The ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT function
This document describes the ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT function, which you can use
to compute the data drift between two sets of serving data. This
function computes and compares the statistics for the two data sets, and then
identifies where there are anomalous differences between the two
data sets.
For example, you might want to compare the current serving
data to historical serving data from a
table snapshot, or to the features
served at a particular point in time, which you can get by using the
ML.FEATURES_AT_TIME function.
You can optionally visualize the function output by using Vertex AI model monitoring. For more information, see Monitoring visualization.
Syntax
ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT( { TABLE `PROJECT_ID.DATASET.BASE_TABLE_NAME` | (BASE_QUERY_STATEMENT) }, { TABLE `PROJECT_ID.DATASET.STUDY_TABLE_NAME` | (STUDY_QUERY_STATEMENT) }, STRUCT( [NUM_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS AS num_histogram_buckets] [, NUM_QUANTILES_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS AS num_quantiles_histogram_buckets] [, NUM_VALUES_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS AS num_values_histogram_buckets,] [, NUM_RANK_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS AS num_rank_histogram_buckets] [, CATEGORICAL_DEFAULT_THRESHOLD AS categorical_default_threshold] [, CATEGORICAL_METRIC_TYPE AS categorical_metric_type] [, NUMERICAL_DEFAULT_THRESHOLD AS numerical_default_threshold] [, NUMERICAL_METRIC_TYPE AS numerical_metric_type] [, THRESHOLDS AS thresholds]) [, MODEL `PROJECT_ID.DATASET.MODEL_NAME`] )
Arguments
ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT takes the following arguments:
PROJECT_ID: the BigQuery project that contains the resource.DATASET: the BigQuery dataset that contains the resource.BASE_TABLE_NAME: the name of the input table of serving data that you want to use as the baseline for comparison.BASE_QUERY_STATEMENT: a query that generates the serving data that you want to use as the baseline for comparison. For the supported SQL syntax of theBASE_QUERY_STATEMENTclause, see GoogleSQL query syntax.STUDY_TABLE_NAME: the name of the input table that contains the serving data that you want to compare to the baseline.STUDY_QUERY_STATEMENT: a query that generates the serving data that you want to compare to the baseline. For the supported SQL syntax of theSTUDY_QUERY_STATEMENTclause, see GoogleSQL query syntax.NUM_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS: anINT64value that specifies the number of buckets to use for a histogram with equal-width buckets. Only applies to numerical,ARRAY<numerical>, andARRAY<STRUCT<INT64, numerical>>columns. TheNUM_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETSvalue must be in the range[1, 1,000]. The default value is10.NUM_QUANTILES_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS: anINT64value that specifies the number of buckets to use for a quantiles histogram. Only applies to numerical,ARRAY<numerical>, andARRAY<STRUCT<INT64, numerical>>columns. TheNUM_QUANTILES_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETSvalue must be in the range[1, 1,000]. The default value is10.NUM_VALUES_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS: anINT64value that specifies the number of buckets to use for a quantiles histogram. Only applies toARRAYcolumns. TheNUM_VALUES_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETSvalue must be in the range[1, 1,000]. The default value is10.NUM_RANK_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETS: anINT64value that specifies the number of buckets to use for a rank histogram. Only applies to categorical andARRAY<categorical>columns. TheNUM_RANK_HISTOGRAM_BUCKETSvalue must be in the range[1, 10,000]. The default value is50.CATEGORICAL_DEFAULT_THRESHOLD: aFLOAT64value that specifies the custom threshold to use for anomaly detection for categorical andARRAY<categorical>features. The value must be in the range[0, 1). The default value is0.3.CATEGORICAL_METRIC_TYPE: aSTRINGvalue that specifies the metric used to compare statistics for categorical andARRAY<categorical>features. Valid values are as follows:L_INFTY: use L-infinity distance. This value is the default.JENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCE: use Jensen–Shannon divergence.
NUMERICAL_DEFAULT_THRESHOLD: aFLOAT64value that specifies the custom threshold to use for anomaly detection for numerical features. The value must be in the range[0, 1). The default value is0.3.NUMERICAL_METRIC_TYPE: aSTRINGvalue that specifies the metric used to compare statistics for numerical,ARRAY<numerical>, andARRAY<STRUCT<INT64, numerical>>features. The only valid value isJENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCE.THRESHOLDS: anARRAY<STRUCT<STRING, FLOAT64>>value that specifies the anomaly detection thresholds for one or more columns for which you don't want to use the default threshold. TheSTRINGvalue in the struct specifies the column name, and theFLOAT64value specifies the threshold. TheFLOAT64value must be in the range[0,1). For example,[('col_a', 0.1), ('col_b', 0.8)].MODEL: The name of a BigQuery ML model that is registered with Vertex AI. When you specify this argument, theML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFToutput includes thevisualization_linkcolumn. Thevisualization_linkcolumn provides URLs that link to visualizations of the function results in Vertex AI model monitoring.
Output
ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT returns one row for each column in the input data.
ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT output contains the following columns:
input: aSTRINGcolumn that contains the input column name.metric: aSTRINGcolumn that contains the metric used to compare theinputcolumn statistical value between the two data sets. This column value isJENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCEfor numerical features, and eitherL_INFTYorJENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCEfor categorical features.threshold: aFLOAT64column that contains the threshold used to determine whether the statistical difference in theinputcolumn value between the two data sets is anomalous.value: aFLOAT64column that contains the statistical difference in theinputcolumn value between the two data sets.is_anomaly: aBOOLcolumn that indicates whether thevaluevalue is higher than thethresholdvalue.visualization_link: a URL that links to a Vertex AI visualization of the results for the given feature. The URL is formatted as follows:https://console.cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/model-monitoring/locations/region/model-monitors/vertex_model_monitor_id/model-monitoring-jobs/vertex_model_monitoring_job_id/feature-drift?project=project_id&featureName=feature_name
For example:
https://console.cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/model-monitoring/locations/europe-west4/model-monitors/bq123456789012345647/model-monitoring-jobs/bqjob890123456789012/feature-drift?project=myproject&featureName=units_producedThis column is only returned when you provide a value for the
MODELargument.For more information, see Monitoring visualization.
Examples
The following examples show how to use the ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT function.
Compute data drift
The following example computes data drift between a snapshot of the
serving data table and the current serving data table,
with a categorical feature threshold of 0.2:
SELECT * FROM ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT( TABLE `myproject.mydataset.previous_serving_data`, TABLE `myproject.mydataset.serving`, STRUCT(0.2 AS categorical_default_threshold) );
The output looks similar to the following:
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+
| input | metric | threshold | value | is_anomaly |
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+
| dropoff_latitude | JENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCE| 0.2 | 0.7 | true |
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+
| payment_type | L_INTFY | 0.3 | 0.2 | false |
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+
Compute data drift and visualize
The following example computes data drift between a snapshot of the
serving data table and the current serving data table,
with a categorical feature threshold of 0.2:
SELECT * FROM ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT( TABLE `myproject.mydataset.previous_serving_data`, TABLE `myproject.mydataset.serving`, STRUCT(0.2 AS categorical_default_threshold), MODEL `myproject.mydataset.registered_model` );
The output looks similar to the following:
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------+
| input | metric | threshold | value | is_anomaly | visualization_link |
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------+
| dropoff_latitude | JENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCE| 0.2 | 0.7 | true | https://console.cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/ |
| | | | | | model-monitoring/locations/us-central1/model-monitors/ |
| | | | | | bq1111222233334444555/model-monitoring-jobs/ |
| | | | | | bqjob1234512345123451234/feature-drift?project= |
| | | | | | myproject&featureName=dropoff_latitude |
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------+
| payment_type | L_INTFY | 0.3 | 0.2 | false | https://console.cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/ |
| | | | | | model-monitoring/locations/us-central1/model-monitors/ |
| | | | | | bq1111222233334444555/model-monitoring-jobs/ |
| | | | | | bqjob1234512345123451234/feature-drift?project= |
| | | | | | myproject&featureName=payment_type |
+------------------+--------------------------+-----------+--------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------+
Copying and pasting the visualization link into a browser tab returns results similar to the following for numerical features:
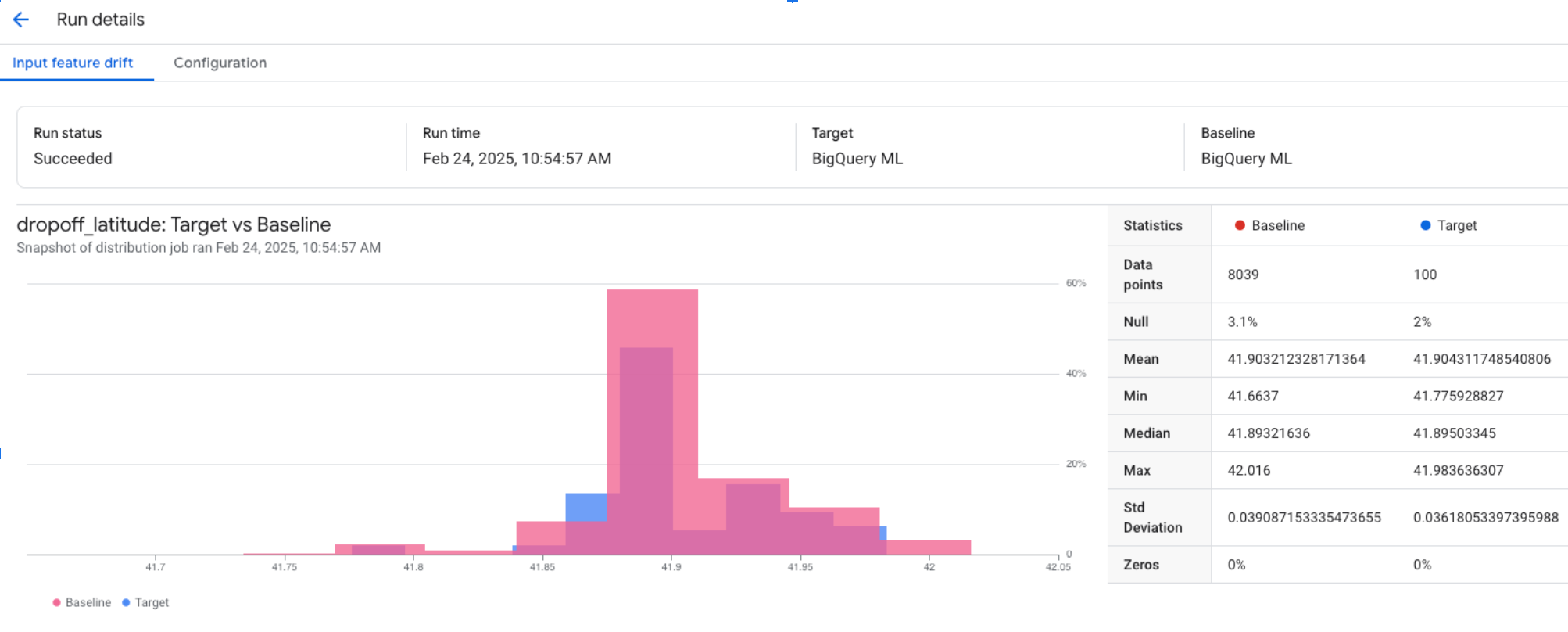
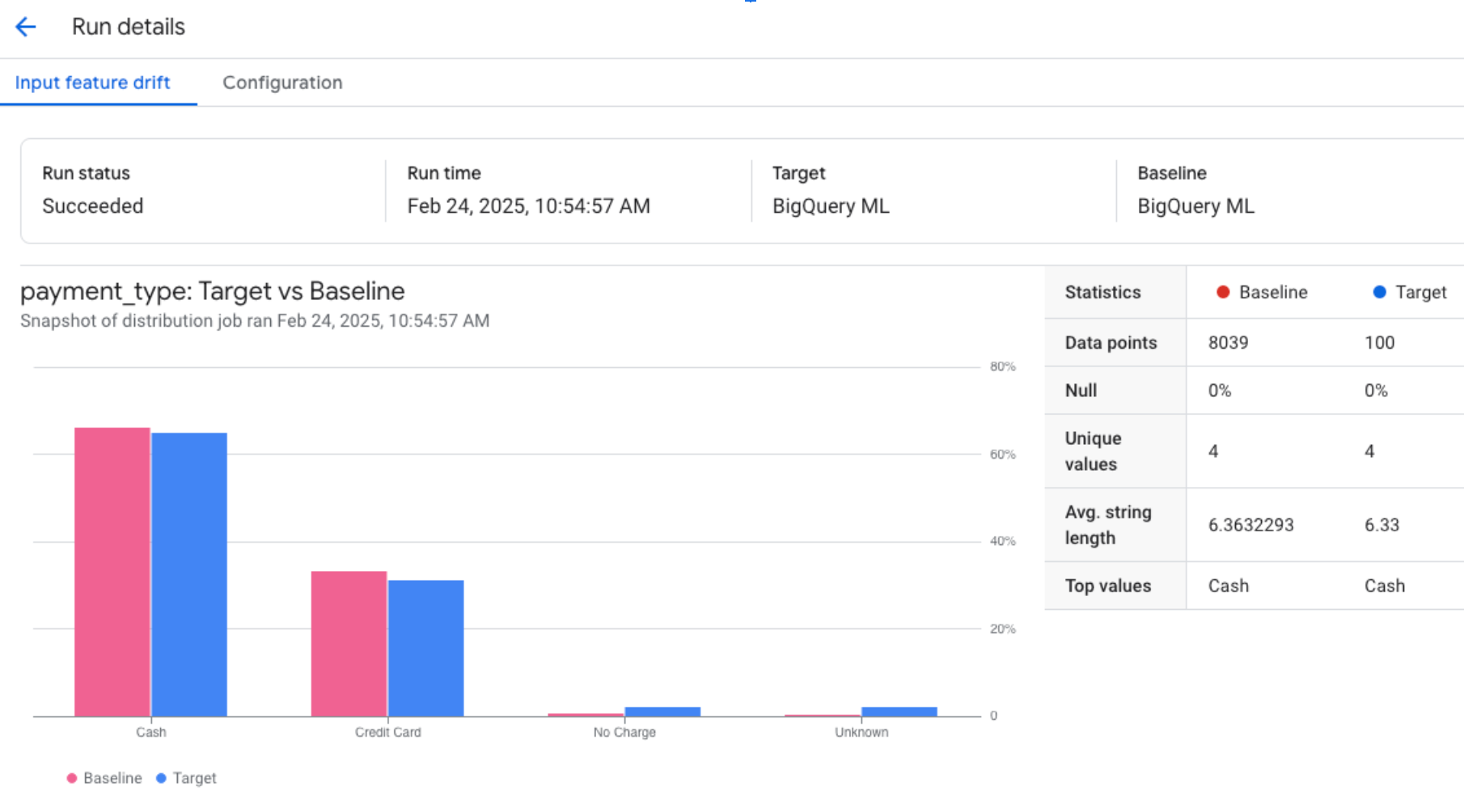
Copying and pasting the visualization link into a browser tab returns results similar to the following for categorical features:
Limitations
Running the
ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFTfunction on a large amount of input data can cause the query to return the errorDry run query timed out. To resolve the error, disable retrieval of cached results for the query.ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFTdoesn't conduct schema validation between the two sets of input data, and so handles data type mismatches as follows:- If you specify
JENSEN_SHANNON_DIVERGENCEfor thecategorical_default_thresholdornumerical_default_thresholdargument, the feature isn't included in the final anomaly report. - If you specify
L_INFTYfor thecategorical_default_thresholdargument, the function outputs the computed feature distance as expected.
- If you specify
However, when you run inference on the serving data, the
ML.PREDICT function
handles schema validation.
Pricing
The ML.VALIDATE_DATA_DRIFT function uses
BigQuery on-demand compute pricing.
What's next
- For more information about model monitoring in BigQuery ML, see Model monitoring overview.
- For more information about supported SQL statements and functions for ML models, see End-to-end user journeys for ML models.
