When you use the Dataproc service to create clusters and run jobs on your clusters, the service sets up the necessary Dataproc roles and permissions in your project to access and use the Google Cloud resources it needs to accomplish these tasks. However, if you do cross-project work, for example to access data in another project, you will need to set up the necessary roles and permissions to access cross-project resources.
To help you do cross-project work successfully, this document lists the different principals that use the Dataproc service and the roles that contain the necessary permissions for those principals to access and use Google Cloud resources.
There are three principals (identities) that access and use the Dataproc:
- User Identity
- Control Plane Identity
Data Plane Identity
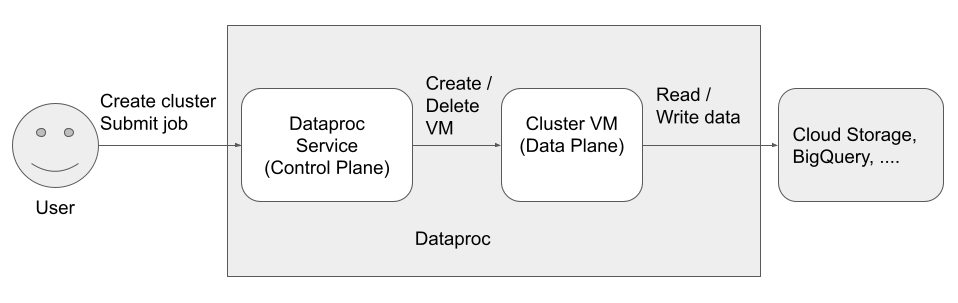
Dataproc API User (User identity)
Example: username@example.com
This is the user that calls the Dataproc service to create clusters, submit jobs, and make other requests to the service. The user is usually an individual, but it can also be a service account if Dataproc is invoked through an API client or from another Google Cloud service such as Compute Engine, Cloud Run functions, or Cloud Composer.
Related roles
Notes
- Dataproc API-submitted jobs run as
rooton Linux. Dataproc clusters inherit project-wide Compute Engine SSH metadata unless explicitly blocked by setting
--metadata=block-project-ssh-keys=truewhen you create your cluster (see Cluster metadata).HDFS user directories are created for each project-level SSH user. These HDFS directories are created at cluster deployment time, and a new (post-deployment) SSH user is not given an HDFS directory on existing clusters.
Dataproc Service Agent (Control Plane identity)
Example: service-project-number@dataproc-accounts.iam.gserviceaccount.com
The Dataproc Service Agent service account is used to perform a broad set of system operations on resources located in the project where a Dataproc cluster is created, including:
- Creation of Compute Engine resources, including VM instances, instance groups, and instance templates
getandlistoperations to confirm the configuration of resources such as images, firewalls, Dataproc initialization actions, and Cloud Storage buckets- Auto-creation of the Dataproc staging and temp buckets if the staging or temp bucket is not specified by the user
- Writing cluster configuration metadata to the staging bucket
- Accessing VPC networks in a host project
Related roles
Dataproc VM service account (Data Plane identity)
Example: project-number-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com
Your application code runs as the VM service account on Dataproc VMs. User jobs are granted the roles (with their associated permissions) of this service account.
The VM service account does the following:
- Communicates with the Dataproc control plane.
- Reads and writes data from and to the Dataproc staging and temp buckets.
- As needed by your Dataproc jobs, reads and writes data from and to Cloud Storage, BigQuery, Cloud Logging, and other Google Cloud resources.
Related roles
What's next
- Learn more about Dataproc roles and permissions.
- Learn more about Dataproc service accounts.
- See BigQuery Access Control.
- See Cloud Storage Access Control options.
