This page explains the network configuration options for Looker (Google Cloud core) instances.
You set an instance's network configuration during instance creation. It is a good idea to determine what networking options you want to use before beginning your instance creation process. This page also helps you determine which of these options is most appropriate for your organization's needs.
Overview
The following network configuration options for Looker (Google Cloud core) are available:
- Use public secure connections: An instance that uses an external internet accessible IP address.
Use private connections: Private connections use private networks for access to and from Looker (Google Cloud core) instances. There are two options for using private networks:
- Private Service Connect: An instance enabled for Private Service Connect uses an internal, Google-hosted Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) IP address and uses Private Service Connect to connect privately to Google and third-party services.
- private services access: An instance enabled for private services access uses an internal, Google-hosted Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) IP address and uses private services access to connect privately to Google and third-party services.
Use hybrid connections: An instance that supports a public IP address for ingress and an internal, Google-hosted VPC IP address and private services access or Private Service Connect for egress.
When considering a network configuration for your Looker (Google Cloud core) instance, the following information may be helpful as you make your decision:
- Network configuration must be set when the instance is created. An instance configured for public secure connections can't be changed after instance creation. An instance configured for hybrid connections can by changed to private connections, or an instance with private connections can be changed to a hybrid connections configuration after the instance is created.
- Feature availability varies by network option. See the Feature availability in Looker (Google Cloud core) documentation page for more information.
- All connections to BigQuery are through Google's private network, regardless of the network configuration.
- If a third-party identity provider is configured for single-sign on, the user's browser communicates to the identity provider and is then redirected to the Looker (Google Cloud core) instance. As long as the redirect URL is accessible over the user's network, third-party identity providers work for all networking configurations.
Also see the table in the How to choose a networking option section of this documentation page for more information about how to decide on the right networking configuration for your team.
Public secure connections
Looker (Google Cloud core) deployed as a public secure connection instance is accessible from an external internet-accessible IP address. In this configuration, inbound (northbound) traffic to Looker (Google Cloud core) is supported in addition to Looker (Google Cloud core) outbound (southbound) access to internet endpoints. This configuration is similar to the configuration of a Looker (original) instance that is hosted by Looker.
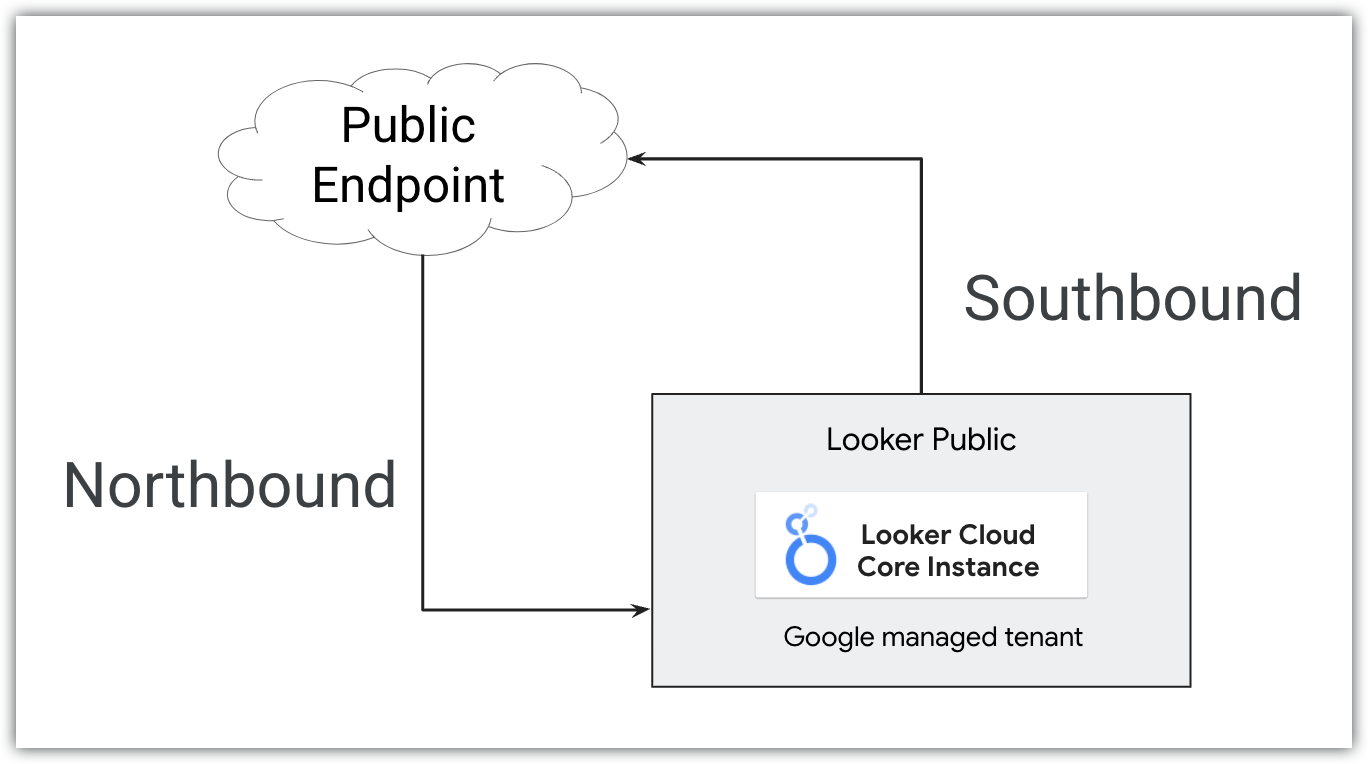
Public secure connections allow only HTTPS traffic into Looker (Google Cloud core). Google auto-provisions an SSL certificate when the CNAME is updated and Google can locate the DIG records. This certificate is automatically rotated every four months. To securely connect to external databases from a public secure connection Looker (Google Cloud core) instance, you can set up an encrypted SSL connection.
Public secure connections configurations are straightforward to set up and connect to and don't require advanced network configuration or expertise.
To create a Looker (Google Cloud core) public secure connection instance, see the Create a public secure connection Looker (Google Cloud core) instance documentation page.
Private connections
A Looker (Google Cloud core) instance configured to use private connections uses an internal, Google-hosted VPC IP address. You can use this address to communicate with other resources that can access the VPC. Private connections make services reachable without going through the public internet or using external IP addresses. Because they don't traverse the internet, private connections over private typically provide lower latency and limited attack vectors.
In a private connections configuration, internal certificates are completely managed by Google and aren't exposed to anyone. If you are provisioning a private connections instance with custom certificates, you don't need to manage the internal private certificates. Instead, use your own custom certificate, and ensure that the rotation of that certificate is maintained.
In a private connections configuration, Looker (Google Cloud core) doesn't have a public URL. You control all inbound (northbound) traffic, and all outbound (southbound) traffic will be routed through your VPC.
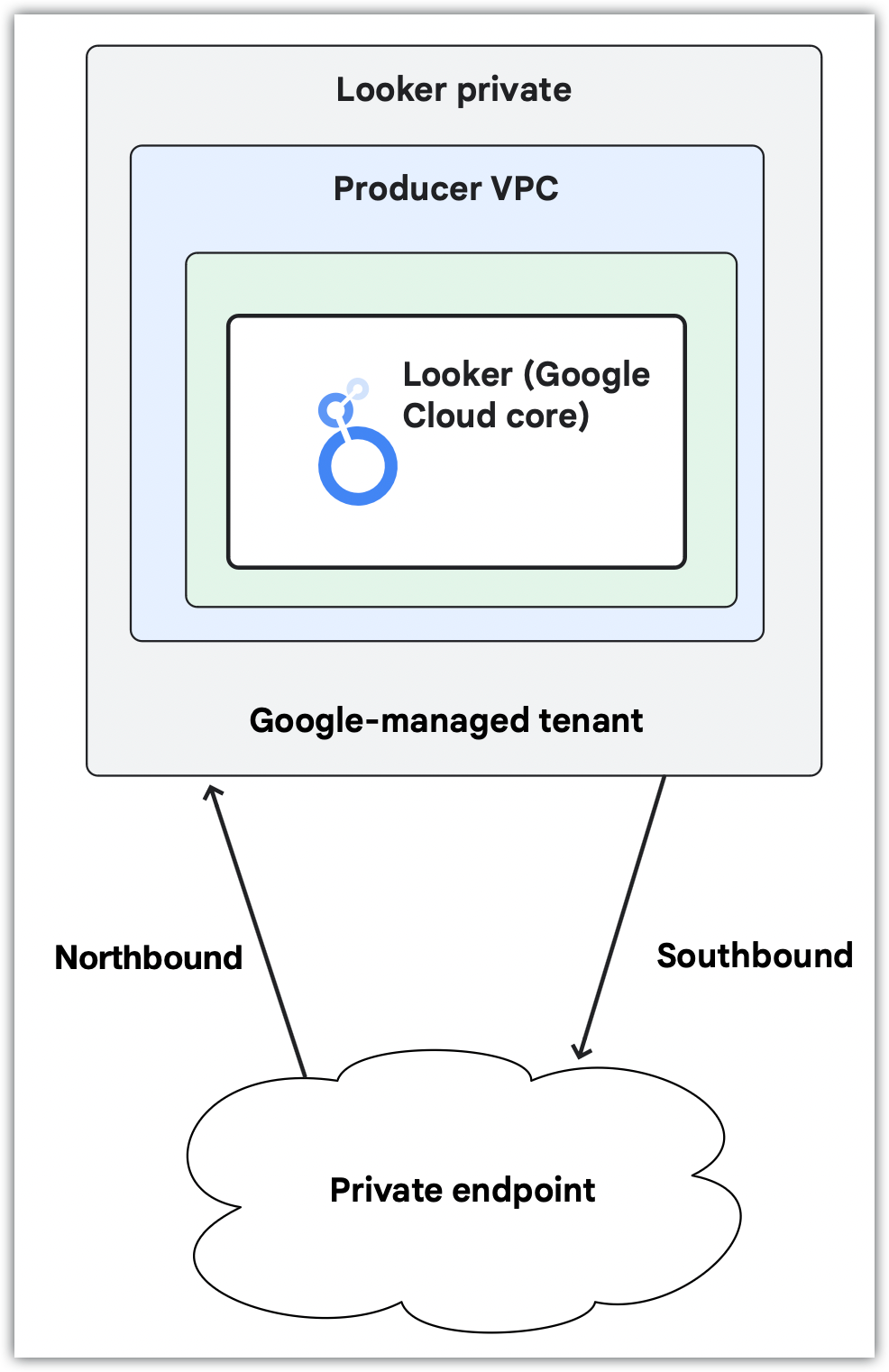
If your instance uses only a private connection, additional configuration is necessary to set up a custom domain and user access to the instance; use some Looker (Google Cloud core) features; or connect to external resources, such as Git providers. In-house networking expertise is helpful to plan and execute this configuration.
Looker (Google Cloud core) supports the following two options for private connections:
The use of private services access or Private Service Connect must be decided at the time of instance creation.
Private Service Connect
The use of Private Service Connect with Looker (Google Cloud core) must be set at the time of instance creation.
When used with Looker (Google Cloud core), Private Service Connect differs from private services access in the following ways:
- Endpoints and backends support public or private access methods.
- Looker (Google Cloud core) can connect to other Google services, such as Cloud SQL, that are accessible through Private Service Connect.
- There is no need to allocate large IP blocks.
- Direct connections allow for transitive communication.
- There is no need to share a network with other services.
- Supports multi-tenancy.
Private Service Connect backends can be used to access Looker (Google Cloud core) Private Service Connect instances.
Looker (Google Cloud core) (Private Service Connect) instances use endpoints to connect to Google Cloud or external resources. If a resource is external, a network endpoint group (NEG) and load balancer need to be set up as well. Additionally, each outbound connection to a unique service requires that the service be published using Private Service Connect. On the Looker (Google Cloud core) end, each unique egress connection must be created and maintained for each service that you want to connect to.
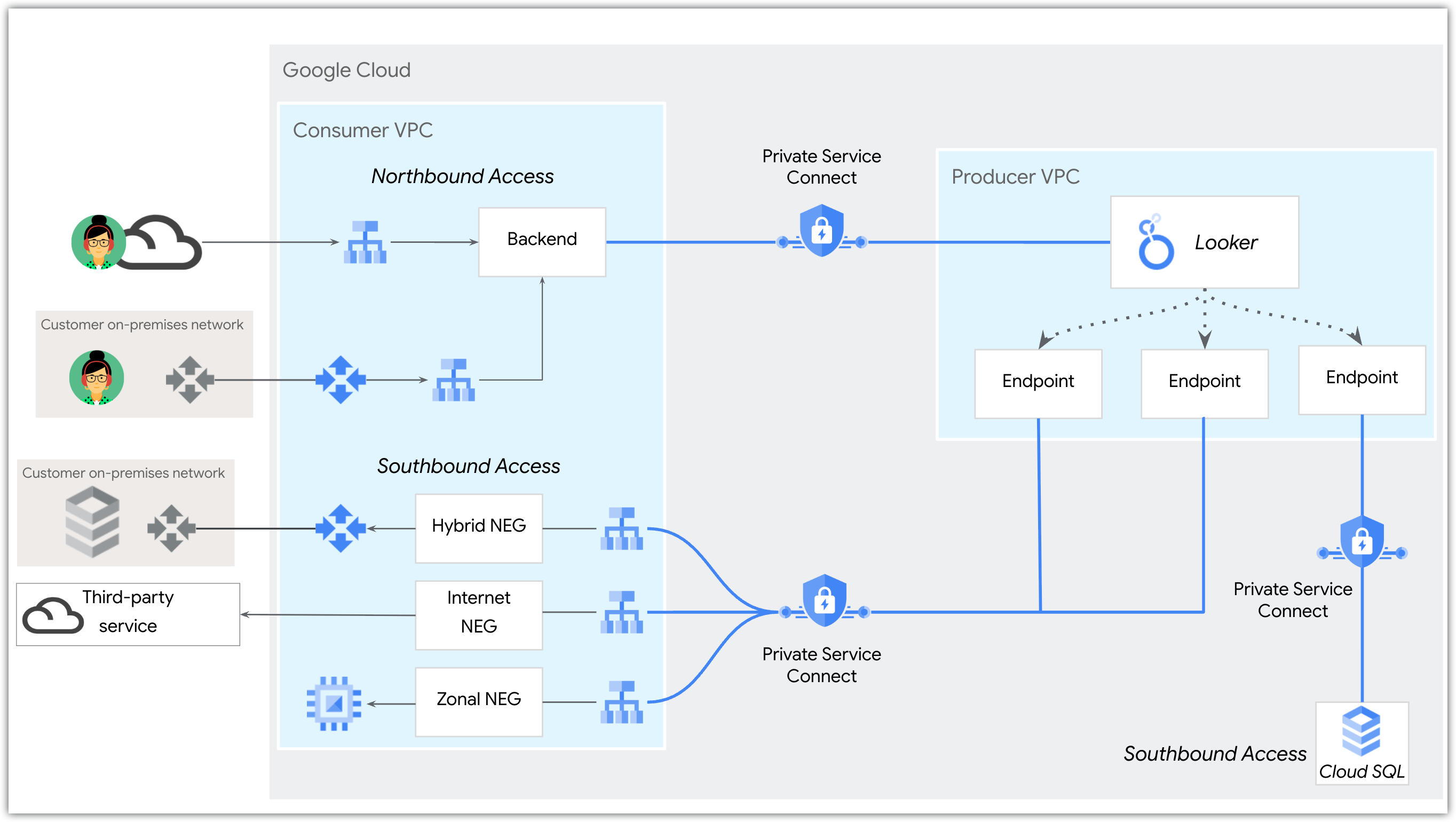
In-house networking expertise is helpful to plan and execute Private Service Connect configurations.
For an example of connecting to an external service, see the Looker PSC Southbound HTTPS Internet NEG codelab.
To learn more about Private Service Connect instances, see the Use Private Service Connect with Looker (Google Cloud core) documentation page.
Private services access
The use of private services access private connections with Looker (Google Cloud core) must be set at the time of instance creation. Looker (Google Cloud core) instances can optionally include a public secure connection with their private (private services access) connection. After creation of an instance that uses private services access, you can add or remove a private connection to that instance.
To create a private (private services access) connection, you must allocate a /22 CIDR range in your VPC to Looker (Google Cloud core).
To set up user access to an instance that uses only a private (private services access) connection, you must set up a custom domain and configure access to the domain depending on your organization's needs. To connect to external resources, you will need to perform additional configuration. In-house networking expertise is helpful to plan and execute this configuration.
To create a Looker (Google Cloud core) private services access instance, see the Create a private connections instance documentation page.
Hybrid connections configuration
Looker (Google Cloud core) instances that use private services access or Private Service Connect for their private connection support a hybrid connections configuration.
A Looker (Google Cloud core) instance that uses private services access and that has a hybrid connection has a public URL, and all incoming (northbound) traffic will go through the public connection using HTTPS. Outgoing (southbound) traffic is routed through your VPC, which can be configured to allow only private connection traffic, using HTTPS or encryption. All traffic in transit is encrypted.
A Looker (Google Cloud core) instance that is enabled for Private Service Connect uses a customer-defined IP address accessible in a VPC for ingress. Communication to the VPC and on-premises or multi-cloud workloads use service attachments that you deploy for egress traffic.
A hybrid connections configuration enables the use of some Looker (Google Cloud core) features that are not available for private connections configurations, such as the Connected Sheets BI connector.
How to choose a networking option
The following table shows the feature availability for different networking options.
| Network requirements | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | Public secure connections | Hybrid connections (PSA) | Private connections (PSA) | Hybrid connections (PSC) | Private connections (PSC) |
| Requires IP range allocation for instance creation | No | Yes (/22 per instance, per region)
|
Yes (/22 per instance, per region)
|
No | No |
| Cloud Armor | Yes. Looker (Google Cloud core) uses default Cloud Armor rules, which are managed by Google. These rules are not configurable. | Yes. Looker (Google Cloud core) uses default Cloud Armor rules, which are managed by Google. These rules are not configurable. | No | Yes. Looker (Google Cloud core) uses default Cloud Armor rules, which are managed by Google. These rules are not configurable. | Supported with customer-managed regional external Application Load Balancer, Private Service Connect backend, and customer-managed Google Cloud Armor |
| Custom domain | Yes | Supported as a public URL | Yes | Supported as a public URL | Yes |
| Inbound access | |||||
| Feature | Public secure connections | Hybrid connections (PSA) | Private connections (PSA) | Hybrid connections (PSC) | Private connections (PSC) |
| Public internet | Yes | Yes | No | Supported with Google-managed regional external Application Load Balancer | Supported with customer-managed regional external Application Load Balancer, Private Service Connect backend, and custom domain |
| VPC peering (private services access) | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| PSC-based routing | No | No | No |
Supported with the following:
Global access is supported by Private Service Connect backends, but not by Private Service Connect consumer endpoints. |
|
| Hybrid networking | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Outbound access | |||||
| Feature | Public secure connections | Hybrid connections (PSA) | Private connections (PSA) | Hybrid connections (PSC) | Private connections (PSC) |
| Internet | Yes | No | No | Supported with regional TCP proxy internal load balancer, internet NEG, and Cloud NAT gateway. | |
| VPC peering (private services access) | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Private Service Connect-based routing | No | No | No | Supported with regional TCP proxy internal load balancer and hybrid NEG | |
| Hybrid networking (multi-cloud and on-premises) | No | Yes | Yes | Supported with regional TCP proxy internal load balancer, hybrid NEG, and Google Cloud networking products | |
| Application | |||||
| Feature | Public secure connections | Hybrid connections (PSA) | Private connections (PSA) | Hybrid connections (PSC) | Private connections (PSC) |
| GitHub | Yes | Supported with TCP proxy internal load balancer and internet NEG | Yes. For an example, see the Looker PSC Southbound HTTPS Internet NEG codelab. | ||
| GitHub Enterprise | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cloud SQL | Yes | Supported with Cloud SQL deployed in the same VPC as Looker (Google Cloud core) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| BigQuery | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Embed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Marketplace | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Connected Sheets | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| SMTP | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes. Requires outbound connectivity. | |
| Benefits | |||||
| Feature | Public secure connections | Hybrid connections (PSA) | Private connections (PSA) | Hybrid connections (PSC) | Private connections (PSC) |
| Benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
| Considerations | |||||
| Feature | Public secure connections | Hybrid connections (PSA) | Private connections (PSA) | Hybrid connections (PSC) | Private connections (PSC) |
| Considerations | If you want a custom URL, you have to configure a fully qualified domain name (for example, looker.examplepetstore.com). You cannot have a custom URL like examplepetstore.looker.com.
|
|
|
|
|
What's next
- Create a public secure connections Looker (Google Cloud core) instance
- Use Private Service Connect with Looker (Google Cloud core)
- Create a Looker (Google Cloud core) private connections Private Service Connect instance
- Follow a tutorial on how to perform a outbound HTTPS connection to GitHub from a PSC.
- Create a private connections (private services access) Looker (Google Cloud core) instance

