Domain restricted sharing lets you limit resource sharing based on a domain or organization resource. When domain restricted sharing is active, only principals that belong to allowed domains or organizations can be granted IAM roles in your Google Cloud organization.
There are three types of organization policies that you can use to restrict identities by domain:
- The
iam.managed.allowedPolicyMembersmanaged constraint - Custom organization policies referencing the
iam.googleapis.com/AllowPolicyresource - The
iam.allowedPolicyMemberDomainslegacy managed constraint
Before you begin
Choose which method you will use to implement domain restricted sharing. To learn more about the benefits and drawbacks of each method, see Methods for restricting sharing by domain.
Required roles
To get the permissions that
you need to enforce domain restricted sharing,
ask your administrator to grant you the
Organization policy administrator (roles/orgpolicy.policyAdmin)
IAM role on the organization.
For more information about granting roles, see Manage access to projects, folders, and organizations.
You might also be able to get the required permissions through custom roles or other predefined roles.
Use the iam.managed.allowedPolicyMembers constraint to implement domain restricted sharing
Console
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Organization policies page.
From the project picker, select the project, folder, or organization for which you want to edit the organization policy. The Organization policies page that appears displays a filterable list of organization policy constraints that are available for this resource.
From the list, select the Restrict allowed policy members in IAM allow policies managed constraint.
On the Policy details page, click Manage policy.
On the Edit policy page, select Override parent's policy.
Select Add a rule and then update the organization policy rule.
Under Enforcement, select On.
Optionally, to make the organization policy conditional on a tag, click Add condition. If you add a conditional rule to an organization policy, you must add at least one unconditional rule or the policy cannot be saved. For more details, see Setting an organization policy with tags.
In the Parameters section, configure the members and principal sets that you want to grant roles to in your organization, and then click Save.
Optionally, to preview the effect of your organization policy change before it is enforced, click Test changes. For more information about testing organization policy changes, see Test organization policy changes with Policy Simulator.
To enforce the organization policy in dry-run mode, click Set dry run policy. For more information, see Create an organization policy in dry-run mode.
After you verify that the organization policy in dry-run mode works as intended, set the live policy by clicking Set policy.
gcloud
Create a YAML file to define the organization policy:
name: organizations/ORG_ID/policies/iam.managed.allowedPolicyMembers spec: rules: - enforce: true parameters: allowedMemberSubjects: - ALLOWED_MEMBER_1 - ALLOWED_MEMBER_2 allowedPrincipalSets: - ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_1 - ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_2Replace the following:
ORG_ID: the numeric ID of your Google Cloud organization.ALLOWED_MEMBER_1,ALLOWED_MEMBER_2: The members that you want to grant roles to in your organization—for example,user:example-user@example.com.ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_1,ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_2: The principal sets that you want to grant roles to in your organization. For example,//cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/organizations/0123456789012.
Optionally, to make the organization policy conditional on a tag, add a
conditionblock to therules. If you add a conditional rule to an organization policy, you must add at least one unconditional rule or the policy cannot be saved. For more details, see Setting an organization policy with tags.Set the policy with the
org-policies set-policycommand and thespecflag:gcloud org-policies set-policy POLICY_PATH \ --update-mask=specReplace
POLICY_PATHwith the full path to your organization policy YAML file.
To learn how to test the policy in dry-run mode before applying it, see Create an organization policy in dry-run mode.
To learn how to simulate the policy before you enforce it, see Test organization policy changes with Policy Simulator.
REST
To set the organization policy, use the
organizations.policies.create
method.
POST https://orgpolicy.googleapis.com/v2/{parent=organizations/ORGANIZATION_ID}/policies
The request JSON body contains the definition of an organization policy.
If this constraint doesn't support parameters, omit the parameters block
under rules.
{
"name": "organizations/ORG_ID/policies/CONSTRAINT_NAME",
"spec": {
"rules": [
{
"enforce": true,
"parameters": {
"allowedMemberSubjects": [
"ALLOWED_MEMBER_1",
"ALLOWED_MEMBER_2"
],
"allowedPrincipalSets": [
"ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_1",
"ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_2"
]
}
}
]
}
}
Replace the following:
ORG_ID: the numeric ID of your Google Cloud organization.CONSTRAINT_NAME: the name of the constraint that you want to set.ALLOWED_MEMBER_1,ALLOWED_MEMBER_2: The members that you want to grant roles to in your organization—for example,user:example-user@example.com.ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_1,ALLOWED_PRINCIPAL_SET_2: The principal sets that you want to grant roles to in your organization. For example,//cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/organizations/0123456789012.
Optionally, to make the organization policy conditional on a tag, add a
condition block to the rules. If you add a conditional rule to an
organization policy, you must add at least one unconditional rule or the
policy cannot be saved. For more details, see
Setting an organization policy with tags.
To learn how to test the policy in dry-run mode before applying it, see Create an organization policy in dry-run mode.
To learn how to simulate the policy before you enforce it, see Test organization policy changes with Policy Simulator.
Use custom organization policies to implement domain restricted sharing
Create a custom constraint that restricts which principals can be granted roles in your organization:
Use the
memberInPrincipalSetCEL function with your organization principal set to restrict role grants to members in your organization. To learn how to find your organization ID, see Retrieving an organization principal set.For example, the following constraint restricts role grants to members in your organization:
name: organizations/ORG_ID/customConstraints/custom.allowInternalIdentitiesOnly resourceTypes: iam.googleapis.com/AllowPolicy methodTypes: - CREATE - UPDATE condition: "resource.bindings.all( binding, binding.members.all(member, MemberInPrincipalSet(member, ['//cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/organizations/ORG_ID']) ) )" actionType: ALLOW displayName: Only allow organization members to be granted rolesOptionally, refine the constraint by adding additional CEL functions, joined with logical operators (
&&,||, or!). You can add any of the following functions:For example, the following constraint restricts role grants to members in your organization and to
admin@example.com:name: organizations/ORG_ID/customConstraints/custom.allowInternalIdentitiesOnly resourceTypes: iam.googleapis.com/AllowPolicy methodTypes: - CREATE - UPDATE condition: "resource.bindings.all( binding, binding.members.all(member, ( MemberInPrincipalSet(member, ['//cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/organizations/ORG_ID']) || MemberSubjectMatches(member, ['user:admin@example.com']) ) ) )" actionType: ALLOW displayName: Only allow organization members and service agents to be granted roles
Set up the custom constraint:
After you have created the YAML file for a new custom constraint, you must set it up to make it available for organization policies in your organization. To set up a custom constraint, use thegcloud org-policies set-custom-constraintcommand:gcloud org-policies set-custom-constraint CONSTRAINT_PATH
CONSTRAINT_PATHwith the full path to your custom constraint file. For example,/home/user/customconstraint.yaml. Once completed, your custom constraints are available as organization policies in your list of Google Cloud organization policies. To verify that the custom constraint exists, use thegcloud org-policies list-custom-constraintscommand:gcloud org-policies list-custom-constraints --organization=ORGANIZATION_ID
ORGANIZATION_IDwith the ID of your organization resource. For more information, see Viewing organization policies.Enforce the custom organization policy:
You can enforce a constraint by creating an organization policy that references it, and then applying that organization policy to a Google Cloud resource.Console
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the Organization policies page.
- From the project picker, select the project for which you want to set the organization policy.
- From the list on the Organization policies page, select your constraint to view the Policy details page for that constraint.
- To configure the organization policy for this resource, click Manage policy.
- On the Edit policy page, select Override parent's policy.
- Click Add a rule.
- In the Enforcement section, select whether enforcement of this organization policy is on or off.
- Optional: To make the organization policy conditional on a tag, click Add condition. Note that if you add a conditional rule to an organization policy, you must add at least one unconditional rule or the policy cannot be saved. For more information, see Setting an organization policy with tags.
- Click Test changes to simulate the effect of the organization policy. Policy simulation isn't available for legacy managed constraints. For more information, see Test organization policy changes with Policy Simulator.
- To finish and apply the organization policy, click Set policy. The policy requires up to 15 minutes to take effect.
gcloud
To create an organization policy with boolean rules, create a policy YAML file that references the constraint:
name: projects/PROJECT_ID/policies/CONSTRAINT_NAME spec: rules: - enforce: true
Replace the following:
-
PROJECT_ID: the project on which you want to enforce your constraint. -
CONSTRAINT_NAME: the name of the constraint you want to enforce. For example,compute.disableAllIpv6.
To enforce the organization policy containing the constraint, run the following command:
gcloud org-policies set-policy POLICY_PATH
Replace
POLICY_PATHwith the full path to your organization policy YAML file. The policy requires up to 15 minutes to take effect.
Use the iam.allowedPolicyMemberDomains constraint to implement domain restricted sharing
The domain restriction constraint is a legacy managed constraint with the
list constraint_type.
You can specify an organization principal set or a Google Workspace customer
ID in the allowed_values list of a domain restriction constraint. For more
information, see
Organization principal set versus Google Workspace customer ID.
Your organization principal set and Google Workspace ID are not automatically allowed. To allow principals in your organization to access resources in your organization, either your organization principal set or Google Workspace ID must be included as an allowed principal set.
The domain restriction constraint doesn't support denying values, and an
organization policy can't be saved with IDs in the denied_values list.
You can make an organization policy enforcing the domain restriction constraint conditional on any resource included in the list of supported resources. For example, Cloud Storage buckets, BigQuery datasets, or Compute Engine VMs.
Console
To set an organization policy including a domain restriction constraint, do the following:
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Organization policies page.
From the project picker, select the organization resource on which you want to set the organization policy.
On the Organization policies page, select Domain Restricted Sharing from the list of constraints.
On the Policy details page, click Manage policy.
Under Applies to, select Override parent's policy.
Click Add a rule.
Under Policy values, select custom.
Under Policy type, select Allow.
Under Custom values, enter an organization principal set or Google Workspace customer ID into the field.
If you want to add multiple IDs, click New policy value to create an additional field.
Click Done.
Optionally, to make the domain restriction constraint conditional on a tag, click Add condition.
In the Title field, enter a name for the condition.
In the Description field, give your condition a description. The description provides context on the tags that are required and how they impact resources.
You can use the Condition builder to create a condition that requires a particular tag for the constraint to take effect.
In the Condition type menu in the Condition builder tab, select Tag.
Select the Operator for your condition. To match an entire tag, use the matches operator. To match a tag key and a tag value, use the matches ID operator.
If you selected the matches operator, enter the value namespaced name of the tag. If you selected the matches ID operator, enter the key and value IDs.
You can create multiple conditions by clicking Add. If you add another condition, you can set the conditional logic to require all of them by toggling And. You can set the conditional logic to require only one of the conditions to be true by toggling Or.
You can delete an expression by clicking the large X to the right of the condition fields.
When you have finished editing your conditions, click Save.
To enforce the policy, click Set policy.
gcloud
Policies can be set through the Google Cloud CLI. To create a policy that includes the domain restriction constraint, run the following command:
To set an organization policy that includes the domain restriction constraint, run the following command:
gcloud org-policies set-policy POLICY_PATH
Where POLICY_PATH is the full path to your
organization policy YAML file, which should look like the following:
name: organizations/ORGANIZATION_ID/policies/iam.allowedPolicyMemberDomains
spec:
rules:
- condition: # This condition applies to the values block.
expression: "resource.matchTag('ORGANIZATION_ID/environment', 'dev')"
values:
allowedValues:
- PRINCIPAL_SET
- values:
allowedValues:
- PRINCIPAL_SET
Replace the following:
- ORGANIZATION_ID with the ID of the organization resource on which to set this policy.
- PRINCIPAL_SET for the principal identifiers you want to allow.
You can include either
organization principal sets or
Google Workspace customer IDs. For example,
is:principalSet://cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/organizations/01234567890123oris:C03g5e3bc
Only identities specified in the list of allowed_values will be permitted in
allow policies after this organization policy is enforced. To be allowed,
principals must be in the specified organization principal set or part of a
specified Google Workspace domain.
For example, if you created an organization policy that allowed only the customer ID of your company's Google Workspace domain, then only principals associated with that domain could be added to the allow policy from that point forward.
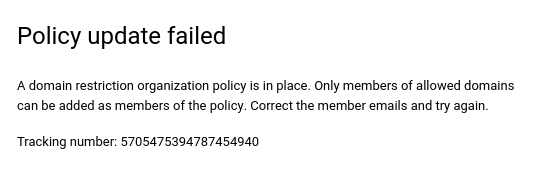
Example error message
When the iam.allowedPolicyMemberDomains legacy managed constraint is
violated by trying to add a principal that is not included in the
allowed_values list, the operation will fail and then an error message will be
displayed.
Console
gcloud
ERROR: (gcloud.projects.set-iam-policy) FAILED_PRECONDITION: One or more users named in the policy do not belong to a permitted customer.
Retrieving an organization principal set
You can get your organization resource ID using the Google Cloud console, the gcloud CLI, or the Cloud Resource Manager API.
console
To get your organization resource ID using the Google Cloud console, do the following:
- Go to the Google Cloud console:
- From the project picker at the top of the page, select your organization resource.
- On the right side, click More, and then click Settings.

The Settings page displays your organization resource ID.
gcloud
To find your organization resource ID, run the following command:
gcloud organizations list
This command lists all the organization resources to which you belong to, and their corresponding organization resource IDs.
API
To find your organization resource ID using the Cloud Resource Manager API, use the
organizations.search()
method, including a query for your domain. For example:
GET https://cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/v3/organizations:search{query=domain:altostrat.com}
The response contains the metadata of the organization resource that
belongs to altostrat.com, which includes the organization resource ID.
After you have your organization resource ID, you need to use the correct identifier for the set of principals belonging to it. For example:
principalSet://iam.googleapis.com/organizations/01234567890123
Entering the organization principal set allows the following principals to be granted roles in your organization:
- All workforce identity pools in your organization
- All service accounts and workload identity pools in any project in the organization
- All service agents associated with resources in your organization.
For more information about IAM principal identifiers, see Principal identifiers.
Retrieving a Google Workspace customer ID
Entering the Google Workspace customer ID allows the following principals to be granted roles in your organization:
- All identities in all domains associated with your Google Workspace customer ID
- All workforce identity pools in your organization
- All service accounts and workload identity pools in any project in the organization
- All service agents associated with resources in your organization.
The Google Workspace customer ID used by the domain restriction constraint can be obtained in two ways:
gcloud
The gcloud organizations list
command can be used to see all organizations that you have the
resourcemanager.organizations.get permission for:
gcloud organizations list
This command will return the DISPLAY_NAME, ID (Organization ID), and
DIRECTORY_CUSTOMER_ID. The Google Workspace customer ID is the
DIRECTORY_CUSTOMER_ID.
API
The Google Workspace Directory API can be used to retrieve a Google Workspace customer ID.
While logged in as a Google Workspace admin, you can visit the Customers: get API method documentation and click Execute. After authorization, the response would show your customer ID.
Alternatively, you can use an API client:
- Obtain an OAuth access token for the
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.customer.readonlyscope. Run the following command to query the Google Workspace directory API:
curl -# -X GET "https://www.googleapis.com/admin/directory/v1/customers/customerKey" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" -H "Content-Type: application/json"
This command will return a JSON response including the customer's
information. The Google Workspace customer ID is the id.
Configure exceptions for domain restricted sharing
Some Google Cloud services use service accounts, service agents, and other accounts to perform actions on your behalf. Domain restricted sharing can prevent these accounts from being automatically granted the IAM roles that they need, which can cause certain actions to fail.
The following table lists actions in Google Cloud that could be impacted by domain restricted sharing. It also lists the accounts that need to be granted roles automatically for these actions to succeed.
If you use custom organization policies or the
iam.managed.allowedPolicyMembers managed constraint to implement domain
restricted sharing, then consider adding these accounts as exceptions to your
domain restricted sharing constraint. To add an account as an exception, add
the principal identifier for the account to the list of allowed members.
If you use the iam.allowedPolicyMemberDomains legacy managed constraint to
implement domain restricted sharing, then you might need to force account
access for these accounts to perform the listed actions.
| Action | Principal identifier |
|---|---|
| Enable BigQuery log sink for a billing account | serviceAccount:bUNIQUE_ID@gcp-sa-logging.iam.gserviceaccount.com |
| Enable storage access logging | serviceAccount:cloud-storage-analytics@google.com |
| Use Pub/Sub as an endpoint for a Google Chat app | serviceAccount:chat-api-push@system.gserviceaccount.com |
| Use Pub/Sub to receive real-time developer notifications from Google Play | serviceAccount:google-play-developer-notifications@system.gserviceaccount.com |
| Use a signed URL with Cloud CDN | serviceAccount:service-PROJECT_NUMBER@cloud-cdn-fill.iam.gserviceaccount.com |
| Private origin authentication with Cloud CDN | serviceAccount:service-PROJECT_NUMBER@https-lb.iam.gserviceaccount.com |
Cloud Run public services
Cloud Run lets you make services public. However, if you implement domain restricted sharing, then users outside of your organization won't be able to access public Cloud Run services.
To allow users to access public Cloud Run services, you must disable the Cloud Run Invoker IAM check for Cloud Run services. For more information, see Disable the Cloud Run Invoker for services.
Share other data publicly
If you use custom organization policies to implement domain restricted sharing, then you can add an exception to your organization policy to allow public data sharing.
Sharing data publicly involves the special principals allUsers and
allAuthenticatedUsers. If you need to share data publicly while using domain
restricted sharing, then you need to add an exception for these principals.
Adding exceptions is only possible if you're using custom organization policies
to implement domain restricted sharing.
To add an exception for allUsers and allAuthenticatedUsers, create a
conditional custom organization policy based on
resource tags.
Create a tag key on your organization resource.
gcloud resource-manager tags keys create allUsersIngress \ --parent=organizations/ORGANIZATION_IDReplace
ORGANIZATION_IDwith your organization's ID.Create a tag value for the tag key that you created.
gcloud resource-manager tags values create True \ --parent=ORGANIZATION_ID/allUsersIngress \ --description="Allow allUsers to access internal Cloud Run services"Attach the tag to resources that you want to share publicly.
Create a custom constraint using the
memberSubjectMatchesCEL function in your constraint's condition expression.For example, the following condition expression restricts role grants to members in your organization,
allUsers, andallAuthenticatedUsers:name: organizations/ORGANIZATION_ID/customConstraints/custom.allowInternalAndSpecialIdentitiesOnly resourceTypes: iam.googleapis.com/AllowPolicy methodTypes: - CREATE - UPDATE condition: "resource.bindings.all( binding, binding.members.all(member, ( MemberInPrincipalSet(member, ['//cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com/organizations/ORG_ID']) || MemberSubjectMatches(member, ['allUsers', 'allAuthenticatedUsers']) ) ) )" actionType: ALLOW displayName: Only allow organization members, allusers, and allAuthenticatedUsers to be granted rolesCreate an organization policy that enforces the custom constraint.
name: organizations/ORGANIZATION_ID/policies/iam.allowedPolicyMemberDomains spec: rules: - allowAll: true condition: expression: resource.matchTag("ORGANIZATION_ID/allUsersIngress", "True") title: allowAllUsersIngressEnforce the organization policy.
gcloud org-policies set-policy POLICY_PATHReplace
POLICY_PATHwith the path and filename of your organization policy.
The conditional organization policy lets you grant permissions to the
allUsers identity on resources tagged with allUsersIngress: true.
Forcing account access
If you need to force account access for a project in violation of domain restrictions:
Remove the organization policy containing the domain restriction constraint.
Grant account access to the project.
Implement the organization policy with the domain restriction constraint again.
Alternatively, you can grant access to a Google group that contains the relevant service accounts:
Create a Google group within the allowed domain.
Use the Google Workspace administrator panel to turn off domain restriction for that group.
Add the service account to the group.
Grant access to the Google group in the allow policy.
