This document shows you how to run Serverless for Apache Spark SQL and PySpark batch workloads to create an Apache Iceberg table with metadata stored in BigLake metastore. For information on other ways to run Spark code, see Run PySpark code in a BigQuery notebook and Run an Apache Spark workload
Before you begin
If you haven't already done so, create a Google Cloud project and a Cloud Storage bucket.
Set up your project
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
-
Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator
(
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission. Learn how to grant roles.
-
Enable the Dataproc, BigQuery, and Cloud Storage APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission. Learn how to grant roles. -
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
-
Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator
(
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission. Learn how to grant roles.
-
Enable the Dataproc, BigQuery, and Cloud Storage APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission. Learn how to grant roles.
Create a Cloud Storage bucket in your project.
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the Cloud Storage Buckets page.
- Click Create.
- On the Create a bucket page, enter your bucket information. To go to the next
step, click Continue.
-
In the Get started section, do the following:
- Enter a globally unique name that meets the bucket naming requirements.
- To add a
bucket label,
expand the Labels section (),
click add_box
Add label, and specify a
keyand avaluefor your label.
-
In the Choose where to store your data section, do the following:
- Select a Location type.
- Choose a location where your bucket's data is permanently stored from the Location type drop-down menu.
- If you select the dual-region location type, you can also choose to enable turbo replication by using the relevant checkbox.
- To set up cross-bucket replication, select
Add cross-bucket replication via Storage Transfer Service and
follow these steps:
Set up cross-bucket replication
- In the Bucket menu, select a bucket.
In the Replication settings section, click Configure to configure settings for the replication job.
The Configure cross-bucket replication pane appears.
- To filter objects to replicate by object name prefix, enter a prefix that you want to include or exclude objects from, then click Add a prefix.
- To set a storage class for the replicated objects, select a storage class from the Storage class menu. If you skip this step, the replicated objects will use the destination bucket's storage class by default.
- Click Done.
-
In the Choose how to store your data section, do the following:
- Select a default storage class for the bucket or Autoclass for automatic storage class management of your bucket's data.
- To enable hierarchical namespace, in the Optimize storage for data-intensive workloads section, select Enable hierarchical namespace on this bucket.
- In the Choose how to control access to objects section, select whether or not your bucket enforces public access prevention, and select an access control method for your bucket's objects.
-
In the Choose how to protect object data section, do the
following:
- Select any of the options under Data protection that you
want to set for your bucket.
- To enable soft delete, click the Soft delete policy (For data recovery) checkbox, and specify the number of days you want to retain objects after deletion.
- To set Object Versioning, click the Object versioning (For version control) checkbox, and specify the maximum number of versions per object and the number of days after which the noncurrent versions expire.
- To enable the retention policy on objects and buckets, click the Retention (For compliance) checkbox, and then do the following:
- To enable Object Retention Lock, click the Enable object retention checkbox.
- To enable Bucket Lock, click the Set bucket retention policy checkbox, and choose a unit of time and a length of time for your retention period.
- To choose how your object data will be encrypted, expand the Data encryption section (), and select a Data encryption method.
- Select any of the options under Data protection that you
want to set for your bucket.
-
In the Get started section, do the following:
- Click Create.
Grant the BigQuery Data Editor (
roles/bigquery.dataEditor) role to the Compute Engine default service account,PROJECT_NUMBER-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com. For instructions, see Grant a single role.Google Cloud CLI example:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \ --member PROJECT_NUMBER-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com \ --role roles/bigquery.dataEditor
Notes:
- PROJECT_ID and PROJECT_NUMBER are listed in the Project info section in the Google Cloud console Dashboard.
OSS resources to BigQuery resources mapping
Note the following mapping between open source resource and BigQuery resource terms:
| OSS resource | BigQuery resource |
|---|---|
| Namespace, Database | Dataset |
| Partitioned or Unpartitioned Table | Table |
| View | View |
Create an Iceberg table
This section shows you how to create an Iceberg table with metadata in BigLake metastore using Serverless for Apache Spark Spark SQL and PySpark batch workloads.
Spark SQL
Run a Spark SQL workload to create an Iceberg table
The following steps show you how to run a Serverless for Apache Spark Spark SQL batch workload to create an Iceberg table with table metadata stored in BigLake metastore.
Copy the following Spark SQL commands locally or in Cloud Shell into an
iceberg-table.sqlfile.USE CATALOG_NAME; CREATE NAMESPACE IF NOT EXISTS example_namespace; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS example_table; CREATE TABLE example_table (id int, data string) USING ICEBERG LOCATION 'gs://BUCKET/WAREHOUSE_FOLDER'; INSERT INTO example_table VALUES (1, 'first row'); ALTER TABLE example_table ADD COLUMNS (newDoubleCol double); DESCRIBE TABLE example_table;
Replace the following:
- CATALOG_NAME: Iceberg catalog name.
- BUCKET and WAREHOUSE_FOLDER: Cloud Storage bucket and folder used as Iceberg warehouse directory.
Run the following command locally or in Cloud Shell from the directory containing
iceberg-table.sqlto submit the Spark SQL workload.gcloud dataproc batches submit spark-sql iceberg-table.sql \ --project=PROJECT_ID \ --region=REGION \ --deps-bucket=BUCKET_NAME \ --version=2.2 \ --subnet=SUBNET_NAME \ --properties="spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME=org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.catalog-impl=org.apache.iceberg.gcp.bigquery.BigQueryMetastoreCatalog,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.gcp_project=PROJECT_ID,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.gcp_location=LOCATION,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.warehouse=gs://BUCKET/WAREHOUSE_FOLDER"
Notes:
- PROJECT_ID: Your Google Cloud project ID. Project IDs are listed in the Project info section on the Google Cloud console Dashboard.
- REGION: An available Compute Engine region to run the workload.
- BUCKET_NAME: The name of your Cloud Storage bucket. Spark uploads
workload dependencies to a
/dependenciesfolder in this bucket before running the batch workload. The WAREHOUSE_FOLDER is located in this bucket. --version: Serverless for Apache Spark runtime version 2.2 or later.- SUBNET_NAME: The name of a VPC subnet in the
REGION. If you omit this flag, Serverless for Apache Spark selects thedefaultsubnet in the session region. Serverless for Apache Spark enables Private Google Access (PGA) on the subnet. For network connectivity requirements, see Google Cloud Serverless for Apache Spark network configuration. - LOCATION: A supported BigQuery location. The default location is "US".
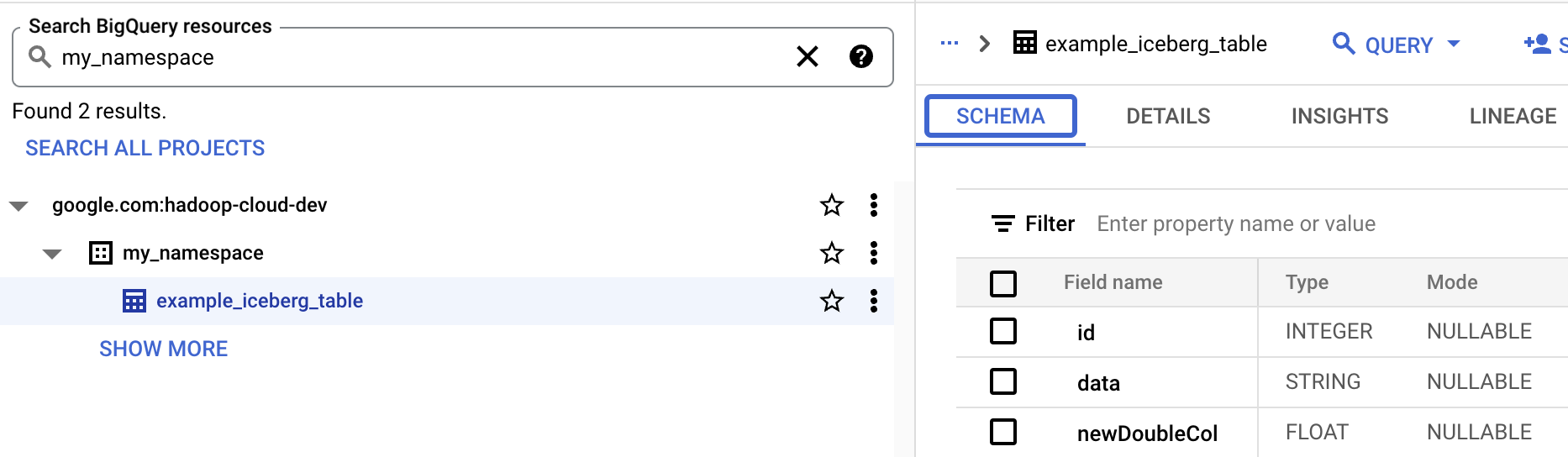
--propertiesCatalog properties.View table metadata in BigQuery
In the Google Cloud console, go to the BigQuery page.
View Iceberg table metadata.
PySpark
The following steps show you how to run a Serverless for Apache Spark PySpark batch workload to create an Iceberg table with table metadata stored in BigLake metastore.
- Copy the following PySpark code locally or in
Cloud Shell
into an
iceberg-table.pyfile.from pyspark.sql import SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("iceberg-table-example").getOrCreate() catalog = "CATALOG_NAME" namespace = "NAMESPACE" spark.sql(f"USE `{catalog}`;") spark.sql(f"CREATE NAMESPACE IF NOT EXISTS `{namespace}`;") spark.sql(f"USE `{namespace}`;") # Create table and display schema spark.sql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS example_iceberg_table") spark.sql("CREATE TABLE example_iceberg_table (id int, data string) USING ICEBERG") spark.sql("DESCRIBE example_iceberg_table;") # Insert table data. spark.sql("INSERT INTO example_iceberg_table VALUES (1, 'first row');") # Alter table, then display schema. spark.sql("ALTER TABLE example_iceberg_table ADD COLUMNS (newDoubleCol double);") spark.sql("DESCRIBE example_iceberg_table;")
Replace the following:
- CATALOG_NAME and NAMESPACE: The Iceberg catalog name
and namespace combine to identify the Iceberg table (
catalog.namespace.table_name).
- CATALOG_NAME and NAMESPACE: The Iceberg catalog name
and namespace combine to identify the Iceberg table (
-
Run the following command locally or in
Cloud Shell
from the directory containing
iceberg-table.pyto submit the PySpark workload.gcloud dataproc batches submit pyspark iceberg-table.py \ --project=PROJECT_ID \ --region=REGION \ --deps-bucket=BUCKET_NAME \ --version=2.2 \ --subnet=SUBNET_NAME \ --properties="spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME=org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.catalog-impl=org.apache.iceberg.gcp.bigquery.BigQueryMetastoreCatalog,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.gcp_project=PROJECT_ID,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.gcp_location=LOCATION,spark.sql.catalog.CATALOG_NAME.warehouse=gs://BUCKET/WAREHOUSE_FOLDER"Notes:
- PROJECT_ID: Your Google Cloud project ID. Project IDs are listed in the Project info section on the Google Cloud console Dashboard.
- REGION: An available Compute Engine region to run the workload.
- BUCKET_NAME: The name of your Cloud Storage bucket. Spark uploads
workload dependencies to a
/dependenciesfolder in this bucket before running the batch workload. --version: Serverless for Apache Spark runtime version 2.2 or later.- SUBNET_NAME: The name of a VPC subnet in the
REGION. If you omit this flag, Serverless for Apache Spark selects thedefaultsubnet in the session region. Serverless for Apache Spark enables Private Google Access (PGA) on the subnet. For network connectivity requirements, see Google Cloud Serverless for Apache Spark network configuration. - LOCATION: A supported BigQuery location. The default location is "US".
- BUCKET and WAREHOUSE_FOLDER: Cloud Storage bucket and folder used as the Iceberg warehouse directory.
--properties: Catalog properties.
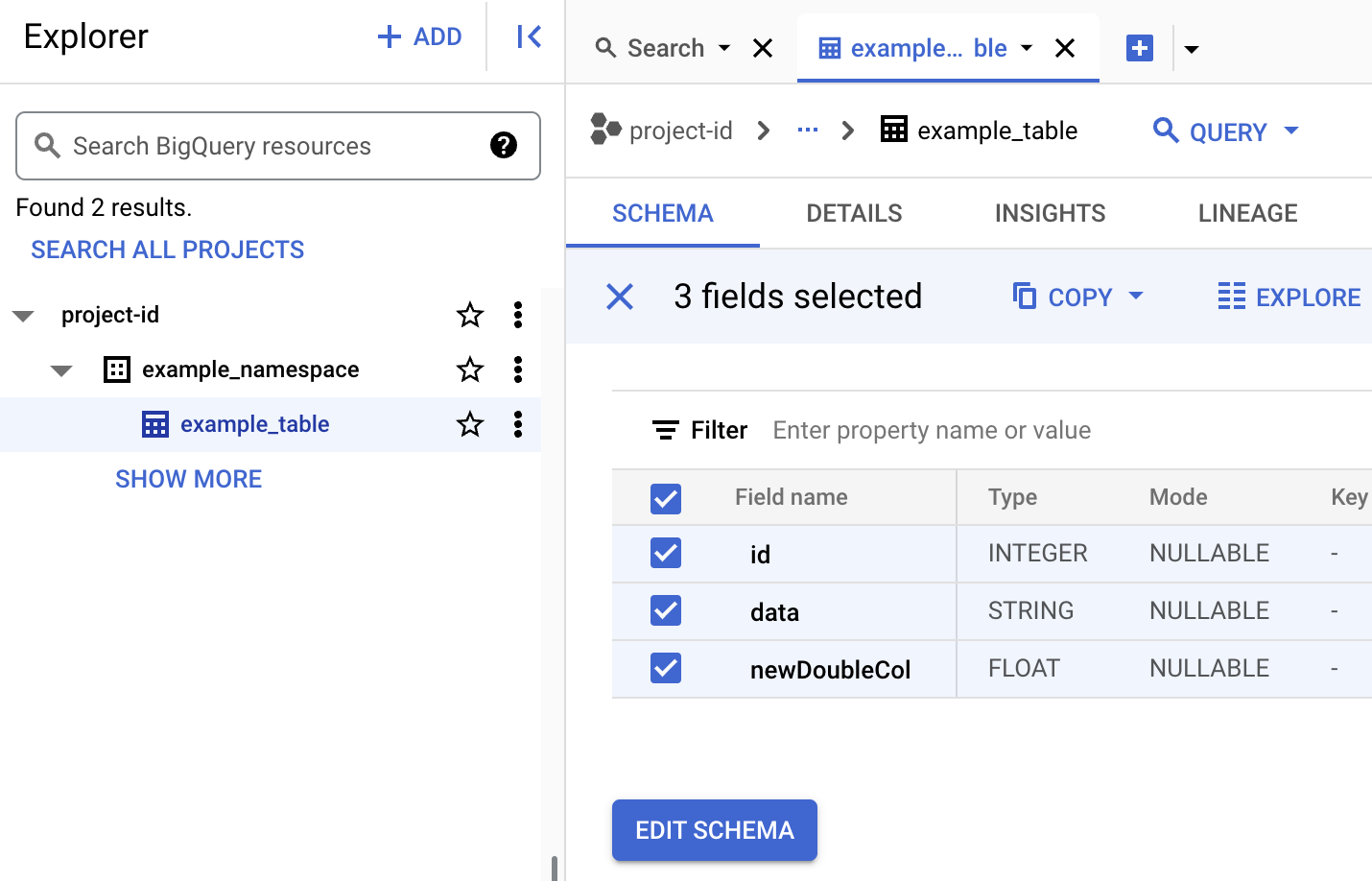
- View table schema in BigQuery.
- In the Google Cloud console, go to the BigQuery page. Go to BigQuery Studio
- View Iceberg table metadata.