The following is a developer's guide on how to integrate conversational product filtering in your API.
Administrator experience
Manage the generative questions and conversational product filtering directly in the API, or in the Search for commerce console, and set it up in the Data quality and Evaluate sections of the Search for commerce console.
Cloud console
The console allows retailers to manage generative questions in a conversational product filtering experience. Learn more about using generative questions in conversational product filtering.
Steps to use the generative question service
Satisfy data requirements.
Configure manual question overrides.
Turn the feature on.
Data requirements
To find out if your search data is ready for conversational product filtering, in the console, under Conversational product filtering and browse, or under Data quality > Conversation, go to the Coverage checks tab.
To enable conversational product filtering, you need to meet certain data requirements.
These are:
- 1,000 queries per day: After you reach this first threshold, a conversation plan is generated that evaluates your inputs and outputs:
- Inputs: filter count in events
- Outputs: conversational coverage
- 25% conversational coverage: Calculated by Vertex AI Search for commerce models, conversational coverage means the percentage of queries that have one question. A frequency-weighted 25% (by volume) of queries should have at least a first question that matches it.
If you don't have 25% conversational coverage yet, but have the first prerequisite 1000 queries per day, blocking and advisory checks begin to be applied to your outputs and inputs, respectively. Here, Vertex AI Search for commerce begins to calculate by how much of a percentage your user-event-applied filters have to increase in order to reach the 25% conversational coverage threshold. The more filters that are uploaded, the higher the coverage reached.
To view your conversational readiness:
- Go to the Conversation tab in the Data quality page in the Search for commerce console. This provides you with a critical check of whether a minimum of 25% of search queries have at least one follow-up question, as well as advisory checks as to what percentage of user events with valid filters is needed to reach that conversational coverage goal.
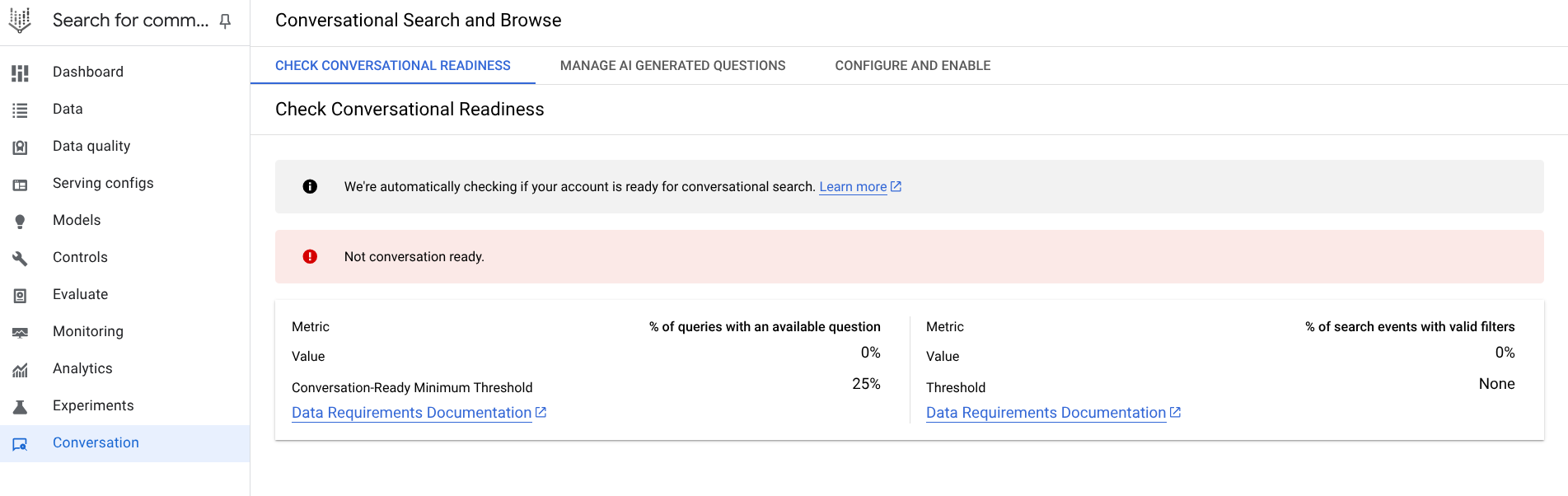 Figure 4. Conversational readiness check.
Figure 4. Conversational readiness check.
If you pass the critical check, with sufficient user events with valid filters, proceed to the next step.
To control how generative questions are served, go to the Conversational product filtering and browse page in the Vertex AI Search for commerce console.
Generative question controls
The generative AI writes a question for every indexable attribute in the catalog, using both names and values of attributes for system and custom attributes. These questions are generated by an LLM and aim to enhance the search experience. For example, for furniture type, values can be indoor or outdoor, the AI synthesizes a question about what type of furniture you are looking for.
Each facet has one generated question. Based on historic user events and facet engagement from past search event data, the questions are sorted by expected frequency of the question appearing. The AI first looks at the questions on top, then finds what is relevant by attribute. The list of questions is generated once. If a new attribute is added, it is reflected in the list in two hours.
Go to the Conversational search and browse page in the Search for commerce console.
Go to the Conversational search and browse page.Under the Manage AI generated questions tab, view all the questions sorted by how often they are used, in query-weighted frequency, meaning how often they are served with common queries. The ranking uses the frequency field in the
GenerativeQuestionConfigconfiguration. This field is responsible for sorting the AI-generated questions by how often they are used.You can use the filter option to filter the questions.
Check the box to enable question visibility for each attribute.
Click edit at the end of each row to open an edit panel for each question.
To make bulk edits, follow these steps:
Select or clear the boxes next to the questions that you want to include or exclude in conversation.
Click either the addAllow in conversation or the removeDisallow in conversation buttons that appear at the top of the list. Alternatively, to edit an individual question, click edit and clear or recheck the box next to Allowed in conversation in the pane that opens:
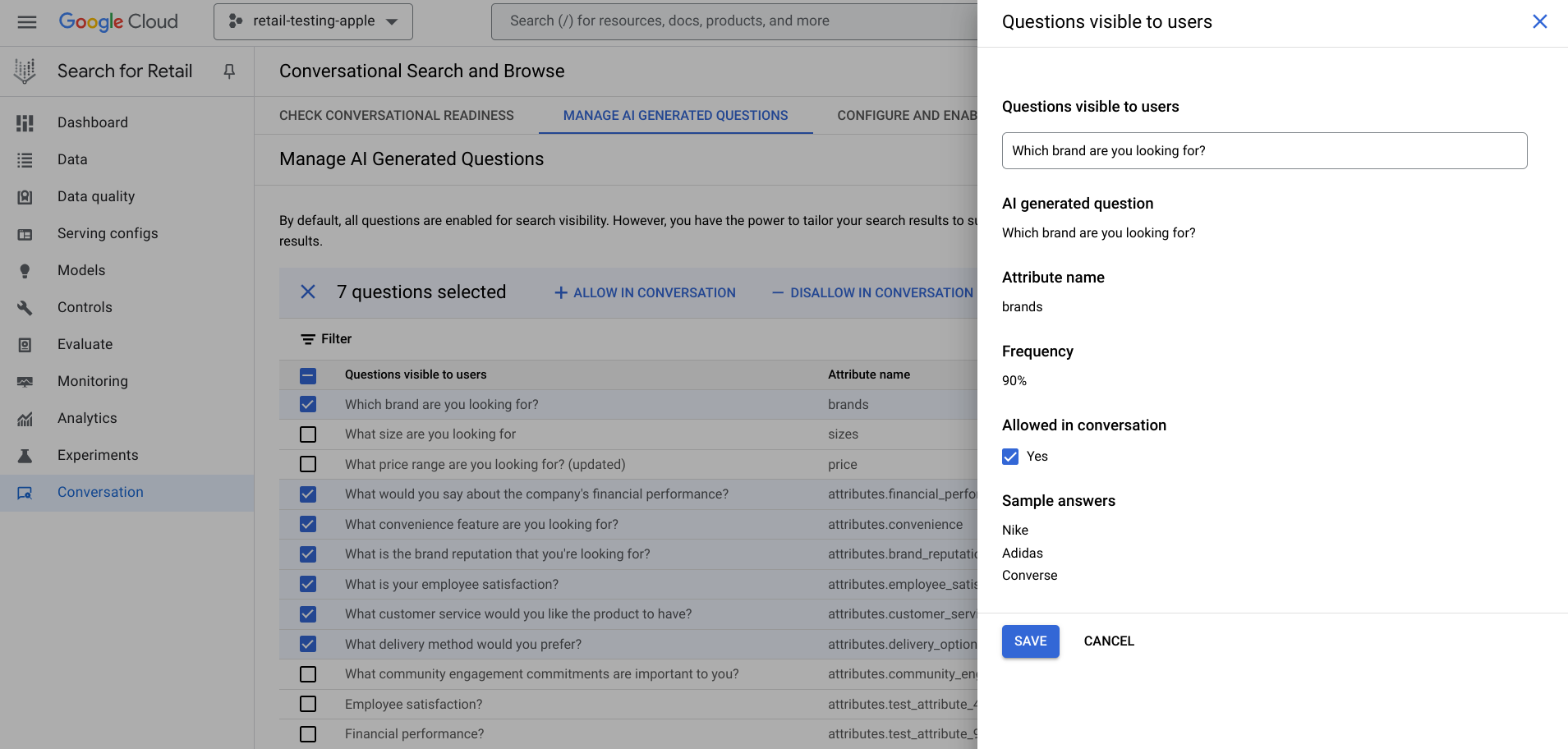 Figure 5. Edit each AI-generated question.
Figure 5. Edit each AI-generated question.
Use generative questions in conversational product filtering
The generative question service API provides controls to mitigate potential inconsistencies in the LLM output. These can be managed from the console. Here, retailers can also configure conversational product filtering by toggling its enabled state and setting the minimum number of products required to trigger it.
You can define the questions, specifying the question itself, potential answers, and whether the question is allowed in the conversation. Individual questions can be generated by an LLM or overridden by the retailer. The console supports reviewing AI-generated questions, allowing retailers to override them or toggle their conversational status. Questions can also be bulk edited.
Edit individual questions
You can also use controls to curate the individual questions. It is recommended to do this before you turn conversational product filtering on.
For each question, there are two options. Click edit in in the last column to access the questions visible to the users panel:
- Turn off a question for all queries: The question is enabled by default. Clear (or check again) the box next to Allowed in conversation. This option skips the question altogether. A retailer may opt to disable a question entirely if it does not relate to the queried attributes or could be misconstrued as inappropriate in some way (a question such as "What dress size are you looking for?" may be perceived as prying about a shopper's weight.)
- Rewrite a question: In the pane, you can see the AI-generated question, what attribute it is attached to and what values the attribute has. Click the pencil to rewrite it.
Turn on conversational filtering
After you have edited your generative AI questions in the console, you are ready to turn on conversational product filtering.
To enable conversational product filtering, go to the Conversational product filtering and browse page in the Search for commerce console.
Go to the Conversational search and browse page in the Search for commerce console.
Go to the Conversational search and browse page.Consider the minimum amount of products in your catalog you want returned in the search before questions are generated. This number can be higher but never lower than 2. One row to a page is often the right amount for triggering a conversation.
Configure the number and switch the toggle to On. If fewer products match the number, they get filtered out.
 Figure 6. Switch toggle on to Enable conversational search.
Figure 6. Switch toggle on to Enable conversational search.
This page provides information as to the status of your blocking and advisory checks. If you have enough search queries with at least one follow-up question, your site is now conversational search-enabled.
Evaluate and test
Evaluate lets you preview the serving experience by running a test search and testing your questions against displayed facets. This part of the console provides you with a preview of your serving experience with conversational product filtering.
To evaluate and test, follow these steps. In the Evaluate section on the Search or Browse tabs on the Evaluate page of the Search for commerce console.
Go to the Evaluate page in the Search for commerce console.
Go to the Evaluate pageClick Search or Browse.
In the Search Evaluation field, enter a test query that makes sense based on the catalog you have uploaded to search, such as shoes if your catalog consists of clothing items.
Click Search preview to see search results.
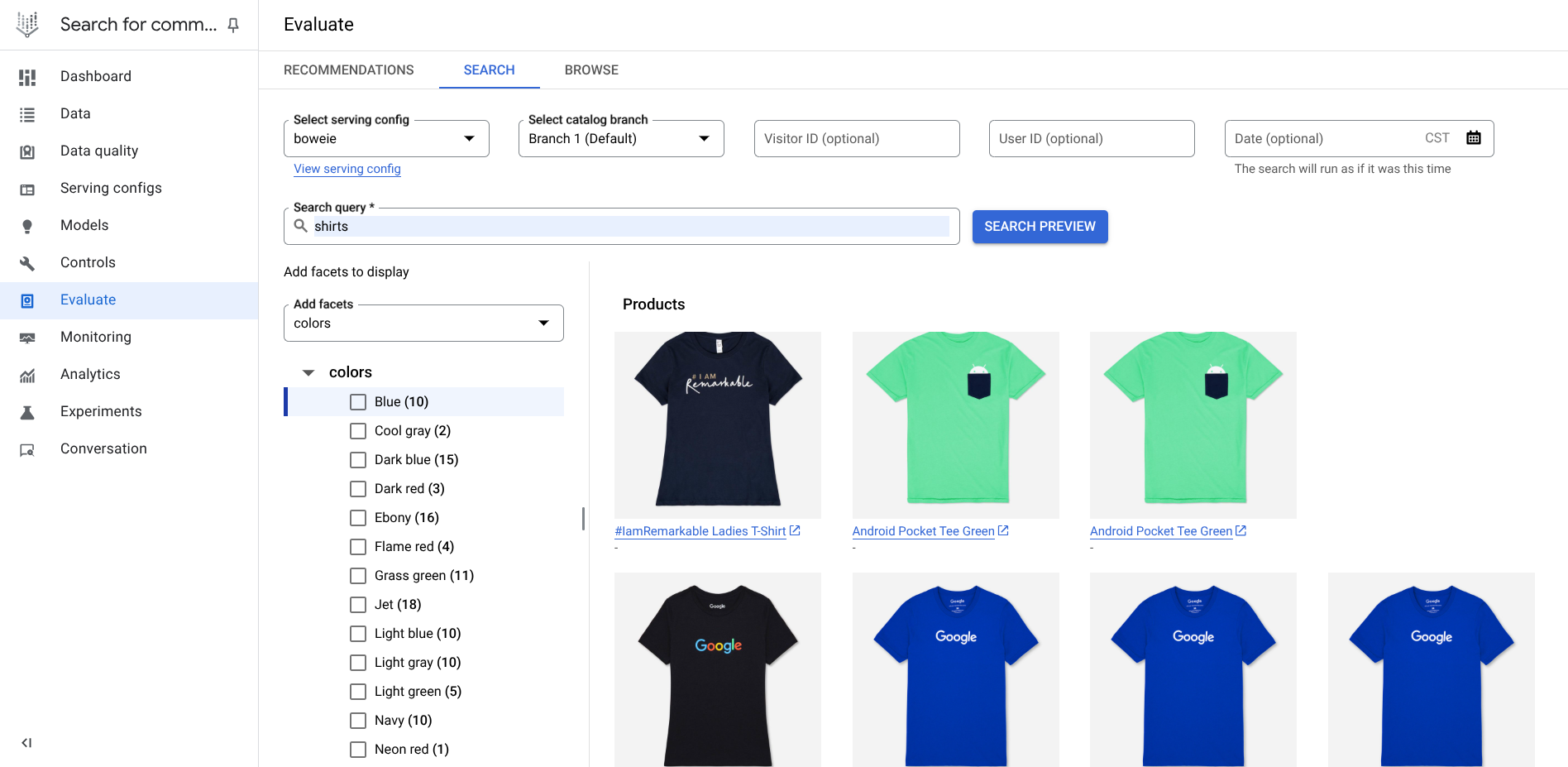 Figure 7. Preview results.
Figure 7. Preview results.
If you have conversational product filtering enabled, generative questions are enabled.
Generative Question API
This section describes how to use the generative question API to integrate the Conversational API into your web interface, manage the generative questions, and serve conversational product filtering on your site.
API integration
Objects:
- GenerativeQuestionsFeatureConfig
- GenerativeQuestionConfig
- GenerativeQuestions Service
- UpdateGenerativeQuestionsFeatureConfiguration
- UpdateGenerativeQuestionConfig
- ListGenerativeQuestionConfigs
- GetGenerativeQuestionFeatureConfig
- BatchUpdateGenerativeQuestionConfigs
The core to integrating conversational product filtering is defining the question resource. This includes the question itself and whether the question is allowed in the conversation. The question is by default generated by an LLM but can be overridden by the administrator.
Enable conversational product filtering
Object:
- GenerativeQuestionsFeatureConfig
This object is a control configuration file for enabling conversational product filtering for generative questions to manage the overall serving experience. GenerativeQuestionsFeatureConfig uses a GET method to obtain attribute information and whether the attributes are indexable or not from the catalog associated with the project.
The feature_enabled switch determines whether questions are used at serving time. It manages the top-level toggles in the console.
Serving experience
Conversational product filtering is based on engaging your user with an ongoing conversation of multiple turns. Therefore, there's at least a second response required for conversational product filtering to work. Your user is presented with a follow-up question and suggested answers in the response, and your user can respond to this follow-up question either by either entering their answer or by clicking on a suggested answer (multiple choice option).
The multiple choice option functions behind the scenes like a facet (an event type filter), which narrows the query using filtering. In the background, when the user clicks on a multiple choice response, a filter is applied to the query. Applying a filter using conversational multiple choice is identical to applying the same filter using dynamic facets or tiles.
Service enabled by conversational product filtering
The generative questions service (service GenerativeQuestionService{...}) is used for managing LLM-generated questions. Its parent object is the catalog, where it retrieves information from to return questions for a given catalog. The service is used to manage the overall generative question state, make individual or batch changes, and toggle questions on or off. Data requirements must be met to interface with the Service API, and the questions must be initialized before the questions can be managed.
The service interacts with the feature-level and question-level configuration files with two sets of handlers:
GenerativeQuestionsFeatureConfighandlers (feature-level):- Update Lets you change minimum products and enable fields.
- Get Returns an object.
GenerativeQuestion Config handlers (question-level):
- List Returns all questions for a given catalog.
- Update Performs individual question management.
- Batch Update Performs grouped question management.
The service returns a semantically appropriate question based on the initial query.
A follow-up question is generated by the LLM model and can be overridden. The questions are displayed based on how likely it is used by customers by calling the search event history. If there is no search event history, the fallback is on the commerce search logs.
Different questions are generated based on the previous query. There are no fixed weights. The AI that drives the LLM-generated questions learns from the queries and changes the weighting for every query, so that "shirt", for example, weighs the category very heavily, but "XL red shirt" weighs category, size and color.
Configure the serving experience
Configure the serving experience by integrating the conversational filtering configuration API with the Search API.
The configuration API ConversationalFilteringSpec for the feature sits on top of the Conversational API. You can either call both APIs in parallel or in this order:
- Conversational API
- Search API
ConversationalFilteringSpec: This optional field has been added toConversationalSearchRequestbut is required if you want to use conversational product filtering. The field reuses theSearchRequestfields, query and filter. It also includes a field to enable a follow-up question served to the user after an initial query and a `conversation_id` to maintain the state of the conversation between the client and server.ConversationalFilteringResult: A proto file contains extra information needed to be returned for the conversational CRS flow inConversationalSearchResponse. This includes aconversation_id,refined_query,additional_filters,follow_up_question, andsuggested_answers.
User journey in the conversational API
The user initiates a search with an initial query and sets the mode flag to CONVERSATIONAL_FILTER_ONLY. The user then selects an answer, which is sent back to the API using the user_answer field.
The Conversational API provides the additional_filter field in the response. The user must apply these filters to the Search API follow-up request. The search results are based on the user's input and provide a new follow-up question, prompting a follow-up query and continuing the conversation in multiple turns until the user finds what they're looking for on the retailer website.
Assuming conversational product filtering is enabled on the website, the user journey and subsequent interaction with Vertex AI Search for commerce follows this path:
Step 1. First query comes from user to both Search and Conversational API. The Search API only returns search results. The Conversational API returns the suggested answers and follow-up questions. Call the Search API for the same query or
page_categoryand fetch the search results. Follow-up conversation requested is sent to conversational search. Call the Conversational API with the right conversation filtering mode.Step 2. Initial search response with search results only. The Conversational API refines the query by returning the suggested answers and follow-up questions. The end user then selects multiple choice:
- The selected answer filter is sent to the Conversational API.
- Conversation and Search APIs run with the applied filter.
Initial user query
The first query is when your user starts a conversation in Vertex AI Search for commerce and looks for dress in the search box.
- User action: The end user searches for dress.
- Your implementation: Make two API calls.
- Conversational API request:
query: "dress"conversational_search_spec:mode:"CONVERSATIONAL_FILTER_ONLY"This is the key parameter.
- Search API request:
query: dress
- Conversational API response:
conversation_id: "c15..." Store this variable.followup_question: What is the color? question is generated.suggested_answers:[ {name: "colors", value: "yellow"}, {name: "colors", value: "blue"}, ... ]
- Action: Display the
followup_questionandsuggested_answersto the user.
Send request to Search API
Send a request to the Search API by creating the following search request by setting dress as the query (or whatever the actual query is):
There is no change in the search API request as part of the conversational product filtering.
Send request to the Conversational API
Send a request to the Conversational API by doing the following:
Create a conversational search request by setting
dressas the query (or whatever the actual query is).Set
modetoCONVERSATIONAL_FILTER_ONLYin order to get a conversational response. If it's set toDISABLED, no follow-up question is supplied.Populate
SearchParamsin the conversational search request. The search parameters should be the same as the Search API call.
Conversational API response
Your response from the Conversational API then looks like this:
What you should do with the response:
conversation_id: This ID can be stored in the browser session storage and can be used to continue the conversational search with the server. Because one shopper might have multiple tabs open with more than one conversation, theconversation_idis used to track the conversations.refined_query: Identifies the current query. You must use this response to call the Search API to fetch the product results.followup_question: Identifies the question to show to the user.suggested_answers: An ordered list of the multiple-choice answers that should be shown to your users. If you want to show fewer answers, just show the first N results. The list is sorted in the order the results should be shown.
The initial query then has the conversation enabled.
Search handles multiple choice answers
- User action: Clicks yellow.
- Your implementation: Make two new API calls.
- Conversational API request:
query: dressconversation_id:"c15..."Use the stored ID.user_answer: {selected_answer: {product_attribute_value: { name: "colors", value: "yellow" } } }
- Search API request:
query: dress.
- Conversational API response:
additional_filter: {product_attribute_value: { name: "colors", value: "yellow" } }followup_question: What is the occasion?
- Action: Use
additional_filterto update the web interface, such as check the yellow filter box, and display the new question.
Conversational product filtering serves these options for continued conversational engagement, leading to faster search refinement:
When your user is served search results, they can select a multiple-choice option.
This code sample demonstrates that the user selected the multiple choice answer yellow, and a new conversational request is sent to the Search API by sending the query again along with the correct user filter applied.
To send a request to the Conversational API:
- Restore the
conversation_idfrom session storage. - Set
modeto beCONVERSATIONAL_FILTER_ONLY. - Set
user_answerfor what the user selects.
The response from the Conversational API then looks like this:
What you should do with the response:
- The Google response is basically identical to the response to the first query, except the
additional_filterfield can be used to check off the filter box forcolor = yellowand should be added to any other filters that the user has selected. - The
additional_filtershould also be added to the filter field event sent to Google for this follow-up query and the follow-up search request. It should be applied in the search request to fetch search products and should also be applied to the conversational search request to fetch the follow-up conversation. - The
refined_queryshould be sent to the Search API to fetch more relevant products.
