Collect Apache web server metrics with the Ops Agent
Learn how to collect and monitor metrics from an Apache web server installed on a Compute Engine virtual machine (VM) instance by using the Ops Agent:
- Create a Compute Engine VM instance and install the Ops Agent.
- Install an Apache web server.
- Configure the Ops Agent for the Apache web server.
- Generate traffic to the Apache web server.
- View metrics on the predefined Apache dashboard.
- Create an alerting policy.
- Test the alerting policy.
- Clean up.
To follow step-by-step guidance for this task directly in the Google Cloud console, click Guide me:
Before you begin
-
Security constraints defined by your organization might prevent you from completing the following steps. For troubleshooting information, see Develop applications in a constrained Google Cloud environment.
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the Compute Engine, Cloud Monitoring, and Cloud Logging APIs.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the Compute Engine, Cloud Monitoring, and Cloud Logging APIs.
Create a VM instance
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Compute Engine.
- Create a VM by clicking Create instance. Configure your instance by using the options in the navigation menu.
- In the Machine configuration option, do the following:
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive name.
- In the Machine type preset drop-down, select Shared-core > e2-small.
- Verify that the OS and storage option displays Debian GNU/Linux. If not, click the OS and storage option and click Change. In the Boot disk dialog, set Version to Debian GNU/Linux.
- In the Networking option, for Firewall, select both Allow HTTP traffic and Allow HTTPS traffic.
- Verify that the Observability option displays Install Ops Agent. If not, click the Observability option and select Install Ops Agent for Monitoring and Logging.
- Click Create.
Install an Apache web server
To install an Apache web server on your Compute Engine VM instance, do the following:
On the VM instances page, locate your new VM, go to the Connect column, and then click SSH.
Having trouble connecting? Refer to Troubleshooting SSH.
To update the package lists, copy the following command to your clipboard, paste the command into the SSH terminal, and then press enter:
sudo apt-get updateAfter you see the message "Reading package lists... Done", in the SSH terminal, run the following command to install an Apache2 web server:
sudo apt-get install apache2 php7.0When asked to continue the installation, enter
Y. If the install command fails, then usesudo apt-get install apache2 php.When your command prompt returns, go to the VM instances page and copy the VM's external IP address into the following URL:
http://EXTERNAL_IPTo connect to your Apache web server, open a new browser tab, and then enter the URL from the previous step.
When the web server is successfully installed, the browser tab displays the Apache2 Debian default page.
Collect Apache web server logs and metrics
In these steps, you configure the Ops Agent to collect logs and metrics from your Apache web server:Go to the SSH terminal for your VM instance. If you don't have a terminal open, then do the following:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Compute Engine.
- Locate your new VM and then click SSH.
-
Copy the following command, then paste it into the terminal for your instance, and then press enter:
The previous command creates the configuration to collect and ingest logs and metrics from the Apache web server. For more information, see Configure the Ops Agent for Apache web server.
- Restart the Ops Agent:
- To restart the agent, run the following command on your instance:
sudo systemctl restart google-cloud-ops-agent
- To confirm that the agent restarted, run the following command and
verify that the components "Metrics Agent" and "Logging Agent" started:
sudo systemctl status "google-cloud-ops-agent*"
- To restart the agent, run the following command on your instance:
Generate traffic
To generate traffic to your Apache web server, do the following:
Go to the SSH terminal for your VM instance. If you don't have a terminal open, then do the following:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Compute Engine.
- Locate your new VM and then click SSH.
-
In the SSH terminal, run the following command, which generates requests to your Apache web server:
timeout 120 bash -c -- 'while true; do curl localhost; sleep $((RANDOM % 4)) ; done'- Wait two minutes for the command prompt to return or for the terminal to close. While the command is running, HTML text is shown in the terminal.
View Apache metrics
To view the Apache Overview dashboard, which is automatically created, do the following:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the
 Dashboards page:
Dashboards page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Monitoring.
In the My Dashboards pane, select the Apache Overview dashboard from the list.
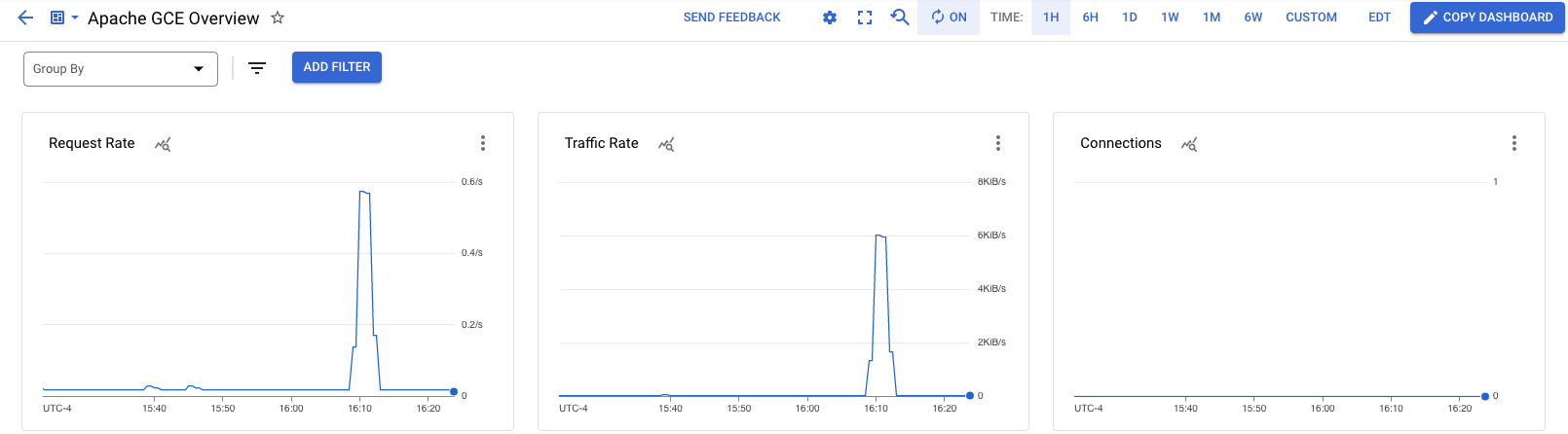
You've configured the Ops Agent to collect logs and metrics from your Apache web server, and you've viewed the metrics. The next step is to create an alerting policy so that you're notified when load on your Apache web server exceeds a threshold.
Create an email notification channel
Before you create an alerting policy, configure the notification channels that you want the alerting policy to use. Cloud Monitoring supports many different types of notification channels, including email, Slack, PagerDuty, and Pub/Sub. For more information, see Create and manage notification channels. To get notifications by e-mail, do the following:-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the notifications Alerting page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Monitoring.
- In the toolbar, click Edit Notification Channels.
- On the Notification channels page, scroll to
Email , and then click Add new. - Enter your email address, a display name such as
My email, and then click Save.
Create an alerting policy
In this section, you create an alerting policy so that you are notified when the traffic to your Apache web server exceeds a defined threshold:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the notifications Alerting page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Monitoring.
- Click Create policy.
Select the time series to be monitored:
- Click Select a metric and select VM instance.
- In the Active metric categories list, select Apache.
- In the Active metrics list, select workload/apache.traffic.
- Click Apply.
The chart for Apache traffic is shown.
Advance to the Configure trigger fields, and then set the Threshold value field to
1500.The chart displays the threshold as a dashed line. Ensure that the dashed line is much less than the peak traffic level.
Advance to the Notifications and name fields, and then use the Notification channels menu to select your email address.
For the policy name, enter
Apache traffic above threshold.Advance to the Review alert fields, review the alerting policy, and then click Create policy.
Test the alerting policy
To test the alerting policy, generate traffic that exceeds the threshold:
Go to the SSH terminal for your VM instance. If you don't have a terminal open, then do the following:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Compute Engine.
- Locate your new VM and then click SSH.
-
In the SSH terminal, run the following command, which generates requests to your Apache web server:
timeout 120 bash -c -- 'while true; do curl localhost; sleep $((RANDOM % 4)) ; done'- Wait two minutes for the command prompt to return or for the terminal to close. While the command is running, HTML text is shown in the terminal.
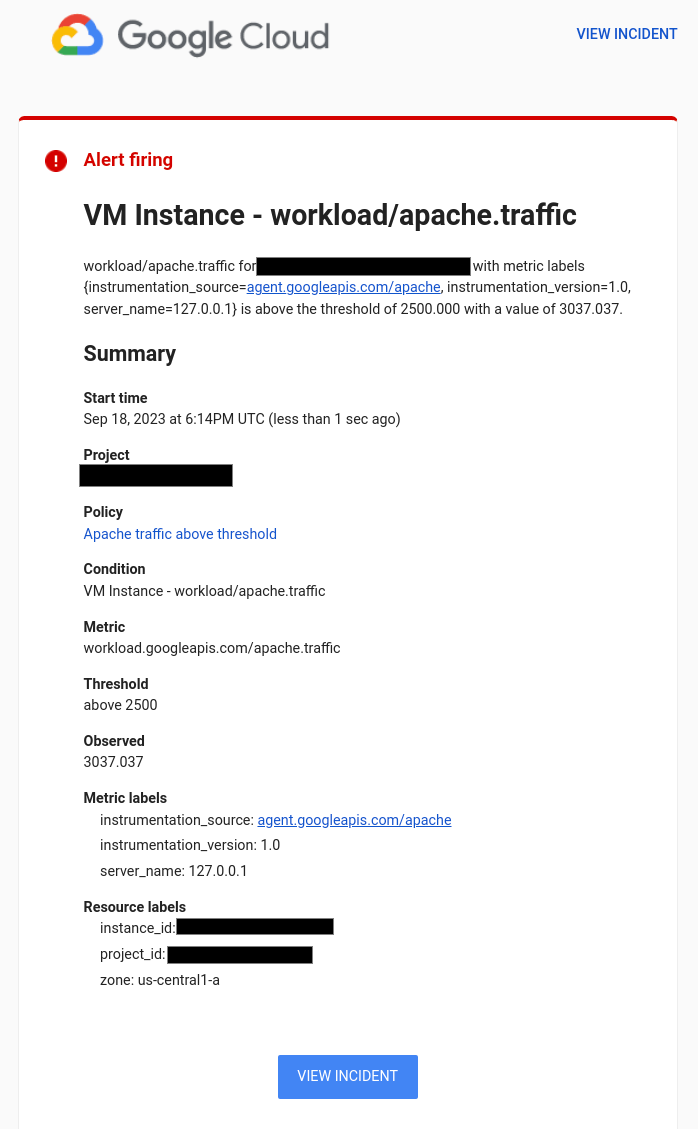
When the command prompt returns, check your email for a message whose subject line begins with
[ALERT].If you don't see an email, then examine the chart on the alerting policy to verify that the traffic level exceeded the threshold. You might need to run the previous command again. Otherwise, wait a minute or two for the email to arrive.
The notification provides a summary of the alerting policy and a link to an incident. Each incident contains a record of the failure, and these are typically helpful when troubleshooting.
You've configured the Ops Agent to collect logs and metrics from your Apache web server, but you've only viewed metrics. For information about how to view Apache web server logs, see the quickstart View Apache web server logs.
Clean up
To avoid incurring charges to your Google Cloud account for the resources used on this page, follow these steps.
If you created a new project and you no longer need the project, then delete the project.
If you used an existing project, then do the following:
If you created a VM, then delete it:
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the VM instances page.
- Select the checkbox for the instance that you want to delete.
- To delete the instance, click More actions, click Delete, and then follow the instructions.
Delete the alerting policy that you created:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the notifications Alerting page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading is Monitoring.
- Select the alerting policy that you created, and then click
Delete .
-
What's next
To learn about the Ops Agent and supported integrations, see:
To learn how to test whether a URL is responding to requests and to simulate a failure, see the quickstart Get notified if your application stops responding.
To view logs from your Apache web server, see the quickstart Cloud Logging for Compute Engine VMs.
To learn about charting and viewing performance data, see Dashboards overview.
For a list of metrics supported by Google Cloud, see Metrics list.
To create your own Monitoring metrics, see Custom metrics.
