Dokumen ini menjelaskan cara Cloud Monitoring membuat model pengukuran yang dikumpulkannya. Pengukuran tersebut membantu Anda memahami performa aplikasi dan layanan sistem Anda. Model Cloud Monitoring untuk memantau data terdiri dari tiga konsep utama, yaitu jenis resource yang dimonitor, jenis metrik, deret waktu:
Jenis resource yang dimonitor adalah sumber pengukuran, seperti aplikasi dan layanan sistem Anda. Ada lebih dari 270 jenis resource yang dimonitor yang tersedia. Untuk daftar saat ini, lihat Daftar resource yang dimonitor.
Jenis metrik menentukan properti yang diukur, seperti penggunaan CPU. Ada lebih dari 6.500 jenis metrik yang tersedia di Monitoring, untuk memantau Google Cloud, AWS, dan berbagai software pihak ketiga. Untuk daftar jenis metrik, lihat Daftar metrik. Dan jika Anda memerlukan sesuatu yang belum ditentukan, Anda dapat membuatnya sendiri.
Deret waktu adalah kumpulan pengukuran dari resource tertentu yang dipantau.
Untuk pengantar konsep ini dan hubungannya, baca dokumen ini. Dokumen berikut memberikan informasi selengkapnya:
- Untuk informasi tentang label dan kardinalitas deret waktu, serta contoh resource yang dimonitor dan jenis metrik, lihat Komponen model metrik.
- Untuk mengetahui informasi mendetail tentang deret waktu, termasuk cara deret waktu direpresentasikan oleh Cloud Monitoring API, lihat Struktur deret waktu. Informasi ini sangat relevan bagi Anda jika Anda berencana menggunakan Monitoring API atau metrik kustom.
Model metrik Cloud Monitoring
Metrik adalah serangkaian pengukuran terkait dari beberapa atribut resource yang Anda pantau. Pengukuran dapat mencakup latensi permintaan ke layanan, jumlah ruang disk yang tersedia di komputer, jumlah tabel di database SQL Anda, jumlah widget yang terjual, dan sebagainya. Resource dapat mencakup virtual machine (VM), instance database, disk, dan sebagainya.
Istilah umum metrik di Cloud Monitoring mencakup tiga komponen utama:
- Informasi tentang sumber pengukuran.
- Kumpulan pengukuran beberapa properti. Setiap pengukuran dicatat sebagai nilai dengan stempel waktu.
- Informasi tentang nilai properti yang diukur.
Misalnya, ada metrik yang melacak jumlah widget yang terjual oleh toko. Komponen model dipetakan ke contoh ini dengan cara berikut:
Sumber pengukuran
Model metrik mencatat informasi tentang setiap resource yang dimonitor. Informasi tertentu yang diambil bergantung pada jenis resource yang dipantau: informasi tersebut dapat mencakup lokasi geografis, nama metode, ID disk, dan sebagainya, apa pun yang mungkin menjadi sumber pengukuran.

Sumber data pemantauan disebut resource yang dimonitor.
Contoh: Dalam contoh penjualan widget, resource yang dimonitor adalah toko yang menjual widget.
Pengukuran
Model metrik merekam pengukuran properti sebagai kumpulan titik data, yang terdiri dari nilai berstempel waktu.

Nilai biasanya berupa angka, tetapi bergantung pada apa yang Anda ukur.
Contoh: Dalam contoh penjualan widget, pengukuran mencatat informasi penjualan pada titik waktu tertentu. Pengukuran tersebut mungkin terlihat seperti berikut:
[(150, 2024-05-23T17:37:00-04:00), (229, 2024-05-23T17:38:00-04:00), (138, 2024-05-23T17:39:00-04:00), ...]
Informasi tentang nilai
Nilai pengukuran tidak akan berarti tanpa informasi tentang cara menafsirkannya. Anda harus memiliki beberapa informasi "jenis" tentang nilai, seperti jenis data, satuan, dan jenis setiap pengukuran:
- Apakah nilainya berupa bilangan bulat atau string?
- Apakah nilainya mewakili mil per jam atau radian?
- Apakah nilai tersebut mewakili total pada saat itu, atau perubahan sejak nilai sebelumnya?

Cloud Monitoring menyebut setiap kumpulan karakteristik tentang sesuatu yang ingin Anda ukur sebagai jenis metrik.
Contoh: Dalam contoh penjualan widget, informasi ini mungkin memberi tahu Anda hal berikut:
- Setiap nilai dicatat sebagai bilangan bulat 64-bit.
- Setiap nilai mewakili jumlah widget yang terjual.
- Setiap nilai mewakili jumlah widget yang terjual sejak pengukuran terakhir yang dicatat.
Deret waktu: menggabungkan komponen
Di Cloud Monitoring, struktur data yang mendasari model ini adalah deret waktu (bentuk tunggal dan jamak sama).
Setiap deret waktu mencakup tiga komponen model:
- Deskripsi resource yang dimonitor tempat pengukuran berasal.
- Kumpulan pengukuran yang terkait dengan satu resource yang dipantau.
- Deskripsi jenis metrik yang menjelaskan hal yang Anda ukur.
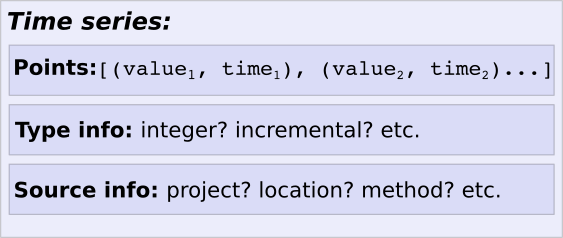
Contoh: Dalam contoh penjualan widget, deret waktu mencakup hal berikut:
- Deskripsi toko yang menjual widget yang dihitung dalam deret waktu ini.
- Kumpulan pengukuran yang dicatat untuk toko ini.
- Deskripsi nilai: Bilangan bulat 64-bit yang mengukur jumlah widget yang terjual sejak nilai yang dicatat sebelumnya.
Satu jenis metrik Cloud Monitoring atau jenis resource yang dimonitor dapat dikaitkan dengan banyak deret waktu terkait. Dalam contoh penjualan widget, setiap toko yang menjual widget menyimpan datanya dalam deret waktu, sehingga jika ada 15 toko yang menjual widget, dapat ada 15 deret waktu yang mencatat penjualan widget.
Langkah selanjutnya
- Untuk informasi selengkapnya tentang struktur metrik Cloud Monitoring, lihat
- Komponen model metrik untuk melihat lebih dalam tentang metrik, resource, dan deret waktu.
- Struktur deret waktu untuk mengetahui informasi tentang cara deret waktu dipetakan ke Cloud Monitoring API.
- Untuk informasi tentang operasi deret waktu seperti agregasi, pengelompokan, dan pemfilteran, lihat Pemfilteran dan agregasi: memanipulasi deret waktu.
- Untuk mendapatkan bantuan terkait terminologi, lihat Catatan tentang terminologi.

