Bei Streamingpipelines ist ein Nachzügler als Arbeitselement mit folgenden Merkmalen definiert:
- Es verhindert für eine längere Zeit (in der Größenordnung von Minuten), dass das Wasserzeichen vorangebracht wird.
- Seine Verarbeitung dauert relativ zu anderen Arbeitselementen in derselben Phase lange.
Nachzügler halten das Wasserzeichen zurück und erhöhen die Latenz des Jobs. Wenn die Verzögerung für Ihren Anwendungsfall akzeptabel ist, müssen Sie nichts unternehmen. Wenn Sie die Latenz eines Jobs reduzieren möchten, beginnen Sie mit etwaigen Nachzüglern.
Streaming-Nachzügler in der Google Cloud -Console aufrufen
Nachdem Sie einen Dataflow-Job gestartet haben, können Sie in der Google Cloud Console alle erkannten Nachzügler aufrufen.
Streaming-Nachzügler können Sie in der Ansicht „Phasenfortschritt“ oder in der Ansicht „Phasenworkflow“ sehen.
Nachzügler nach Phasenfortschritt aufrufen
So rufen Sie Nachzügler nach Phasenfortschritt auf:
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Dataflow-Seite Jobs auf.
Klicken Sie auf den Namen des Jobs.
Klicken Sie auf der Seite Jobdetails auf den Tab Ausführungsdetails.
Wählen Sie in der Liste Grafikansicht die Option Phasenfortschritt aus. Das Fortschrittsdiagramm zeigt die aggregierten Anzahl aller Nachzügler, die in den einzelnen Phasen erkannt wurden.
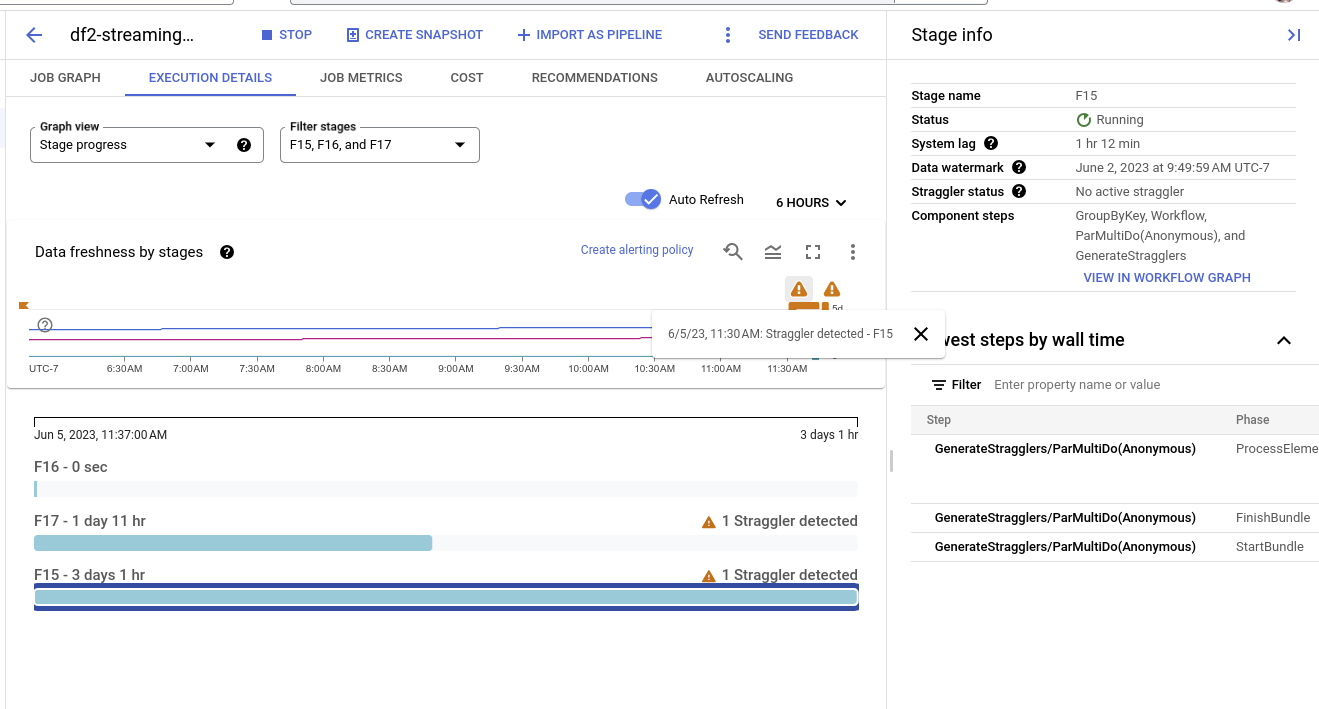
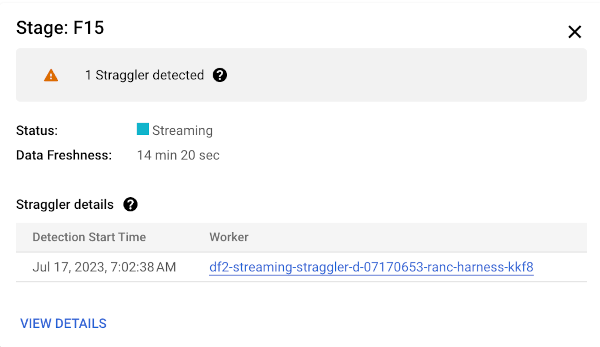
Details zu einer Phase erhalten Sie, wenn Sie den Mauszeiger über den Balken für die Phase bewegen. Der Detailbereich enthält einen Link zu den Worker-Logs. Wenn Sie auf diesen Link klicken, wird Cloud Logging in Bezug auf den Worker und den Zeitraum geöffnet, in dem der Nachzügler erkannt wurde.
Nachzügler nach Phasenworkflow aufrufen
So rufen Sie einen Nachzügler nach Phasenworkflow auf:
Rufen Sie in der Google Cloud Console die Dataflow-Seite Jobs auf.
Zu Jobs
Klicken Sie auf den Namen des Jobs.
Klicken Sie auf der Seite mit den Jobdetails auf den Tab Ausführungsdetails.
Wählen Sie in der Liste Grafikansicht die Option Phasenworkflow aus. Der Phasenworkflow zeigt die Ausführungsphasen des Jobs an, die als Workflowgrafik dargestellt werden.
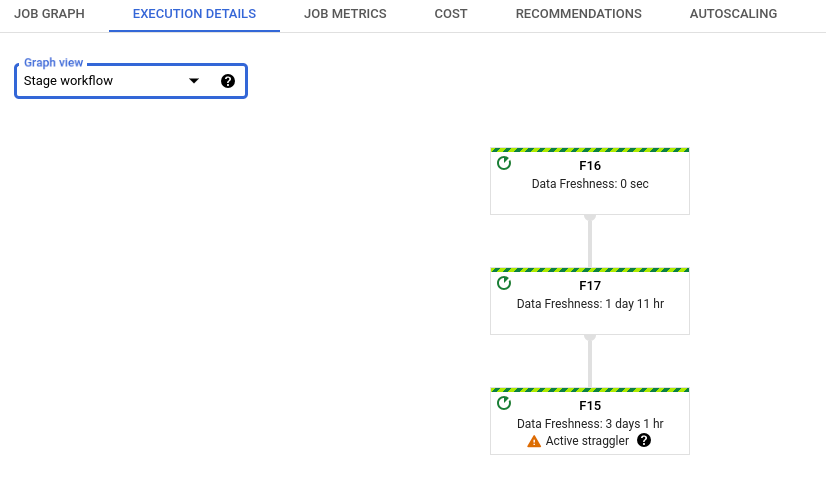
Probleme mit Streaming-Nachzüglern beheben
Wenn ein Nachzügler erkannt wird, bedeutet dies, dass ein Vorgang in der Pipeline seit ungewöhnlich langer Zeit ausgeführt wird.
Prüfen Sie zur Fehlerbehebung zuerst, ob Dataflow-Statistiken Probleme aufzeigen.
Wenn Sie die Ursache immer noch nicht ermitteln können, prüfen Sie die Worker-Logs für die Phase, die den Nachzügler gemeldet hat. Informationen zu den relevanten Worker-Logs finden Sie in den Nachzügler-Details im Phasenfortschritt. Klicken Sie dann auf den Link für den Worker. Über diesen Link wird Cloud Logging in Bezug auf den Worker und den Zeitraum geöffnet, in dem der Nachzügler erkannt wurde. Suchen Sie nach Problemen, die die Ausführung der Phase verlangsamen könnten, z. B.:
- Programmfehler im
DoFn-Code oder festhängendeDoFns. Suchen Sie in den Logs nach Stacktraces in der Nähe des Zeitstempels, in dem der Nachzügler erkannt wurde. - Aufrufe externer Dienste, die sehr lange dauern. Sie können dieses Problem umgehen, indem Sie Batchanfragen an externe Dienste weiterleiten und Zeitlimits für RPCs festlegen.
- Kontingentlimits in Senken. Wenn Ihre Pipeline in einen Google Cloud-Dienst ausgegeben wird, können Sie das Kontingent möglicherweise erhöhen. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der Dokumentation zu Cloud-Kontingenten. Prüfen Sie darüber hinaus die Dokumentation des jeweiligen Dienstes auf Optimierungsstrategien hin und schlagen Sie in der Dokumentation zum E/A-Connector nach.
DoFns, die große Lese- oder Schreibvorgänge im nichtflüchtigen Status ausführen. Erwägen Sie eine Refaktorierung des Codes, um kleinere Lese- oder Schreibvorgänge im nichtflüchtigen Status auszuführen.
Sie können auch den Bereich Nebeninformationen verwenden, um die langsamsten Schritte in der Phase zu ermitteln. Einer dieser Schritte kann möglicherweise den Nachzügler verursachen. Klicken Sie auf den Namen des Schritts, um die Worker-Logs für diesen Schritt aufzurufen.
Nachdem Sie die Ursache ermittelt haben, aktualisieren Sie Ihre Pipeline mit neuem Code und beobachten Sie das Ergebnis.
Nächste Schritte
- Dataflow-Monitoring-Oberfläche verwenden
- Informationen zum Tab Ausführungsdetails in der Monitoring-Benutzeroberfläche.

