Konektor BigQuery untuk Apache Spark memungkinkan Data Scientist memadukan kecanggihan mesin SQL yang dapat diskalakan secara lancar dari BigQuery dengan kemampuan Machine Learning Apache Spark. Dalam tutorial ini, kami menunjukkan cara menggunakan Dataproc, BigQuery, dan Apache Spark ML untuk melakukan machine learning pada set data.
Membuat subset data natalitas BigQuery
Di bagian ini, Anda akan membuat set data di project, lalu membuat tabel di set data yang akan Anda salin ke subset data tingkat kelahiran dari set data BigQuery natality yang tersedia untuk publik. Nanti dalam tutorial ini, Anda akan menggunakan data subset dalam tabel ini untuk memprediksi berat lahir sebagai fungsi dari usia ibu, usia ayah, dan minggu kehamilan.
Anda dapat membuat subset data menggunakan konsol Google Cloud atau menjalankan skrip Python di mesin lokal Anda.
Konsol
Buat set data di project Anda.
- Buka UI Web BigQuery.
- Di panel navigasi kiri, klik nama project Anda, lalu klik BUAT SET DATA.
- Dalam dialog Create dataset:
- Untuk Dataset ID, masukkan "natality_regression".
- Untuk Lokasi data, Anda dapat memilih
lokasi
untuk set data. Lokasi nilai defaultnya adalah
US multi-region. Setelah set data dibuat, lokasi tidak dapat diubah. - Untuk Default table expiration, pilih salah satu opsi berikut:
- Tidak pernah (default): Anda harus menghapus tabel secara manual.
- Jumlah hari: Tabel akan dihapus setelah jumlah hari yang ditentukan sejak waktu pembuatannya.
- Untuk Enkripsi, pilih salah satu opsi berikut:
- Google-owned and Google-managed encryption key (default).
- Kunci yang dikelola pelanggan: Lihat Melindungi data dengan kunci Cloud KMS.
- Klik Create dataset.
Jalankan kueri terhadap set data publik kelahiran, lalu simpan hasil kueri dalam tabel baru di set data Anda.
- Salin dan tempel kueri berikut ke Editor Kueri, lalu klik Jalankan.
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE natality_regression.regression_input as SELECT weight_pounds, mother_age, father_age, gestation_weeks, weight_gain_pounds, apgar_5min FROM `bigquery-public-data.samples.natality` WHERE weight_pounds IS NOT NULL AND mother_age IS NOT NULL AND father_age IS NOT NULL AND gestation_weeks IS NOT NULL AND weight_gain_pounds IS NOT NULL AND apgar_5min IS NOT NULL
- Setelah kueri selesai (dalam waktu sekitar satu menit), hasilnya
akan disimpan sebagai tabel BigQuery "regression_input"
dalam set data
natality_regressiondi project Anda.
- Salin dan tempel kueri berikut ke Editor Kueri, lalu klik Jalankan.
Python
Sebelum mencoba contoh ini, ikuti petunjuk penyiapan Python di Panduan memulai Dataproc menggunakan library klien. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat dokumentasi referensi Python API Dataproc.
Untuk melakukan autentikasi ke Dataproc, siapkan Kredensial Default Aplikasi. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya, lihat Menyiapkan autentikasi untuk lingkungan pengembangan lokal.
Lihat Menyiapkan Lingkungan Pengembangan Python untuk mengetahui petunjuk tentang cara menginstal Python dan Library Klien Google Cloud untuk Python (diperlukan untuk menjalankan kode). Sebaiknya instal dan gunakan
virtualenvPython.Salin dan tempel kode
natality_tutorial.py, di bawah, ke dalam shellpythondi komputer lokal Anda. Tekan tombol<return>di shell untuk menjalankan kode guna membuat set data BigQuery "natality_regression" di projectGoogle Cloud default Anda dengan tabel "regression_input" yang diisi dengan subset datanatalitypublik.Konfirmasi pembuatan set data
natality_regressiondan tabelregression_input.
Menjalankan regresi linear
Di bagian ini, Anda akan menjalankan regresi linear PySpark dengan mengirimkan
tugas ke layanan Dataproc menggunakan konsol Google Cloud
atau dengan menjalankan perintah gcloud dari terminal lokal.
Konsol
Salin dan tempel kode berikut ke dalam file
natality_sparkml.pybaru di mesin lokal Anda."""Run a linear regression using Apache Spark ML. In the following PySpark (Spark Python API) code, we take the following actions: * Load a previously created linear regression (BigQuery) input table into our Cloud Dataproc Spark cluster as an RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) * Transform the RDD into a Spark Dataframe * Vectorize the features on which the model will be trained * Compute a linear regression using Spark ML """ from pyspark.context import SparkContext from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors from pyspark.ml.regression import LinearRegression from pyspark.sql.session import SparkSession # The imports, above, allow us to access SparkML features specific to linear # regression as well as the Vectors types. # Define a function that collects the features of interest # (mother_age, father_age, and gestation_weeks) into a vector. # Package the vector in a tuple containing the label (`weight_pounds`) for that # row. def vector_from_inputs(r): return (r["weight_pounds"], Vectors.dense(float(r["mother_age"]), float(r["father_age"]), float(r["gestation_weeks"]), float(r["weight_gain_pounds"]), float(r["apgar_5min"]))) sc = SparkContext() spark = SparkSession(sc) # Read the data from BigQuery as a Spark Dataframe. natality_data = spark.read.format("bigquery").option( "table", "natality_regression.regression_input").load() # Create a view so that Spark SQL queries can be run against the data. natality_data.createOrReplaceTempView("natality") # As a precaution, run a query in Spark SQL to ensure no NULL values exist. sql_query = """ SELECT * from natality where weight_pounds is not null and mother_age is not null and father_age is not null and gestation_weeks is not null """ clean_data = spark.sql(sql_query) # Create an input DataFrame for Spark ML using the above function. training_data = clean_data.rdd.map(vector_from_inputs).toDF(["label", "features"]) training_data.cache() # Construct a new LinearRegression object and fit the training data. lr = LinearRegression(maxIter=5, regParam=0.2, solver="normal") model = lr.fit(training_data) # Print the model summary. print("Coefficients:" + str(model.coefficients)) print("Intercept:" + str(model.intercept)) print("R^2:" + str(model.summary.r2)) model.summary.residuals.show()
Salin file
natality_sparkml.pylokal ke bucket Cloud Storage di project Anda.gcloud storage cp natality_sparkml.py gs://bucket-name
Jalankan regresi dari halaman Dataproc Submit a job.
Di kolom Main python file, masukkan URI
gs://dari bucket Cloud Storage tempat salinan filenatality_sparkml.pyAnda berada.Pilih
PySparksebagai Jenis tugas.Masukkan
gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-latest_2.12.jardi kolom File JAR. Hal ini membuat spark-bigquery-connector tersedia untuk aplikasi PySpark saat runtime agar dapat membaca data BigQuery ke dalam DataFrame Spark.Isi kolom Job ID, Region, dan Cluster.
Klik Submit untuk menjalankan tugas di cluster Anda.
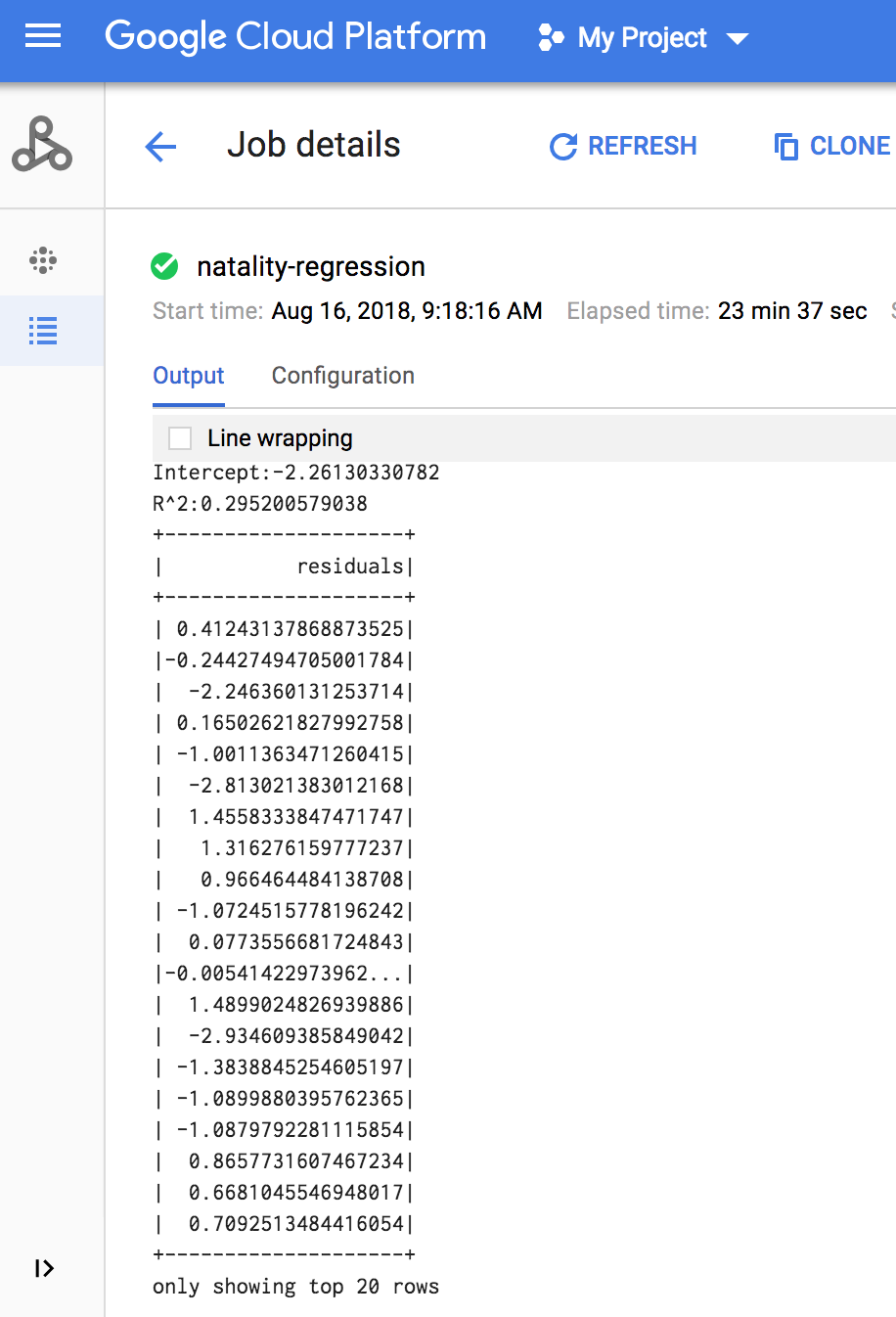
Setelah tugas selesai, ringkasan model output regresi linear akan muncul di jendela detail Tugas Dataproc.
gcloud
Salin dan tempel kode berikut ke dalam file
natality_sparkml.pybaru di mesin lokal Anda."""Run a linear regression using Apache Spark ML. In the following PySpark (Spark Python API) code, we take the following actions: * Load a previously created linear regression (BigQuery) input table into our Cloud Dataproc Spark cluster as an RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) * Transform the RDD into a Spark Dataframe * Vectorize the features on which the model will be trained * Compute a linear regression using Spark ML """ from pyspark.context import SparkContext from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors from pyspark.ml.regression import LinearRegression from pyspark.sql.session import SparkSession # The imports, above, allow us to access SparkML features specific to linear # regression as well as the Vectors types. # Define a function that collects the features of interest # (mother_age, father_age, and gestation_weeks) into a vector. # Package the vector in a tuple containing the label (`weight_pounds`) for that # row. def vector_from_inputs(r): return (r["weight_pounds"], Vectors.dense(float(r["mother_age"]), float(r["father_age"]), float(r["gestation_weeks"]), float(r["weight_gain_pounds"]), float(r["apgar_5min"]))) sc = SparkContext() spark = SparkSession(sc) # Read the data from BigQuery as a Spark Dataframe. natality_data = spark.read.format("bigquery").option( "table", "natality_regression.regression_input").load() # Create a view so that Spark SQL queries can be run against the data. natality_data.createOrReplaceTempView("natality") # As a precaution, run a query in Spark SQL to ensure no NULL values exist. sql_query = """ SELECT * from natality where weight_pounds is not null and mother_age is not null and father_age is not null and gestation_weeks is not null """ clean_data = spark.sql(sql_query) # Create an input DataFrame for Spark ML using the above function. training_data = clean_data.rdd.map(vector_from_inputs).toDF(["label", "features"]) training_data.cache() # Construct a new LinearRegression object and fit the training data. lr = LinearRegression(maxIter=5, regParam=0.2, solver="normal") model = lr.fit(training_data) # Print the model summary. print("Coefficients:" + str(model.coefficients)) print("Intercept:" + str(model.intercept)) print("R^2:" + str(model.summary.r2)) model.summary.residuals.show()
Salin file
natality_sparkml.pylokal ke bucket Cloud Storage di project Anda.gcloud storage cp natality_sparkml.py gs://bucket-name
Kirimkan tugas Pyspark ke layanan Dataproc dengan menjalankan perintah
gcloud, yang ditampilkan di bawah, dari jendela terminal di komputer lokal Anda.- Nilai tanda --jars membuat spark-bigquery-connector tersedia
untuk tugas PySpark saat runtime agar dapat membaca
data BigQuery ke dalam DataFrame Spark.
gcloud dataproc jobs submit pyspark \ gs://your-bucket/natality_sparkml.py \ --cluster=cluster-name \ --region=region \ --jars=gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-with-dependencies_SCALA_VERSION-CONNECTOR_VERSION.jar
- Nilai tanda --jars membuat spark-bigquery-connector tersedia
untuk tugas PySpark saat runtime agar dapat membaca
data BigQuery ke dalam DataFrame Spark.
Output regresi linear (ringkasan model) akan muncul di jendela terminal saat tugas selesai.
<<< # Cetak ringkasan model. ... print "Coefficients:" + str(model.coefficients) Coefficients:[0.0166657454602,-0.00296751984046,0.235714392936,0.00213002070133,-0.00048577251587] <<< print "Intercept:" + str(model.intercept) Intercept:-2.26130330748 <<< print "R^2:" + str(model.summary.r2) R^2:0.295200579035 <<< model.summary.residuals.show() +--------------------+ | residuals| +--------------------+ | -0.7234737533344147| | -0.985466980630501| | -0.6669710598385468| | 1.4162434829714794| |-0.09373154375186754| |-0.15461747949235072| | 0.32659061654192545| | 1.5053877697929803| | -0.640142797263989| | 1.229530260294963| |-0.03776160295256...| | -0.5160734239126814| | -1.5165972740062887| | 1.3269085258245008| | 1.7604670124710626| | 1.2348130901905972| | 2.318660276655887| | 1.0936947030883175| | 1.0169768511417363| | -1.7744915698181583| +--------------------+ only showing top 20 rows.

