La transcripción de voz te permite convertir tus datos de audio de transmisión en texto transcrito en tiempo real. El Asistente de agente hace sugerencias basadas en texto, por lo que los datos de audio se deben convertir antes de poder usarlos. También puedes usar audio de transmisión transcrito con Conversational Insights para recopilar datos en tiempo real sobre las conversaciones de los agentes (por ejemplo, modelado de temas).
Existen dos formas de transcribir audio de transmisión para usarlo con Agent Assist: mediante la función SIPREC o realizando llamadas de gRPC con datos de audio como carga útil. En esta página, se describe el proceso de transcripción de datos de audio transmitidos con llamadas a gRPC.
La transcripción de voz funciona con el reconocimiento de voz de transmisión de Speech-to-Text. Speech-to-Text ofrece varios modelos de reconocimiento, tanto estándar como mejorados. La transcripción de voz se admite a nivel de GA solo cuando se usa con el modelo de telefonía.
Requisitos previos
- Crea un proyecto enGoogle Cloud.
- Habilita la API de Dialogflow.
- Comunícate con tu representante de Google para asegurarte de que tu cuenta tenga acceso a los modelos mejorados de Speech-to-Text.
Crea un perfil de conversación
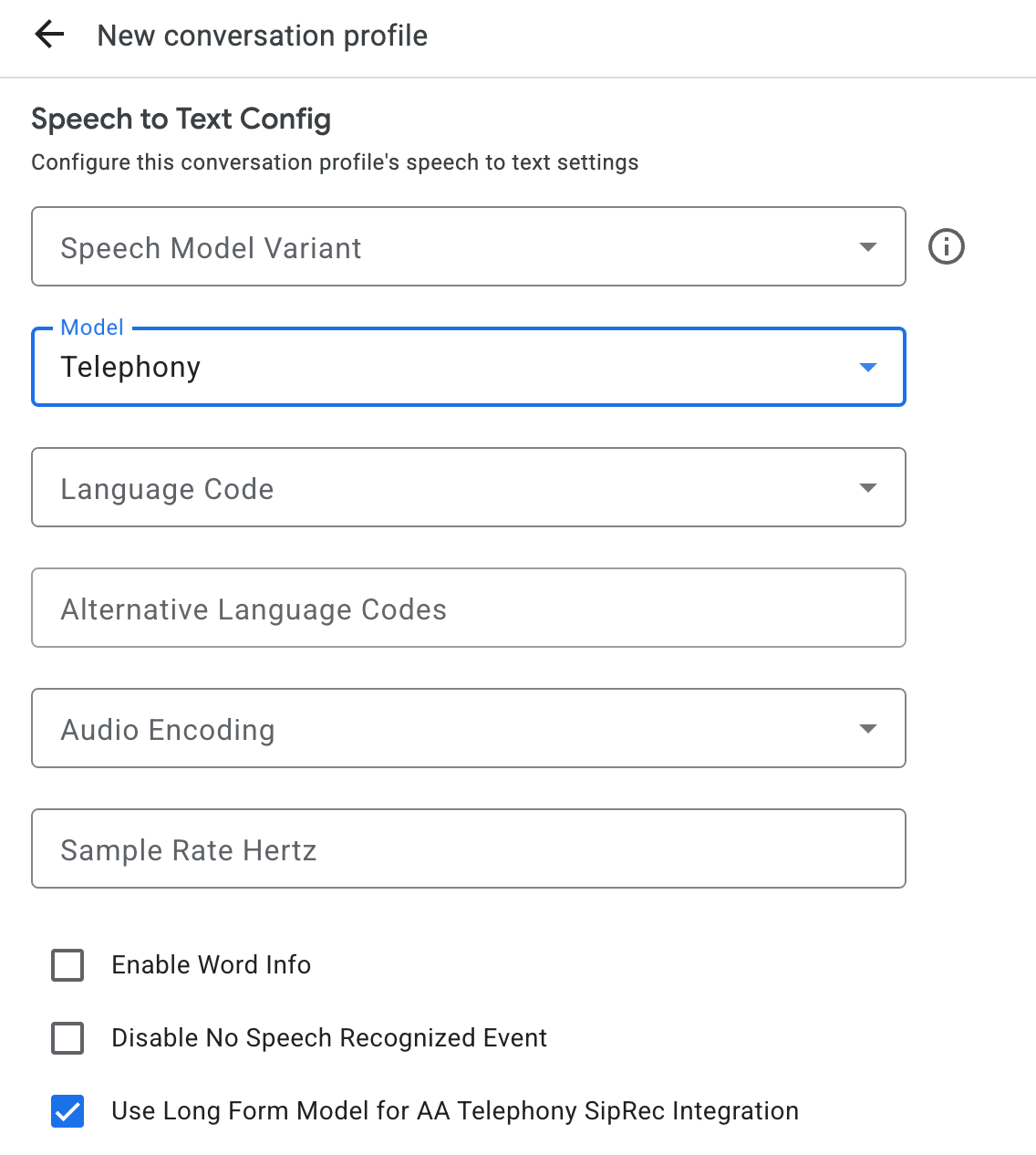
Para crear un perfil de conversación, usa la consola de Agent Assist o llama al método create en el recurso ConversationProfile directamente.
Para la transcripción de voz, te recomendamos que configures ConversationProfile.stt_config como el InputAudioConfig predeterminado cuando envíes datos de audio en una conversación.
Obtén transcripciones durante el tiempo de ejecución de la conversación
Para obtener transcripciones durante el tiempo de ejecución de la conversación, debes crear participantes para la conversación y enviar datos de audio para cada participante.
Cómo crear participantes
Hay tres tipos de participantes.
Consulta la documentación de referencia para obtener más detalles sobre sus roles. Llama al método create en el participant y especifica el role. Solo un participante END_USER o HUMAN_AGENT puede llamar a StreamingAnalyzeContent, lo que se requiere para obtener una transcripción.
Envía datos de audio y obtén una transcripción
Puedes usar StreamingAnalyzeContent para enviar el audio de un participante a Google y obtener la transcripción, con los siguientes parámetros:
La primera solicitud en la transmisión debe ser
InputAudioConfig. (Los campos configurados aquí anulan la configuración correspondiente enConversationProfile.stt_config). No envíes ninguna entrada de audio hasta la segunda solicitud.audioEncodingdebe establecerse enAUDIO_ENCODING_LINEAR_16oAUDIO_ENCODING_MULAW.model: Es el modelo de Speech-to-Text que deseas usar para transcribir tu audio. Establece este campo entelephony. La variante no afecta la calidad de la transcripción, por lo que puedes dejar sin especificar Variante del modelo de voz o elegir Usar la mejor disponible.singleUtterancedebe establecerse enfalsepara obtener la mejor calidad de transcripción. No debes esperarEND_OF_SINGLE_UTTERANCEsisingleUtteranceesfalse, pero puedes depender deisFinal==truedentro deStreamingAnalyzeContentResponse.recognition_resultpara cerrar parcialmente la transmisión.- Parámetros adicionales opcionales: Los siguientes parámetros son opcionales. Para obtener acceso a estos parámetros, comunícate con tu representante de Google.
languageCode: Es ellanguage_codedel audio. El valor predeterminado esen-US.alternativeLanguageCodes: Esta es una función en versión preliminar. Son los idiomas adicionales que se podrían detectar en el audio. El Asistente de agente usa el campolanguage_codepara detectar automáticamente el idioma al comienzo del audio y lo establece de forma predeterminada en todos los turnos de conversación posteriores. El campoalternativeLanguageCodeste permite especificar más opciones para que el Asistente de agente elija.phraseSets: Es el nombre del recursophraseSetde la adaptación del modelo de Speech-to-Text. Para usar la adaptación del modelo con la transcripción de voz, primero debes crear elphraseSetcon la API de Speech-to-Text y especificar el nombre del recurso aquí.
Después de enviar la segunda solicitud con la carga útil de audio, deberías comenzar a recibir algunos
StreamingAnalyzeContentResponsesde la transmisión.- Puedes cerrar el flujo a la mitad (o dejar de enviar en algunos lenguajes, como Python) cuando veas que
is_finalestá establecido entrueenStreamingAnalyzeContentResponse.recognition_result. - Después de que cierres parcialmente la transmisión, el servidor enviará la respuesta que contiene la transcripción final, junto con las posibles sugerencias de Dialogflow o de Agent Assist.
- Puedes cerrar el flujo a la mitad (o dejar de enviar en algunos lenguajes, como Python) cuando veas que
Puedes encontrar la transcripción final en las siguientes ubicaciones:
StreamingAnalyzeContentResponse.message.content- Si habilitas las notificaciones de Pub/Sub, también podrás ver la transcripción en Pub/Sub.
Inicia una nueva transmisión después de que se cierre la anterior.
- Reenvío de audio: Los datos de audio generados después del último
speech_end_offsetde la respuesta conis_final=truea la nueva hora de inicio de la transmisión deben reenviarse aStreamingAnalyzeContentpara obtener la mejor calidad de transcripción.
- Reenvío de audio: Los datos de audio generados después del último
En el siguiente diagrama, se ilustra cómo funciona la transmisión.
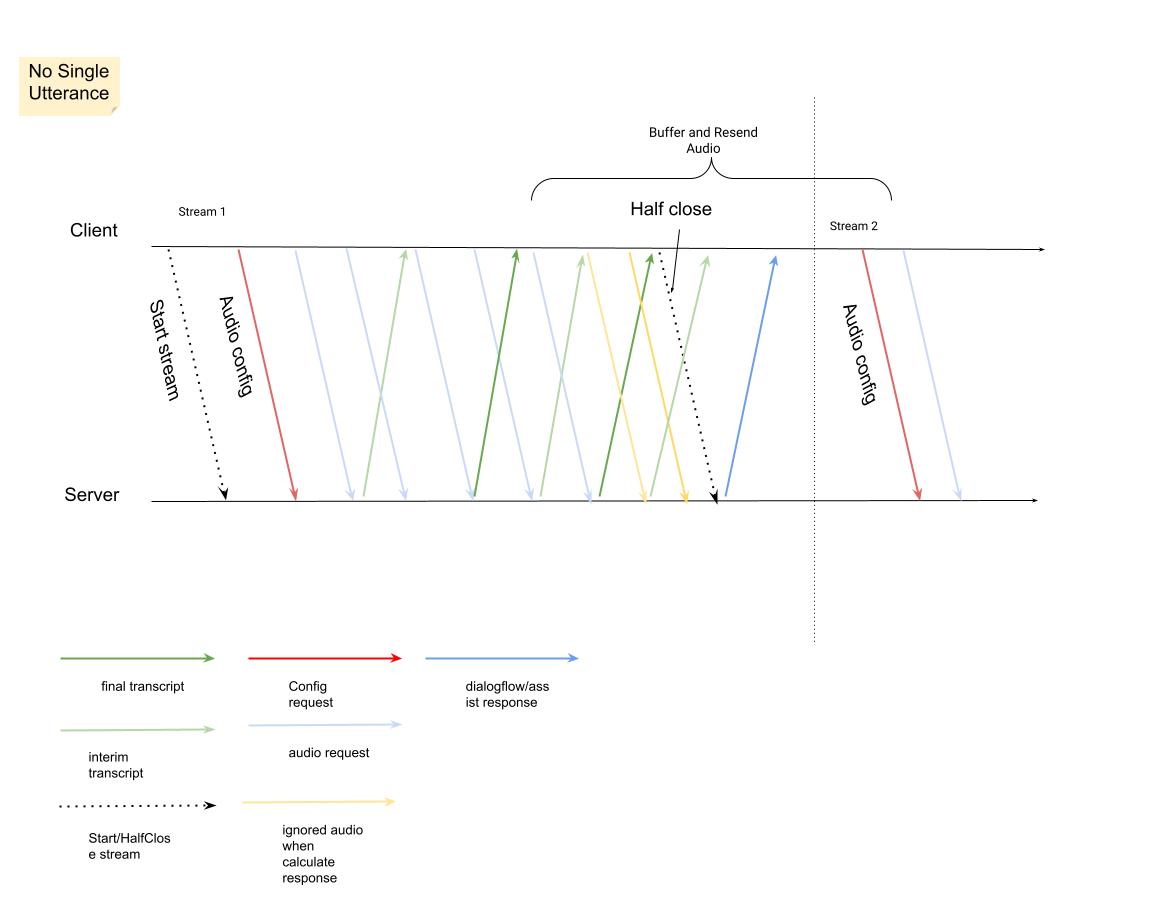
Muestra de código de solicitud de reconocimiento de transmisión continua
En el siguiente muestra de código, se muestra cómo enviar una solicitud de transcripción por transmisión:
Python
Para autenticarte en Agent Assist, configura las credenciales predeterminadas de la aplicación. Si deseas obtener más información, consulta Configura la autenticación para un entorno de desarrollo local.

