Create a metadata bucket
This guide describes how to create a metadata bucket. You can create a metadata bucket using the Configuration API or Manufacturing Data Engine (MDE) web interface.
Before you begin
Before you begin creating a bucket, read how to model metadata section in the MDE documentation.
Buckets naming
When you create a bucket, the name must be unique in a
MDE deployment. Bucket names must not
contain spaces or special characters such
as &, @, or %.
Create a metadata bucket
You can create a metadata bucket using either the terminal or the console interface.
REST
Execute the following REST API request:
POST /metadata/v1/buckets
{
"name": "BUCKET_NAME",
"type": "BUCKET_TYPE",
"schema": "BUCKET_SCHEMA",
"provider": "local",
"attributes": {
"instanceOverwriteMode": "INSTANCE_OVERWRITE_MODE"
}
}
Replace the following:
BUCKET_NAME: The name of the bucket to be created.BUCKET_TYPE: The type of the bucket to be created. Must be one ofTAG,RECORD, orLOOKUP. Thenatural_keyof a metadata instance in aTAGbucket must be a tag name. Thenatural_keyof a metadata instance in aRECORDbucket can be any key. Thenatural_keyof a metadata instance in aLOOKUPbucket can be any key, but records can't reference instances in a lookup bucket, and the instances are not written to any data sink. Lookup buckets only serve as source of reference data that can be retrieved by the parser using the Whistle functionlookupByKeyand used to enrich records.BUCKET_SCHEMA: The JSON schema of the bucket. The schema constrains the instances that may be created in the bucket.INSTANCE_OVERWRITE_MODE: EitherTRUEorFALSE. Determines whether new instances are created by merging the provided instance with the latest instance for a given natural key or if new instances are created as provided.
Console
To add new metadata bucket using the console click the METADATA section of the top menu of Cloud Management section. The Metadata configuration page lists the available Buckets in the MDE instance:
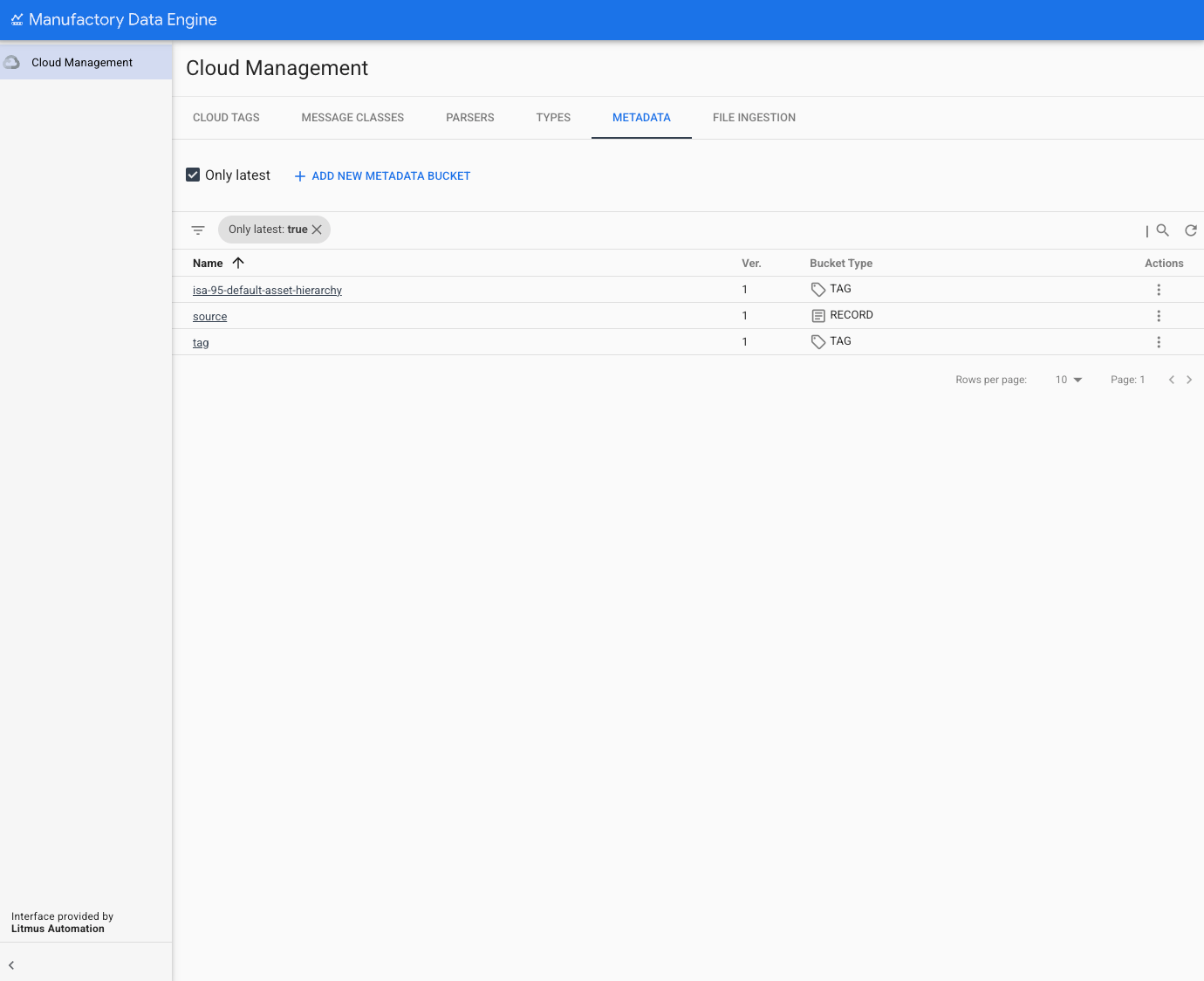
For each Bucket the following information is provided:
- Name: The name of the bucket. Each name needs to be unique.
- Version: The Version of the bucket. Only the latest available version is displayed by default. To display earlier versions un-check the 'Only Latest' check-box.
- Bucket type: It visualizes the type of bucket. Three different bucket
types are supported:
- Tag: Buckets that qualify a given tag. They are associated to a type and inherited by all tags of that given type. They can be instantiated at tag level as they intend to qualify the variable itself and not any of its specific records. An example of a tag Bucket could be the 'Asset hierarchy' or the 'Units of Measure' of the tag.
- Record: Record buckets qualify each of the Records of a given tag. They are also associated to a type and inherited by the tag but are instantiated at the Record level. Each Record is expected to have a different value among a limited set of Bucket Instances. An example of Record Bucket could be the 'Shift' or the 'Operator Name'.
- Reference: Buckets that define a set of key value pairs between a user-defined Key and an instance.
To create a new Bucket click Add new metadata bucket:
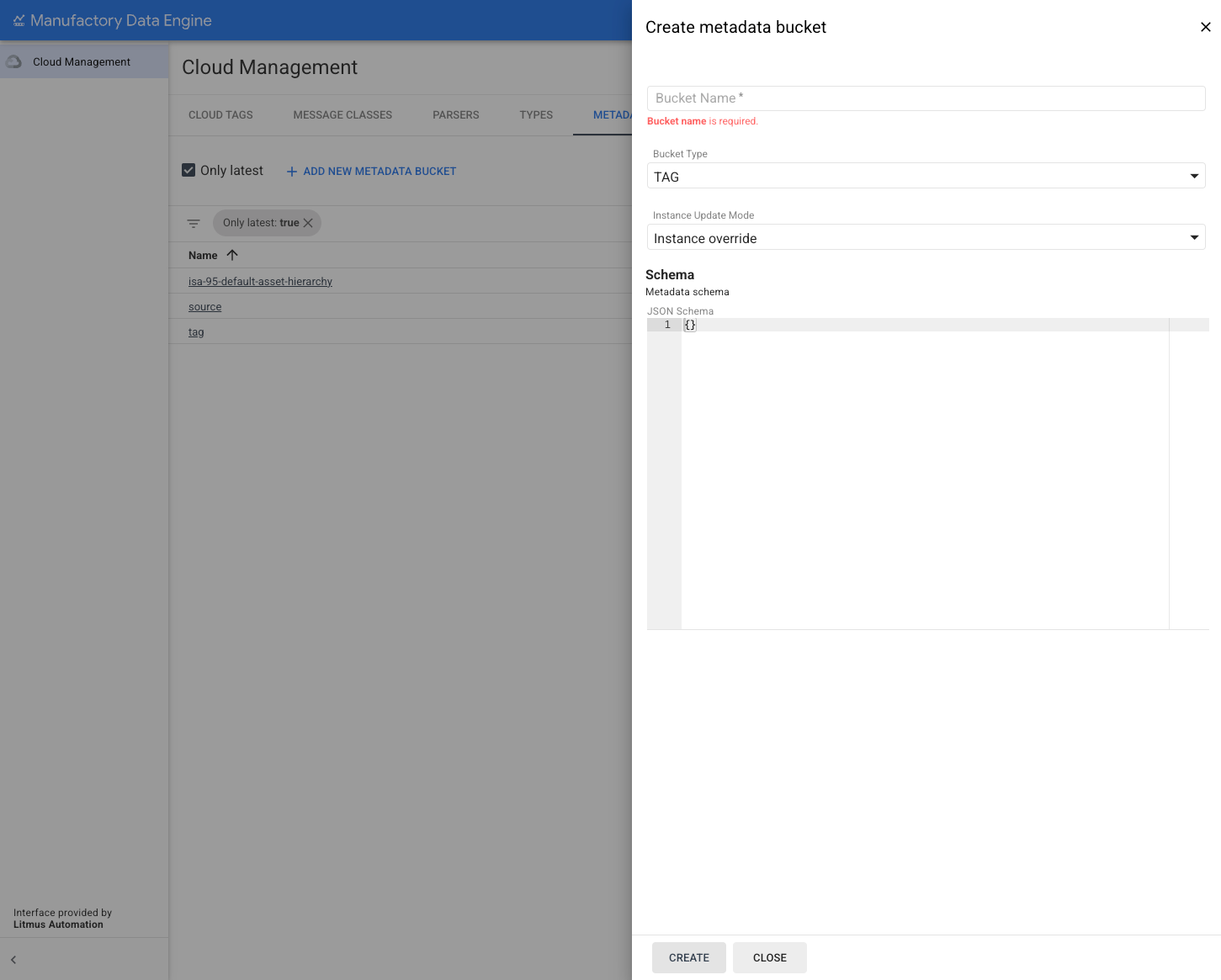
Fill out the form displayed from the side panel with the necessary Bucket parameters:
- Bucket Name: A unique, user defined name for the bucket.
- Bucket type: To define the Bucket class.
- Instance update mode: It specifies the type of instance updates
specified for the metadata bucket:
- Instance Override: The existing instance is replaced by the latest instance received from the edge, even if it's incomplete.
- Instance Merge: The existing instance is merged with the latest instance received from the edge. Only the attributed contained in the new edge instance are replaced.
- JSON Schema: The
JSON Schemadefining the structure of the bucket. Need to be a valid Schema. All metadata instances are validated against the bucket schema.
The following is a sample JSON Schema of a default metadata bucket
provided by the default configuration package:
{
"$id": "https://gmde.cloud/tag.schema.json",
"$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2019-09/schema",
"title": "Tag metadata bucket",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"datatype": {
"type": "string"
},
"description": {
"type": "string"
},
"registerId": {
"type": "string"
},
"edgeTagName": {
"type": "string"
},
"tagName": {
"description": "Tag name",
"type": "string"
},
"deviceID": {
"type": "string"
},
"deviceName": {
"type": "string"
},
"deviceMetadata": {
"type": "object"
}
},
"required": ["tagName"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
