A transcrição de voz permite-lhe converter os seus dados de áudio de streaming em texto transcrito em tempo real. O Agent Assist faz sugestões com base em texto, pelo que os dados de áudio têm de ser convertidos antes de poderem ser usados. Também pode usar áudio em streaming transcrito com as estatísticas de conversação para recolher dados em tempo real sobre as conversas dos agentes (por exemplo, modelagem de tópicos).
Existem duas formas de transcrever áudio de streaming para utilização com o Agent Assist: através da funcionalidade SIPREC ou fazendo chamadas gRPC com dados de áudio como payload. Esta página descreve o processo de transcrever dados de áudio de streaming através de chamadas gRPC.
A transcrição de voz funciona através do reconhecimento de voz em streaming de voz para texto. A API Speech-to-Text oferece vários modelos de reconhecimento, padrão e melhorado. A transcrição de voz é suportada ao nível de GA apenas quando é usada com o modelo de telefonia.
Pré-requisitos
- Crie um projeto em Google Cloud.
- Ative a Dialogflow API.
- Contacte o seu representante da Google para se certificar de que a sua conta tem acesso aos modelos melhorados do Speech-to-Text.
Crie um perfil de conversa
Para criar um perfil de conversa, use a
consola do Agent Assist ou chame o método create no recurso
ConversationProfile diretamente.
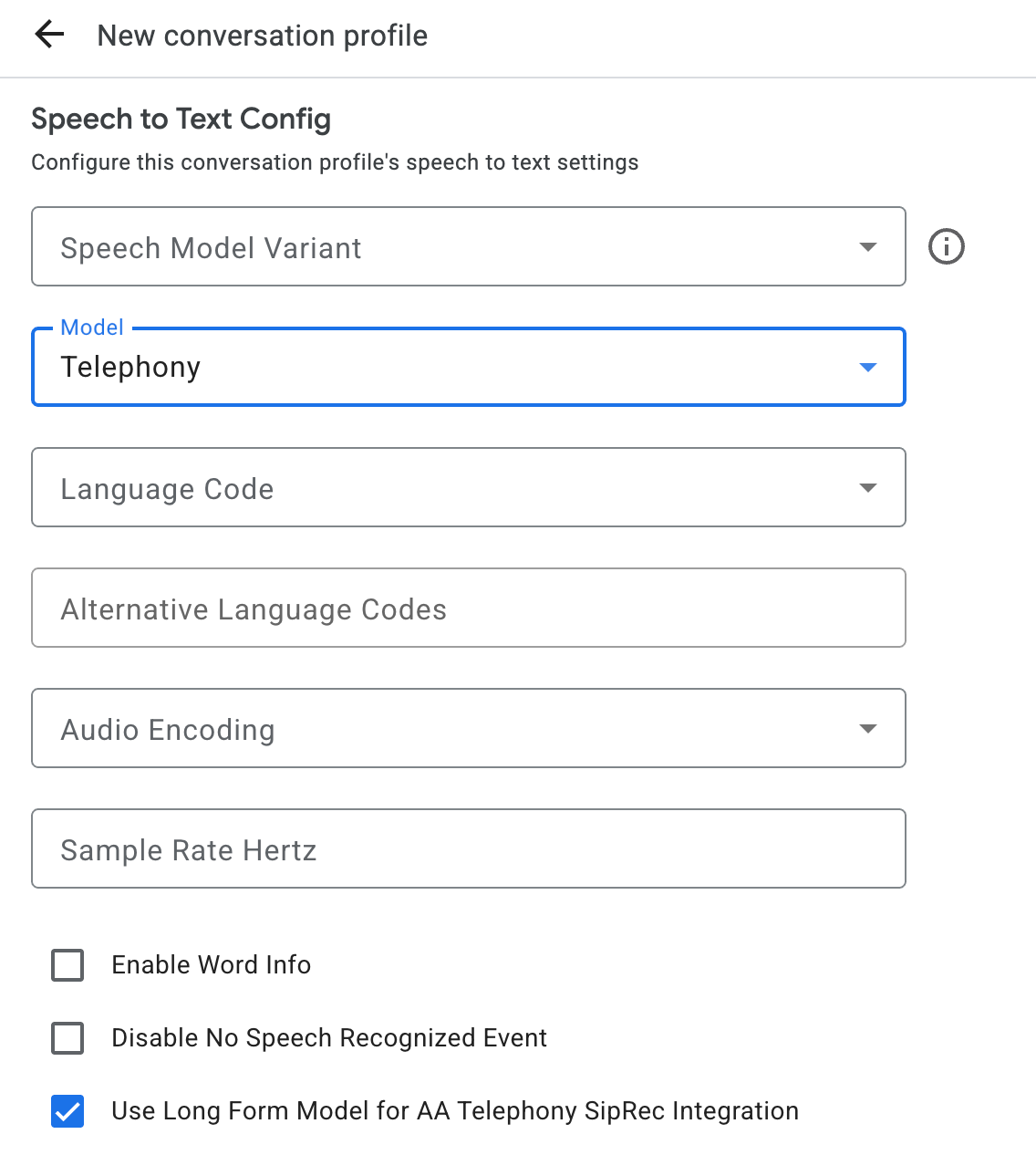
Para a transcrição de voz, recomendamos que configure ConversationProfile.stt_config como o InputAudioConfig predefinido quando enviar dados de áudio numa conversa.
Obtenha transcrições durante a execução da conversa
Para receber transcrições durante o tempo de execução da conversa, tem de criar participantes para a conversa e enviar dados de áudio para cada participante.
Crie participantes
Existem três tipos de
participante.
Consulte a documentação
de referência
para mais detalhes sobre as respetivas funções. Chame o método create no
participant e especifique o role. Apenas um END_USER ou um participante HUMAN_AGENT
pode ligar para o StreamingAnalyzeContent, o que é necessário para obter uma
transcrição.
Envie dados de áudio e receba uma transcrição
Pode usar
StreamingAnalyzeContent
para enviar o áudio de um participante para a Google e receber a transcrição, com os
seguintes parâmetros:
O primeiro pedido na stream tem de ser
InputAudioConfig. (Os campos configurados aqui substituem as definições correspondentes emConversationProfile.stt_config.) Não envie nenhuma entrada de áudio até ao segundo pedido.audioEncodingtem de estar definido comoAUDIO_ENCODING_LINEAR_16ouAUDIO_ENCODING_MULAW.model: este é o modelo de conversão de voz em texto que quer usar para transcrever o seu áudio. Defina este campo comotelephony. A variante não afeta a qualidade da transcrição, pelo que pode deixar a variante do modelo de voz não especificada ou escolher Usar a melhor disponível.singleUtterancedeve ser definido comofalsepara obter a melhor qualidade de transcrição. Não deve esperarEND_OF_SINGLE_UTTERANCEsesingleUtteranceforfalse, mas pode depender deisFinal==truedentro deStreamingAnalyzeContentResponse.recognition_resultpara fechar parcialmente a stream.- Parâmetros adicionais opcionais: os seguintes parâmetros são opcionais. Para aceder a estes parâmetros, contacte o seu representante da Google.
languageCode:language_codedo áudio. O valor predefinido éen-US.alternativeLanguageCodes: esta é uma funcionalidade de pré-visualização. Idiomas adicionais que podem ser detetados no áudio. O Agent Assist usa o campolanguage_codepara detetar automaticamente o idioma no início do áudio e usá-lo por predefinição em todas as interações seguintes. O campoalternativeLanguageCodespermite-lhe especificar mais opções para o Agent Assist escolher.phraseSets: o nome do recurso de adaptação do modelo de conversão de voz em texto.phraseSetPara usar a adaptação de modelos com a transcrição de voz, tem de criar primeiro ophraseSetatravés da API Speech-to-Text e especificar o nome do recurso aqui.
Depois de enviar o segundo pedido com a carga útil de áudio, deve começar a receber alguns
StreamingAnalyzeContentResponsesda stream.- Pode fechar parcialmente a stream (ou parar de enviar em alguns idiomas, como o Python) quando vir
is_finaldefinido comotrueemStreamingAnalyzeContentResponse.recognition_result. - Depois de fechar parcialmente a stream, o servidor envia de volta a resposta com a transcrição final, juntamente com potenciais sugestões do Dialogflow ou sugestões do Agent Assist.
- Pode fechar parcialmente a stream (ou parar de enviar em alguns idiomas, como o Python) quando vir
Pode encontrar a transcrição final nas seguintes localizações:
StreamingAnalyzeContentResponse.message.content.- Se ativar as notificações do Pub/Sub, também pode ver a transcrição no Pub/Sub.
Inicie uma nova stream depois de a stream anterior ser fechada.
- Reenvio de áudio: os dados de áudio gerados após os últimos
speech_end_offsetda resposta comis_final=truepara a nova hora de início da stream têm de ser reenviados paraStreamingAnalyzeContentpara obter a melhor qualidade de transcrição.
- Reenvio de áudio: os dados de áudio gerados após os últimos
O diagrama seguinte ilustra como funciona a stream.
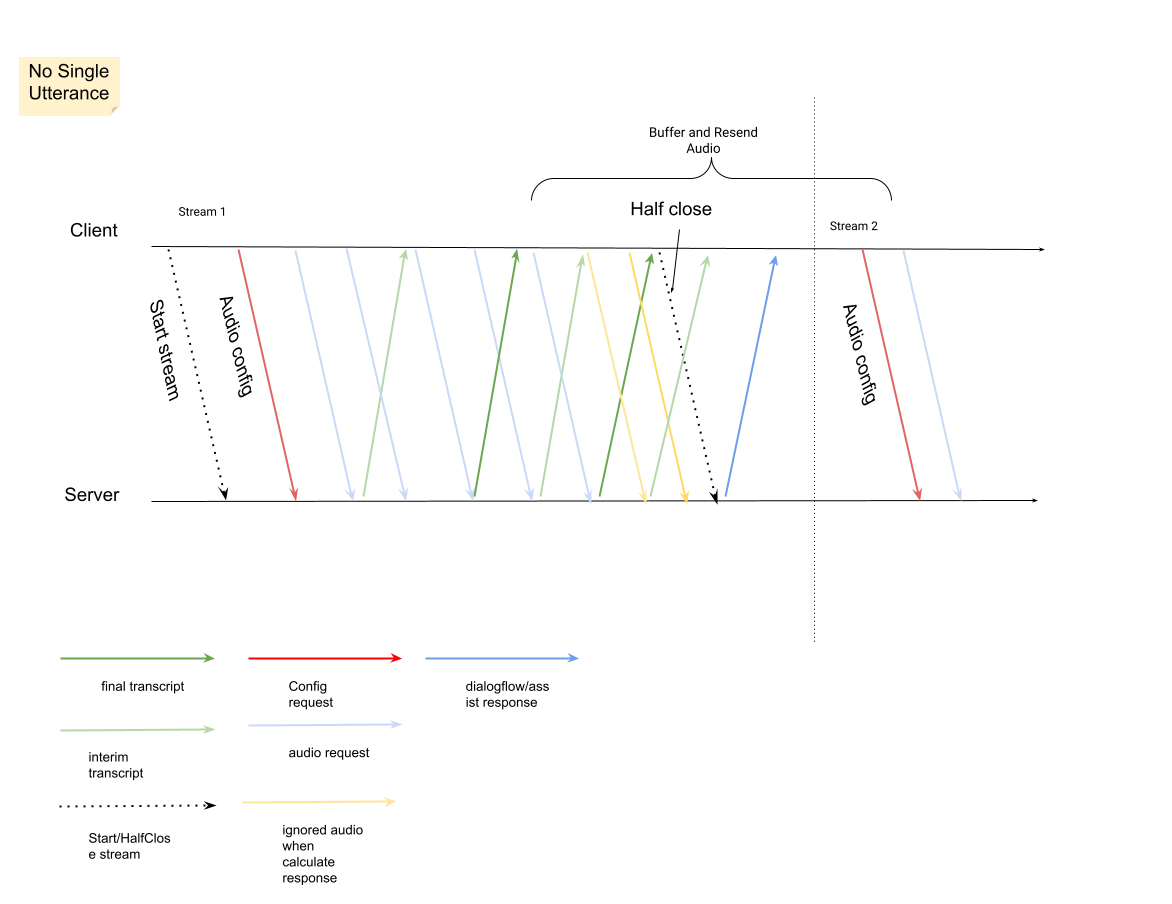
Exemplo de código de pedido de reconhecimento em streaming
O seguinte exemplo de código ilustra como enviar um pedido de transcrição de streaming:
Python
Para se autenticar no Agent Assist, configure as Credenciais padrão da aplicação. Para mais informações, consulte o artigo Configure a autenticação para um ambiente de desenvolvimento local.

