navegação do editor de integração, clique em Tarefas para conferir a lista de tarefas e conectores disponíveis.
- Selecione uma integração atual ou crie uma nova.
- No editor de integração, clique na borda para abrir o respectivo painel de configuração.
- Configure a borda:
- Rótulo (opcional): adicione um nome personalizado para a borda.
- Condição: defina uma condição de borda usando os operadores e funções compatíveis.
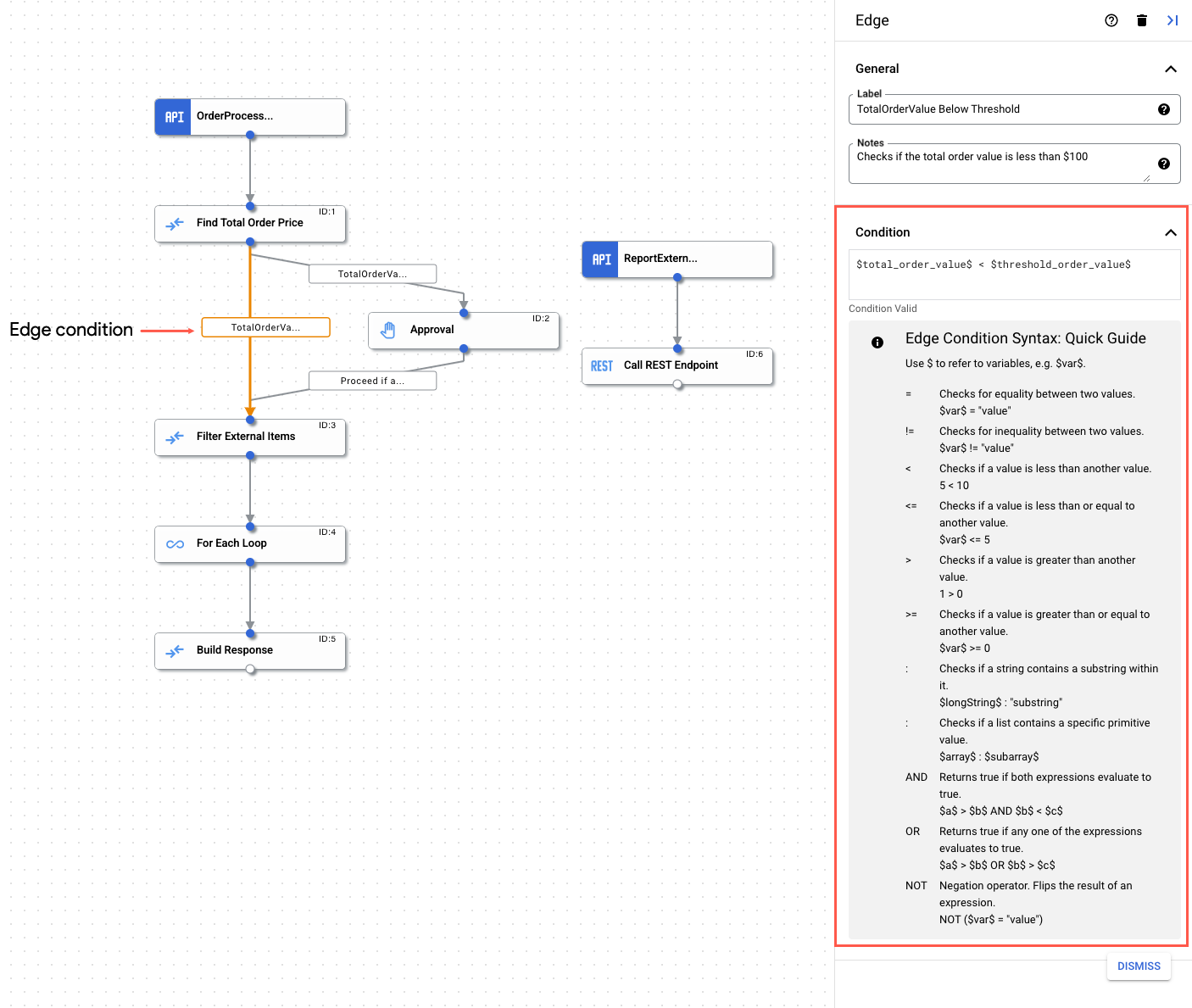

Operadores compatíveis
A tabela a seguir descreve os operadores compatíveis disponíveis para uso nas condições de borda.
| Operador | Descrição | Exemplo |
| = | Verifica a igualdade entre dois valores | $var$ = "value" |
| != | Verifica a desigualdade entre dois valores | $var$ != "value" |
| < | Verifica se um valor é menor que outro | 5 < 10 |
| <= | Verifica se um valor é menor ou igual a outro valor | $var$ <= 5 |
| > | Verifica se um valor é maior que outro | 1 > 0 |
| >= | Verifica se um valor é maior ou igual a outro valor | $var$ >= 0 |
| : | Verifica se uma string contém uma substring nela ou se uma lista contém um valor primitivo específico. |
|
| AND | Verifica duas expressões e retorna verdadeiro se ambas as expressões forem avaliadas como verdadeiras. | $a$ > $b$ AND $b$ < $c$ |
| OU | Verifica duas expressões e retorna verdadeiro se qualquer uma das expressões for avaliada como verdadeira. | $a$ > $b$ OR $b$ < $c$ |
| NOT | Operador de negação. Inverte o resultado de uma expressão. | NOT($var$ = "value") |
Funções compatíveis
A tabela a seguir descreve as funções compatíveis disponíveis para uso nas condições de borda.
| Função | Descrição |
exists(VARIABLE)
|
Verifica se uma determinada variável existe |
does_not_exist(VARIABLE)
|
Verifica se uma determinada variável não existe |
is_empty(VARIABLE)
|
Verifica se uma determinada variável é uma lista AND está vazia. Suporta o tipo de variável de matriz, exceto matriz JSON. |
is_not_empty(VARIABLE)
|
Verifica se uma determinada variável é uma lista AND não está vazia. Suporta o tipo de variável de matriz, exceto matriz JSON. |
Cotas e limites
Para informações sobre o assunto, consulte Cotas e limites.
A seguir
- Saiba mais sobre todas as tarefas e acionadores.
- Saiba como testar e publicar uma integração.
- Saiba mais sobre o tratamento de erros.
- Saiba mais sobre os registros de execução de integração.

