This guide shows you how to use a webhook, so your agent can be more dynamic. Cloud Functions are used to host the webhook due to their simplicity, but there are many other ways that you could host a webhook service. The example also uses the Go programming language, but you can use any language supported by Cloud Functions. You will not need to edit the code for this guide.
The example webhook code does the following:
- Reads parameter values from the webhook request.
- Writes a parameter value to the webhook response.
- Provides a text response in the webhook response.
Before you begin
If you don't plan on using webhooks, you can skip this quickstart.
You should do the following before reading this guide:
- Read flow basics.
- Perform setup steps.
- Perform steps in the Build an agent using flows quickstart guide. Steps below continue working on the same agent. If you no longer have that agent, you can download the agent and restore it.
Create the Cloud Function
Cloud Functions can be created with the Google Cloud console (visit documentation, open console). To create a function for this guide:
- It is important that your Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) agent and the function are both in the same project. This is the easiest way for Conversational Agents (Dialogflow CX) to have secure access to your function. To select your project, go to the project selector.
- Go to the Cloud Functions overview page.
- Click Create Function, and set the following fields:
- Environment: 1st gen
- Function name: shirts-agent-webhook
- Region: If you specified a region for your agent, use the same region.
- HTTP Trigger type: HTTP
- URL: Click the copy button here and save the value. You will need this URL when configuring the webhook.
- Authentication: Require authentication
- Require HTTPS: checked
- Click Save.
- Click Next (You do not need special runtime, build, connections, or security settings).
- Set the following fields:
- Runtime: Select the latest Go runtime.
- Source code: Inline Editor
- Entry point: HandleWebhookRequest
Replace the code with the following:
// Package cxwh contains an example Dialogflow CX webhook package cxwh import ( "encoding/json" "fmt" "log" "net/http" ) type fulfillmentInfo struct { Tag string `json:"tag"` } type sessionInfo struct { Session string `json:"session"` Parameters map[string]interface{} `json:"parameters"` } type text struct { Text []string `json:"text"` } type responseMessage struct { Text text `json:"text"` } type fulfillmentResponse struct { Messages []responseMessage `json:"messages"` } // webhookRequest is used to unmarshal a WebhookRequest JSON object. Note that // not all members need to be defined--just those that you need to process. // As an alternative, you could use the types provided by the Dialogflow protocol buffers: // https://pkg.go.dev/google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/cloud/dialogflow/cx/v3#WebhookRequest type webhookRequest struct { FulfillmentInfo fulfillmentInfo `json:"fulfillmentInfo"` SessionInfo sessionInfo `json:"sessionInfo"` } // webhookResponse is used to marshal a WebhookResponse JSON object. Note that // not all members need to be defined--just those that you need to process. // As an alternative, you could use the types provided by the Dialogflow protocol buffers: // https://pkg.go.dev/google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/cloud/dialogflow/cx/v3#WebhookResponse type webhookResponse struct { FulfillmentResponse fulfillmentResponse `json:"fulfillmentResponse"` SessionInfo sessionInfo `json:"sessionInfo"` } // confirm handles webhook calls using the "confirm" tag. func confirm(request webhookRequest) (webhookResponse, error) { // Create a text message that utilizes the "size" and "color" // parameters provided by the end-user. // This text message is used in the response below. t := fmt.Sprintf("You can pick up your order for a %s %s shirt in 5 days.", request.SessionInfo.Parameters["size"], request.SessionInfo.Parameters["color"]) // Create session parameters that are populated in the response. // The "cancel-period" parameter is referenced by the agent. // This example hard codes the value 2, but a real system // might look up this value in a database. p := map[string]interface{}{"cancel-period": "2"} // Build and return the response. response := webhookResponse{ FulfillmentResponse: fulfillmentResponse{ Messages: []responseMessage{ { Text: text{ Text: []string{t}, }, }, }, }, SessionInfo: sessionInfo{ Parameters: p, }, } return response, nil } // handleError handles internal errors. func handleError(w http.ResponseWriter, err error) { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError) fmt.Fprintf(w, "ERROR: %v", err) } // HandleWebhookRequest handles WebhookRequest and sends the WebhookResponse. func HandleWebhookRequest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { var request webhookRequest var response webhookResponse var err error // Read input JSON if err = json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&request); err != nil { handleError(w, err) return } log.Printf("Request: %+v", request) // Get the tag from the request, and call the corresponding // function that handles that tag. // This example only has one possible tag, // but most agents would have many. switch tag := request.FulfillmentInfo.Tag; tag { case "confirm": response, err = confirm(request) default: err = fmt.Errorf("Unknown tag: %s", tag) } if err != nil { handleError(w, err) return } log.Printf("Response: %+v", response) // Send response if err = json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(&response); err != nil { handleError(w, err) return } }
Click Deploy.
Wait until the status indicator shows that the function has successfully deployed. While waiting, examine the code you just deployed. Code comments describe important details.
Create the webhook
Now that the webhook exists as a Cloud function, you will associate this webhook with your agent. To create the webhook for your agent:
- Open the Dialogflow CX console.
- Choose your Google Cloud project.
- Select your agent.
- Select the Manage tab.
- Click Webhooks.
- Click Create.
- Complete the following fields:
- Display name: shirts-agent-webhook
- Webhook URL: Provide the webhook URL you saved when creating the function.
- Subtype: Standard.
- All other fields use default values.
- Click Save.
Use the webhook
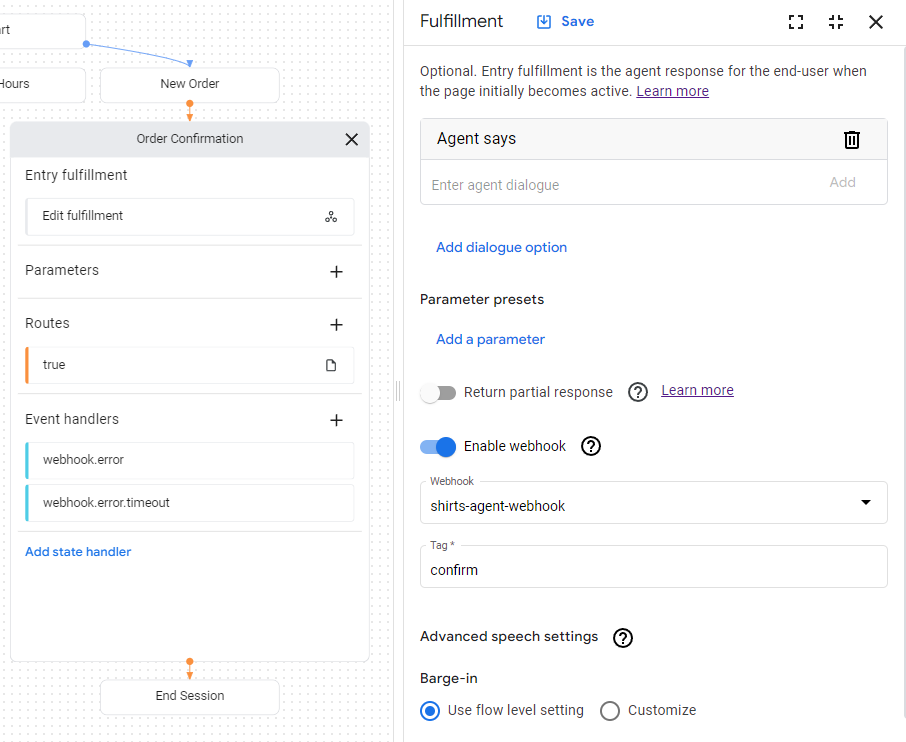
Now that the webhook is available to the agent, you will make use of the webhook in fulfillment. The Order Confirmation page has an entry fulfillment, which currently has a static text response. To update the fulfillment to use your webhook:
- Select the Build tab.
- Click the Order Confirmation page to expand the page on the agent builder graph.
- Click the Entry Fulfillment field on the page to open the fulfillment panel.
- Delete the existing text response under the Agent says heading. When you hover the text, the delete delete button appears.
- Click Enable webhook.
- Select the
shirts-agent-webhookoption from the Webhook dropdown menu. - Enter
confirmfor the Tag field. - Click Save.
- Close the fulfillment panel.
The deployed webhook code sends a response
that creates a
parameter
named cancel-period.
Update the agent to reference this parameter in the final agent response
for the same Order Confirmation page:
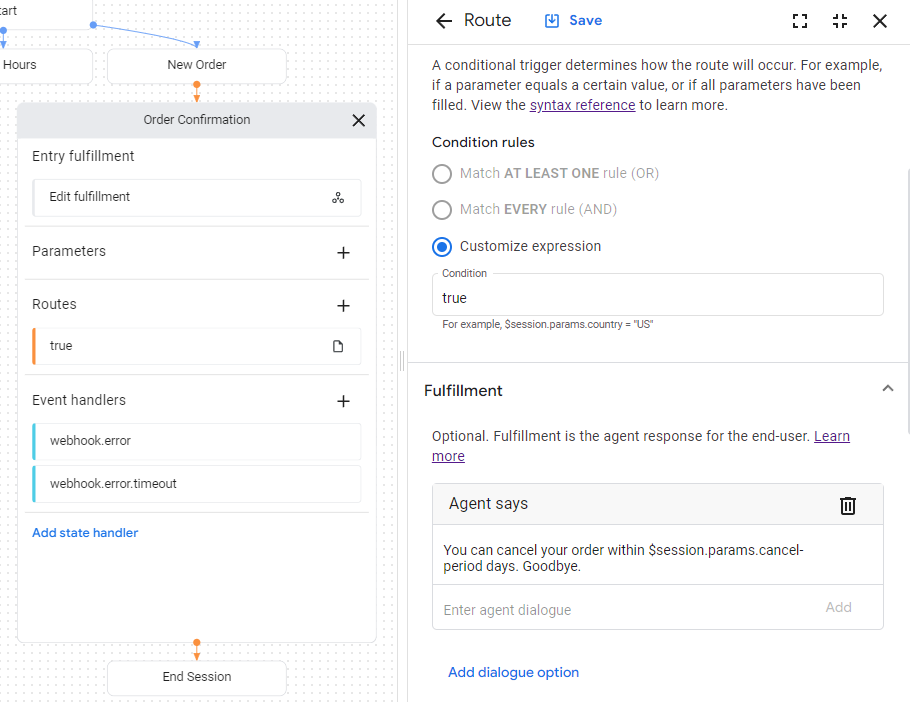
- Click the condition
route
shown with a
truecondition to open the route panel. - Scroll down to the Fulfillment section of the route panel,
and add the following text response under the Agent says heading:
You can cancel your order within $session.params.cancel-period days. Goodbye. - Click Save.
- Close the route panel.
Test the agent in the simulator
Your agent and webhook are ready to test with the simulator:
- Click Test Agent.
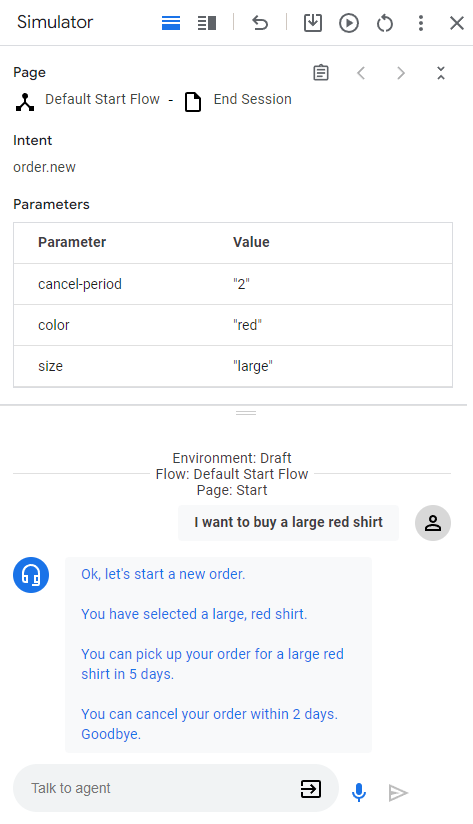
- Enter
I want to buy a large red shirtand press enter.
Since you provided both a size and color, you gave the agent everything it needs to create a shirt order, so it transitions directly to the Order Confirmation page.
The following describes the agent responses:
| Response | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Okay, let's start a new order. | When the New Order page became active, the entry fulfillment was called. The response was triggered from this fulfillment. |
| You have selected a large, red shirt. | When all form parameters have been provided for the New Order page, the condition route checking for form completion is called. The response was triggered from the fulfillment for this route. This route also transitions to the Order Confirmation page. |
| You can pick up your order for a large red shirt in 5 days. | The entry fulfillment for the Order Confirmation page calls the webhook. See the confirm function in the webhook code. That function creates this text response, and it uses the parameters provided in the webhook request. |
| You can cancel your order within 2 days. Goodbye. | The Order Confirmation page has a condition route with a condition that is always true. This response is triggered by the fulfillment for that route. Note that the response makes use of the parameter set by the webhook in the webhook response. |
