适用于 Apache Spark 的 BigQuery 连接器让数据科学家能够将 BigQuery 的无缝可伸缩 SQL 引擎的强大功能与 Apache Spark 的机器学习功能相结合。在本教程中,我们将介绍如何使用 Dataproc、BigQuery 和 Apache Spark ML 在数据集上执行机器学习。
目标
使用线性回归来将出生体重模型建立成由五个因素组成的函数:- 妊娠周数
- 母亲的年龄
- 父亲的年龄
- 母亲在怀孕期间增加的体重
- Apgar 得分
使用以下工具:
- BigQuery,用于准备线性回归输入表,该表将写入到您的 Google Cloud 项目中
- Python,用于在 BigQuery 中查询和管理数据
- Apache Spark,用于访问生成的线性回归表
- Spark ML,用于构建和评估模型
- Dataproc PySpark 作业,用于调用 Spark ML 函数
费用
在本文档中,您将使用 Google Cloud 的以下收费组件:
- Compute Engine
- Dataproc
- BigQuery
准备工作
Dataproc 集群安装了 Spark 组件,包括 Spark ML。要设置 Dataproc 集群并运行此示例中的代码,您需要执行(或已完成)以下各项:
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the Dataproc, BigQuery, Compute Engine APIs.
- Install the Google Cloud CLI.
-
To initialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud init -
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
-
Enable the Dataproc, BigQuery, Compute Engine APIs.
- Install the Google Cloud CLI.
-
To initialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud init - 在项目中创建 Dataproc 集群。您的集群应在 Spark 2.0 或更高版本上运行 Dataproc 版本(包括机器学习库)。
创建 BigQuery natality 数据的子集
在本部分中,你在项目中创建一个数据集,然后在数据集中创建一个表,你可从公开可用的出生率 BigQuery 资料集中复制出生率数据子集至该表。在本教程的后半部,您将使用此表中的子集数据来预测出生体重与产妇年龄、父亲年龄和妊娠周数的函数关系。
您可以使用 Google Cloud 控制台创建数据子集,也可以在本地机器上运行 Python 脚本。
控制台
在项目中创建数据集。
- 转到 BigQuery 网页界面。
- 在左侧导航窗格中,点击您的项目名称,然后点击创建数据集。
- 在创建数据集对话框中执行以下操作:
- 对于数据集 ID,输入“natality_regression”。
- 对于数据位置,您可以选择数据集的位置。默认位置值为
US multi-region。 创建数据集后,就无法再更改此位置。 - 对于默认表到期时间,请选择以下任一选项:
- 从不(默认值):您必须手动删除表格。
- 天数:表格将在创建之时起的指定天数后删除。
- 对于加密,请选择以下任一选项:
- Google 拥有和 Google 管理的密钥(默认值)。
- 客户管理的密钥:请参阅使用 Cloud KMS 密钥保护数据。
- 使用 Web 界面创建数据集时,点击创建数据集
针对公共出生率数据集运行查询,然后将查询结果保存在数据集的新表中。
- 将以下查询复制并粘贴到查询编辑器中,然后点击“运行”。
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE natality_regression.regression_input as SELECT weight_pounds, mother_age, father_age, gestation_weeks, weight_gain_pounds, apgar_5min FROM `bigquery-public-data.samples.natality` WHERE weight_pounds IS NOT NULL AND mother_age IS NOT NULL AND father_age IS NOT NULL AND gestation_weeks IS NOT NULL AND weight_gain_pounds IS NOT NULL AND apgar_5min IS NOT NULL
- 查询完成后(大约需要 1 分钟),结果会保存为项目的
natality_regression数据集中的“regression_input”BigQuery 表。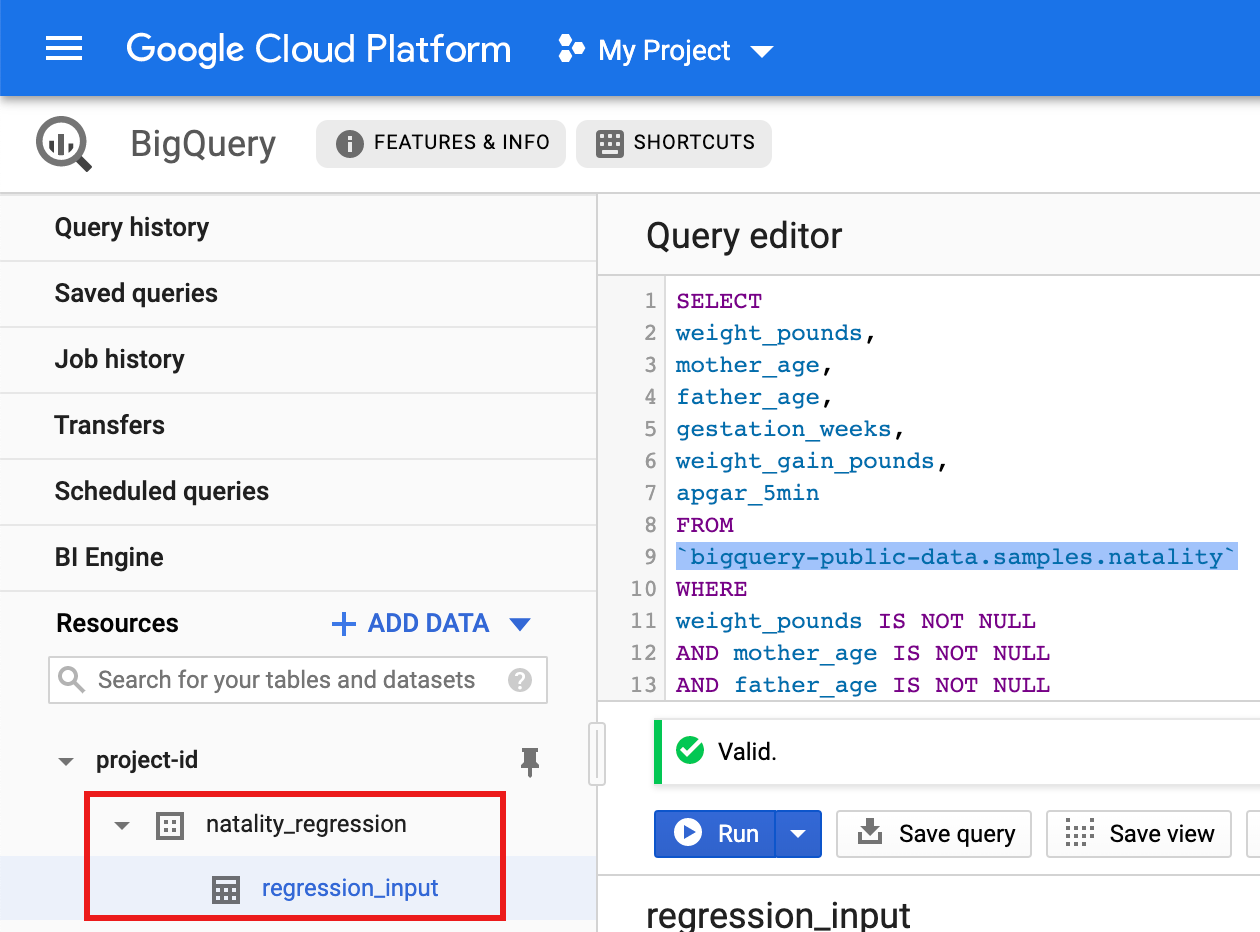
- 将以下查询复制并粘贴到查询编辑器中,然后点击“运行”。
Python
在尝试此示例之前,请按照《Dataproc 快速入门:使用客户端库》中的 Python 设置说明进行操作。 如需了解详情,请参阅 Dataproc Python API 参考文档。
如需向 Dataproc 进行身份验证,请设置应用默认凭据。 如需了解详情,请参阅为本地开发环境设置身份验证。
请参阅设置 Python 开发环境,了解关于安装 Python 和适用于 Python 的 Google Cloud 客户端库(运行代码所需的资源)的说明。建议您安装和使用 Python
virtualenv。将以下
natality_tutorial.py代码复制并粘贴到本地机器的pythonShell 中。 在 Shell 中按下<return>键运行代码,以在默认 Google Cloud 项目中创建“natality_regression”BigQuery 数据集,其中的“regression_input”表填充了公开natality数据的子集。确认创建
natality_regression数据集和regression_input表。
运行线性回归
在本部分中,您将使用 Google Cloud 控制台或通过从本地终端运行 gcloud 命令,将作业提交到 Dataproc 服务以运行 PySpark 线性回归。
控制台
将以下代码复制并粘贴到本地机器上的新
natality_sparkml.py文件中。"""Run a linear regression using Apache Spark ML. In the following PySpark (Spark Python API) code, we take the following actions: * Load a previously created linear regression (BigQuery) input table into our Cloud Dataproc Spark cluster as an RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) * Transform the RDD into a Spark Dataframe * Vectorize the features on which the model will be trained * Compute a linear regression using Spark ML """ from pyspark.context import SparkContext from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors from pyspark.ml.regression import LinearRegression from pyspark.sql.session import SparkSession # The imports, above, allow us to access SparkML features specific to linear # regression as well as the Vectors types. # Define a function that collects the features of interest # (mother_age, father_age, and gestation_weeks) into a vector. # Package the vector in a tuple containing the label (`weight_pounds`) for that # row. def vector_from_inputs(r): return (r["weight_pounds"], Vectors.dense(float(r["mother_age"]), float(r["father_age"]), float(r["gestation_weeks"]), float(r["weight_gain_pounds"]), float(r["apgar_5min"]))) sc = SparkContext() spark = SparkSession(sc) # Read the data from BigQuery as a Spark Dataframe. natality_data = spark.read.format("bigquery").option( "table", "natality_regression.regression_input").load() # Create a view so that Spark SQL queries can be run against the data. natality_data.createOrReplaceTempView("natality") # As a precaution, run a query in Spark SQL to ensure no NULL values exist. sql_query = """ SELECT * from natality where weight_pounds is not null and mother_age is not null and father_age is not null and gestation_weeks is not null """ clean_data = spark.sql(sql_query) # Create an input DataFrame for Spark ML using the above function. training_data = clean_data.rdd.map(vector_from_inputs).toDF(["label", "features"]) training_data.cache() # Construct a new LinearRegression object and fit the training data. lr = LinearRegression(maxIter=5, regParam=0.2, solver="normal") model = lr.fit(training_data) # Print the model summary. print("Coefficients:" + str(model.coefficients)) print("Intercept:" + str(model.intercept)) print("R^2:" + str(model.summary.r2)) model.summary.residuals.show()
将本地
natality_sparkml.py文件复制到项目中的 Cloud Storage 存储分区。gcloud storage cp natality_sparkml.py gs://bucket-name
从 Dataproc 提交作业页面运行回归。
在主 Python 文件字段中,插入您的
natality_sparkml.py文件副本所在的 Cloud Storage 存储分区的gs://URI。选择
PySpark作为作业类型。在 Jar 文件字段中插入
gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-latest_2.12.jar。这可让 PySpark 应用在运行时使用 spark-bigquery-connector 将 BigQuery 数据读取到 Spark DataFrame 中。填写作业 ID、区域和集群字段。
点击提交以在集群上运行作业。
作业完成后,Dataproc 作业详情窗口将显示线性回归输出模型汇总。
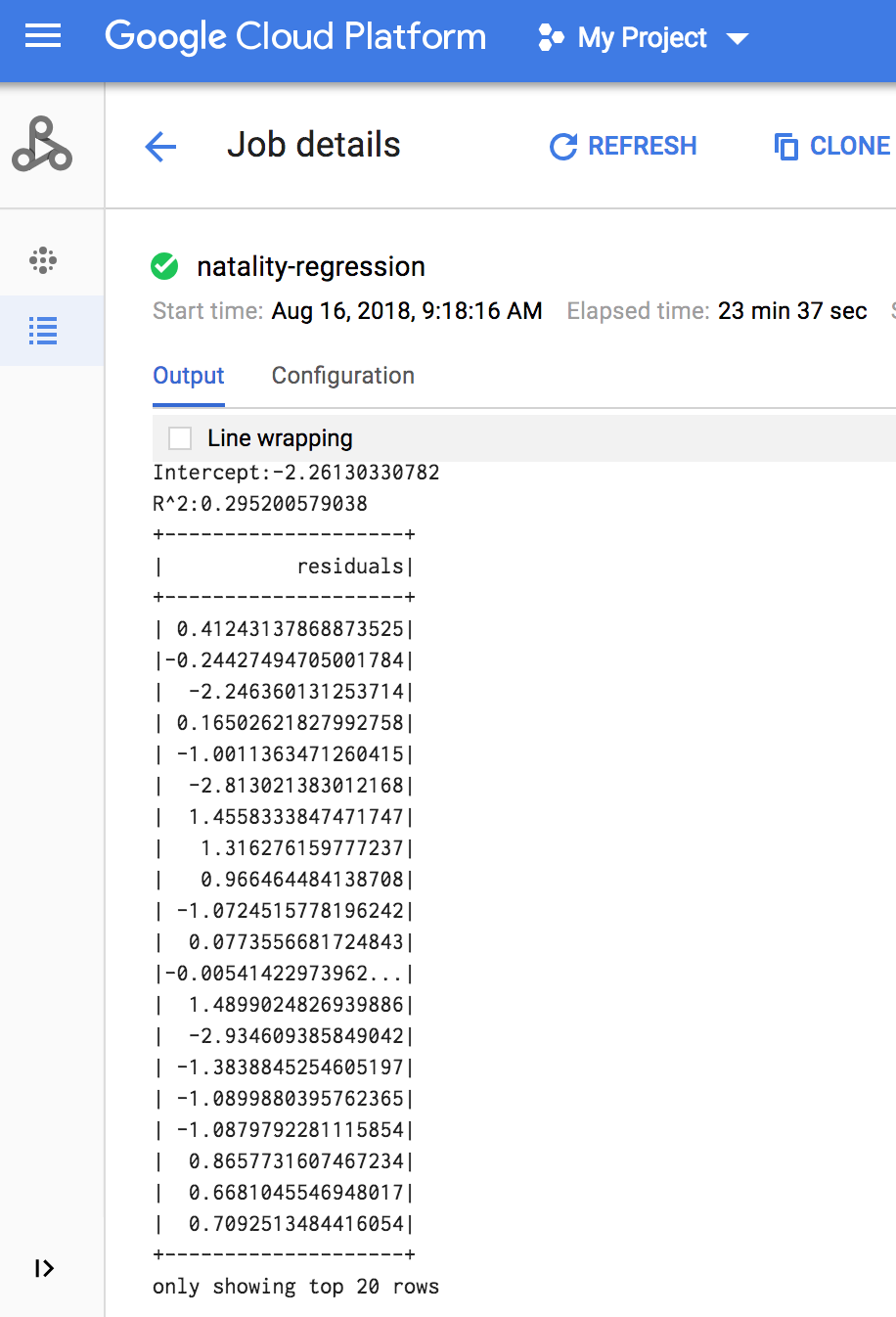
gcloud
将以下代码复制并粘贴到本地机器上的新
natality_sparkml.py文件中。"""Run a linear regression using Apache Spark ML. In the following PySpark (Spark Python API) code, we take the following actions: * Load a previously created linear regression (BigQuery) input table into our Cloud Dataproc Spark cluster as an RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) * Transform the RDD into a Spark Dataframe * Vectorize the features on which the model will be trained * Compute a linear regression using Spark ML """ from pyspark.context import SparkContext from pyspark.ml.linalg import Vectors from pyspark.ml.regression import LinearRegression from pyspark.sql.session import SparkSession # The imports, above, allow us to access SparkML features specific to linear # regression as well as the Vectors types. # Define a function that collects the features of interest # (mother_age, father_age, and gestation_weeks) into a vector. # Package the vector in a tuple containing the label (`weight_pounds`) for that # row. def vector_from_inputs(r): return (r["weight_pounds"], Vectors.dense(float(r["mother_age"]), float(r["father_age"]), float(r["gestation_weeks"]), float(r["weight_gain_pounds"]), float(r["apgar_5min"]))) sc = SparkContext() spark = SparkSession(sc) # Read the data from BigQuery as a Spark Dataframe. natality_data = spark.read.format("bigquery").option( "table", "natality_regression.regression_input").load() # Create a view so that Spark SQL queries can be run against the data. natality_data.createOrReplaceTempView("natality") # As a precaution, run a query in Spark SQL to ensure no NULL values exist. sql_query = """ SELECT * from natality where weight_pounds is not null and mother_age is not null and father_age is not null and gestation_weeks is not null """ clean_data = spark.sql(sql_query) # Create an input DataFrame for Spark ML using the above function. training_data = clean_data.rdd.map(vector_from_inputs).toDF(["label", "features"]) training_data.cache() # Construct a new LinearRegression object and fit the training data. lr = LinearRegression(maxIter=5, regParam=0.2, solver="normal") model = lr.fit(training_data) # Print the model summary. print("Coefficients:" + str(model.coefficients)) print("Intercept:" + str(model.intercept)) print("R^2:" + str(model.summary.r2)) model.summary.residuals.show()
将本地
natality_sparkml.py文件复制到项目中的 Cloud Storage 存储分区。gcloud storage cp natality_sparkml.py gs://bucket-name
通过从本地机器的终端窗口中运行如下所示的
gcloud命令,将 Pyspark 作业提交到 Dataproc 服务。- --jars 标志值可让 PySpark jobv 在运行时使用 spark-bigquery-connector 将 BigQuery 数据读取到 Spark DataFrame 中。
gcloud dataproc jobs submit pyspark \ gs://your-bucket/natality_sparkml.py \ --cluster=cluster-name \ --region=region \ --jars=gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-with-dependencies_SCALA_VERSION-CONNECTOR_VERSION.jar
- --jars 标志值可让 PySpark jobv 在运行时使用 spark-bigquery-connector 将 BigQuery 数据读取到 Spark DataFrame 中。
作业完成时,线性回归输出(模型汇总)将显示在终端窗口中。
<<< # Print the model summary. ... print "Coefficients:" + str(model.coefficients) Coefficients:[0.0166657454602,-0.00296751984046,0.235714392936,0.00213002070133,-0.00048577251587] <<< print "Intercept:" + str(model.intercept) Intercept:-2.26130330748 <<< print "R^2:" + str(model.summary.r2) R^2:0.295200579035 <<< model.summary.residuals.show() +--------------------+ | residuals| +--------------------+ | -0.7234737533344147| | -0.985466980630501| | -0.6669710598385468| | 1.4162434829714794| |-0.09373154375186754| |-0.15461747949235072| | 0.32659061654192545| | 1.5053877697929803| | -0.640142797263989| | 1.229530260294963| |-0.03776160295256...| | -0.5160734239126814| | -1.5165972740062887| | 1.3269085258245008| | 1.7604670124710626| | 1.2348130901905972| | 2.318660276655887| | 1.0936947030883175| | 1.0169768511417363| | -1.7744915698181583| +--------------------+ only showing top 20 rows.
清理
完成本教程后,您可以清理您创建的资源,让它们停止使用配额,以免产生费用。以下部分介绍如何删除或关闭这些资源。
删除项目
为了避免产生费用,最简单的方法是删除您为本教程创建的项目。
要删除项目,请执行以下操作:
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the Manage resources page.
- In the project list, select the project that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
- In the dialog, type the project ID, and then click Shut down to delete the project.
删除 Dataproc 集群
请参阅删除集群。
后续步骤
- 请参阅 Spark 作业微调提示

