Google Agentspace can securely connect to customer-managed, self-hosted, third-party data sources. These connections are established through Private Service Connect producer services.
This connectivity model ensures that sensitive data remains in your control and network boundaries, while allowing Google Agentspace to access and use the information contained within these data sources. Using Private Service Connect lets you establish a secure and scalable communication channel, bypassing the public internet and minimizing potential security risks associated with traditional network configurations.
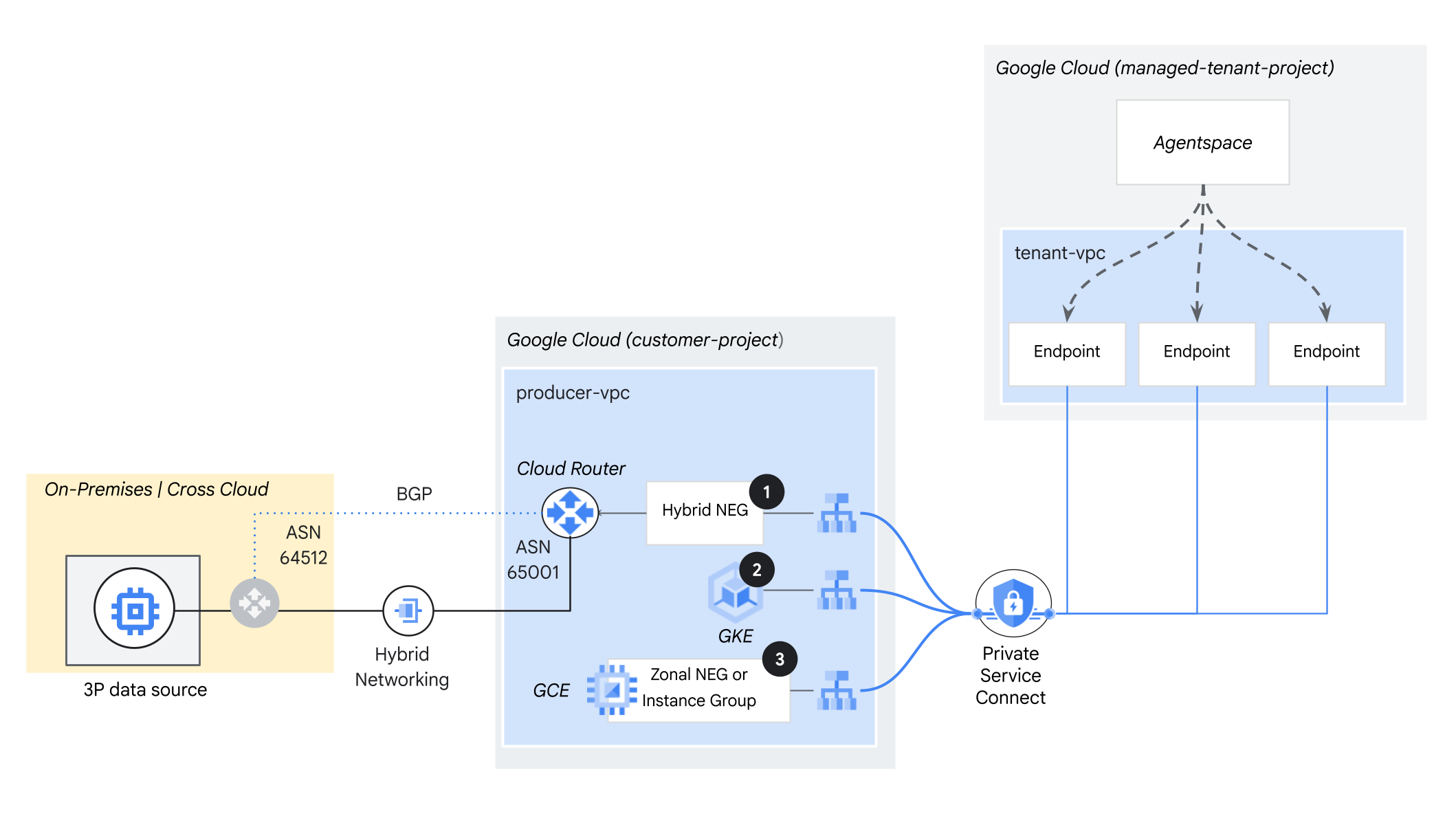
Google Agentspace supports the following self-hosted data source patterns:
On-premises or multi-cloud: Data sources deployed in your data center or in another cloud provider (for example, Amazon Web Services EC2 or EKS, or Microsoft Azure virtual machines), using hybrid network connectivity.
Google Kubernetes Engine: Data sources hosted within GKE clusters.
Google Cloud Compute Engine: Data sources deployed on Google Compute Engine VMs.
Using Private Service Connect with self-hosted services
Private Service Connect is a Google Cloud networking feature that enables private access from a consumer's Virtual Private Cloud network to managed services. It creates a secure, explicit connection between a service consumer and a service producer, eliminating the need for Virtual Private Cloud peering, complex routing, or public IP addresses.
You can set up a Google Agentspace Private Service Connect deployment with the following:
Google Agentspace as the service consumer
Your network, containing load balancers that reference on-premises, multi-cloud, or Google Cloud compute resources, as the service producer
For information about specific aspects of using Private Service Connect to connect your self-hosted service to Agentspace, see the following sections.
VPC network and subnet configuration
Keep the following in mind:
Proxy allocation is at the VPC level, not at the load balancer level. You must create one proxy-only subnet in each region of a virtual network (VPC) in which you use Envoy-based load balancers. If you deploy multiple load balancers in the same region and same VPC network, they share the same proxy-only subnet for load balancing.
Health check probes originate from the Envoy proxies located in the proxy-only subnet within the region. For the health check probes to function correctly, you must create firewall rules in the external environment that allow traffic from the proxy-only subnet to reach your external backends.
The proxy-only subnet is the source subnet targeting the cross cloud database. Ensure that this subnet is advertised by a Cloud Router. For more information, see Advertise specific VPC subnets.
The proxy-only subnet must be on the allowlist for the on-premises or Cross-Cloud firewall.
You must create proxy-only subnets regardless of whether your VPC network is auto mode or custom. A proxy-only subnet must provide 64 or more IP addresses. This corresponds to a prefix length of /26 or shorter. The recommended subnet size is /23 (512 proxy-only addresses).
Private Service Connect NAT subnet
Packets from the consumer VPC network are translated using source NAT (SNAT), so that their original source IP addresses are converted to source IP addresses from the NAT subnet in the producer's VPC network. Private Service Connect for NAT subnets cannot host workloads.
The minimum subnet size for a Private Service Connect NAT is /29. You can add additional NAT subnets to a service attachment at any time, without interrupting traffic.
You can monitor published services using either predefined dashboards or Google Cloud metrics for Private Service Connect NAT consumption.
Load balancer configuration
A service producer places its application or service behind a Google Cloud Internal Load Balancer. We recommend that you use an Internal TCP Proxy Load Balancer. If using Google Kubernetes Engine, you can use an internal passthrough Network Load Balancer.
Because Agentspace is not available in all locations, you must enable global access when creating the internal load balancer forwarding rule. If you don't enable global access, then endpoint creation for Agentspace (the service consumer) can fail. Ensure that you have enabled global access before you create the Private Service Connect service attachment. For more information about client access for internal load balancers, see Client access.
Service attachment configuration
To publish a service using Private Service Connect, a service producer creates a service attachment. This attachment enables service consumers, such as Agentspace, to connect to the producer's service. For information about publishing a service and creating a service attachment, see Publish a service.
The service producer has two primary options for controlling consumer connections, managed using the following connection preferences:
Automatically accept all connections: This allows any consumer to connect, without explicit approval.
Accept connections for selected projects (explicit approval): This requires you to manually approve each project that requests a connection. With this option, you can choose to accept or reject a project.
If you use explicit project approval, then in order to establish a connection to your service attachment, you must do the following:
Create a data store (for example, a Jira Data Center data store).
In the Private Service Connect page of the Google Cloud console, accept the pending connection from the Agentspace tenant project for your new data store. You can identify the tenant project by its project ID, which ends in
-tp. For more information, see Manage requests for access to a published service.In the Agentspace page of the Google Cloud console, in Data stores, click the name of your new data store to see its status. The data store status is shown on its Data page.
You can't see the Agentspace tenant project ID until you create a data store. The data store status remains as Creating until you accept the project connection in Private Service Connect.
When creating a service attachment, don't select the proxy protocol unless it's supported by the self-hosted service. Doing so results in a SSL/TLS error. You can deselect the proxy protocol by editing the service attachment.
Firewall configuration
Configure ingress firewall rules to allow traffic between the Private Service Connect NAT subnet and the backend VMs in the producer service load balancer. If you're using a hybrid or internet NEG as the backend, firewall rules are not required.
What's next
For more information about how Agentspace integrates with Private Service Connect, see the following codelabs on Google Developer Codelabs:
For more information on using an internal load balancer across VPC networks on Google Kubernetes Engine, see Create an internal load balancer across VPC networks.
