The open source Hive-BigQuery connector lets your Apache Hive workloads read and write data from and to BigQuery and BigLake tables. You can store data in BigQuery storage or in open source data formats on Cloud Storage.
The Hive-BigQuery connector implements the Hive Storage Handler API to allow Hive workloads to integrate with BigQuery and BigLake tables. The Hive execution engine handles compute operations, such as aggregates and joins, and the connector manages interactions with data stored in BigQuery or in BigLake-connected Cloud Storage buckets.
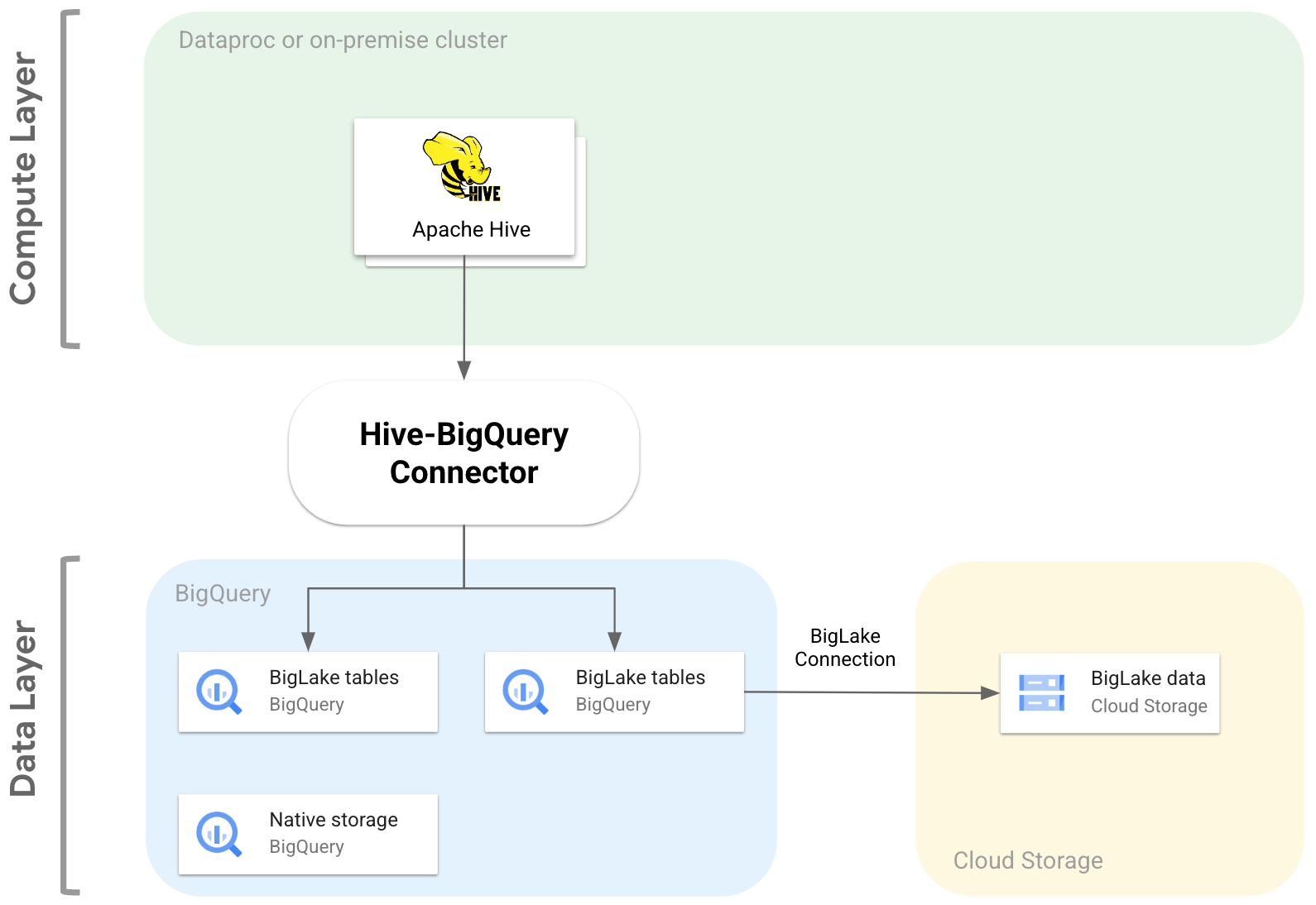
The following diagram illustrates how Hive-BigQuery connector fits between the compute and data layers.
Use cases
Here are some of the ways the Hive-BigQuery connector can help you in common data-driven scenarios:
Data migration. You plan to move your Hive data warehouse to BigQuery, then incrementally translate your Hive queries into BigQuery SQL dialect. You expect the migration to take a significant amount of time due to the size of your data warehouse and the large number of connected applications, and you need to ensure continuity during the migration operations. Here's the workflow:
- You move your data to BigQuery
- Using the connector, you access and run your original Hive queries while you gradually translate the Hive queries to BigQuery ANSI-compliant SQL dialect.
- After completing the migration and translation, you retire Hive.
Hive and BigQuery workflows. You plan to use Hive for some tasks, and BigQuery for workloads that benefit from its features, such as BigQuery BI Engine or BigQuery ML. You use the connector to join Hive tables to your BigQuery tables.
Reliance on an open source software (OSS) stack. To avoid vendor lock-in, you use a full OSS stack for your data warehouse. Here's your data plan:
You migrate your data in its original OSS format, such as Avro, Parquet, or ORC, to Cloud Storage buckets using a BigLake connection.
You continue to use Hive to execute and process your Hive SQL dialect queries.
You use the connector as needed to connect to BigQuery to benefit from the following features:
- Metadata caching for query performance
- Data loss prevention
- Column-level access control
- Dynamic data masking for security and governance at scale.
Features
You can use the Hive-BigQuery connector to work with your BigQuery data and accomplish the following tasks:
- Run queries with MapReduce and Tez execution engines.
- Create and delete BigQuery tables from Hive.
- Join BigQuery and BigLake tables with Hive tables.
- Perform fast reads from BigQuery tables using the Storage Read API streams and the Apache Arrow format
- Write data to BigQuery using the following
methods:
- Direct writes using the BigQuery Storage Write API in pending mode. Use this method for workloads that require low write latency, such as near-real-time dashboards with short refresh time windows.
- Indirect writes by staging temporary Avro files to Cloud Storage, and then loading the files into a destination table using the Load Job API. This method is less expensive than the direct method, since BigQuery load jobs don't accrue charges. Since this method is slower, and finds its best use in workloads that aren't time critical
Access BigQuery time-partitioned and clustered tables. The following example defines the relation between a Hive table and a table that is partitioned and clustered in BigQuery.
CREATE TABLE my_hive_table (int_val BIGINT, text STRING, ts TIMESTAMP) STORED BY 'com.google.cloud.hive.bigquery.connector.BigQueryStorageHandler' TBLPROPERTIES ( 'bq.table'='myproject.mydataset.mytable', 'bq.time.partition.field'='ts', 'bq.time.partition.type'='MONTH', 'bq.clustered.fields'='int_val,text' );
Prune columns to avoid retrieving unnecessary columns from the data layer.
Use predicate pushdowns to pre-filter data rows at the BigQuery storage layer. This technique can significantly improve overall query performance by reducing the amount of data traversing the network.
Automatically convert Hive data types to BigQuery data types.
Read BigQuery views and table snapshots.
Integrate with Spark SQL.
Integrate with Apache Pig and HCatalog.
Get started
See the instructions to install and configure the Hive-BigQuery connector on a Hive cluster.
