Das lokale Transcodieren von Daten auf einem Mainframe ist ein CPU-intensiver Vorgang, der zu einem hohen MIPS-Verbrauch (Millionen von Anweisungen pro Sekunde) führt. Um dies zu vermeiden, können Sie Cloud Run verwenden, um Mainframe-Daten ausGoogle Cloud per Remotezugriff in das optimierte Zeilen/Spalten-Format (ORC) zu verschieben und zu transkodieren und sie dann in Cloud Storage zu verschieben. So wird der Mainframe für geschäftskritische Aufgaben freigegeben und der MIPS-Verbrauch wird reduziert.
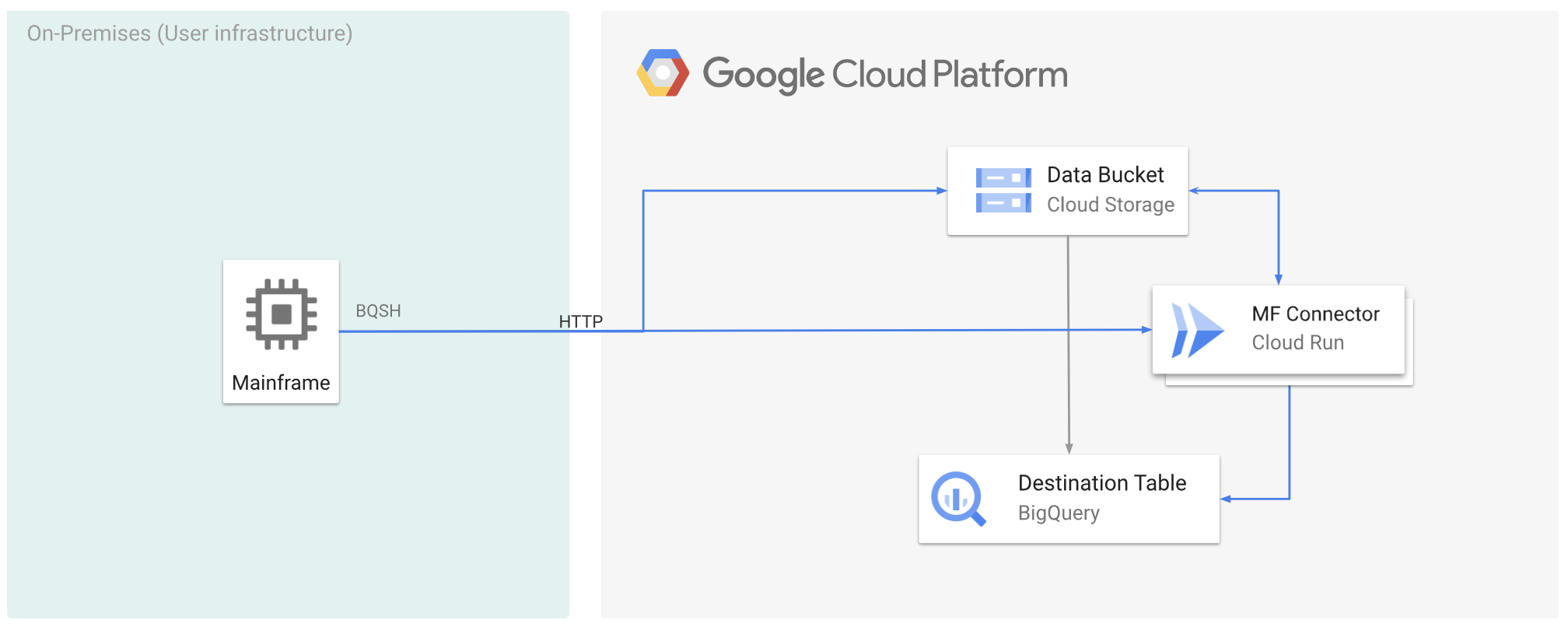
In der folgenden Abbildung wird beschrieben, wie Sie Ihre Mainframe-Daten zuGoogle Cloud verschieben und sie mit Cloud Run aus der Ferne in das ORC-Format umwandeln und dann in BigQuery verschieben.
Hinweise
- Mainframe Connector in Cloud Run bereitstellen
- Erstellen Sie ein Dienstkonto oder identifizieren Sie ein vorhandenes Dienstkonto, das mit Mainframe Connector verwendet werden soll. Dieses Dienstkonto muss Berechtigungen für den Zugriff auf Cloud Storage-Buckets, BigQuery-Datasets und alle anderen Google Cloud Ressourcen haben, die Sie verwenden möchten.
- Prüfen Sie, ob dem von Ihnen erstellten Dienstkonto die Rolle Cloud Run Invoker zugewiesen ist.
Mainframe-Daten zu Google Cloud verschieben und mit Cloud Run per Remote-Zugriff transkodieren Google Cloud
Wenn Sie Ihre Mainframe-Daten zu Google Cloud verschieben und sie per Fernzugriff mit Cloud Run transkodieren möchten, müssen Sie die folgenden Aufgaben ausführen:
- Einen Datensatz auf einem Mainframe lesen und transkodieren und im ORC-Format in Cloud Storage hochladen Die Transcodierung erfolgt während des
gsutil cp-Vorgangs, bei dem ein EBCDIC-Dataset (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) eines Mainframes beim Kopieren in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket in das ORC-Format in UTF-8 konvertiert wird. - Laden Sie das Dataset in eine BigQuery-Tabelle.
- Optional: Führen Sie eine SQL-Abfrage für die BigQuery-Tabelle aus.
- Optional: Daten aus BigQuery in eine Binärdatei in Cloud Storage exportieren.
So führen Sie diese Aufgaben aus:
Erstellen Sie auf Ihrem Mainframe einen Job, um den Datensatz auf Ihrem Mainframe zu lesen und in das ORC-Format umzuwandeln. Gehen Sie dazu so vor: Lesen Sie die Daten aus dem INFILE-Dataset und das Datensatzlayout aus dem COPYBOOK-DD. Der Eingabedatensatz muss eine QSAM-Datei (Queued Sequential Access Method) mit fester oder variabler Datensatzlänge sein.
Eine vollständige Liste der vom Mainframe-Connector unterstützten Umgebungsvariablen finden Sie unter Umgebungsvariablen.
//STEP01 EXEC BQSH //INFILE DD DSN=<HLQ>.DATA.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //COPYBOOK DD DISP=SHR,DSN=<HLQ>.COPYBOOK.FILENAME //STDIN DD * gsutil cp --replace gs://mybucket/tablename.orc --remote \ --remoteHost <mainframe-connector-url>.a.run.app \ --remotePort 443 /*Wenn Sie die während dieses Vorgangs ausgeführten Befehle protokollieren möchten, können Sie Ladestatistiken aktivieren.
Optional: Erstellen und senden Sie einen BigQuery-Abfragejob, der eine SQL-Leseoperation aus der QUERY-DD-Datei ausführt. Normalerweise handelt es sich bei der Abfrage um eine
MERGE- oderSELECT INTO DML-Anweisung, die zur Transformation einer BigQuery-Tabelle führt. Hinweis: Der Mainframe-Connector protokolliert Jobmesswerte, schreibt Abfrageergebnisse aber nicht in eine Datei.Sie können BigQuery auf verschiedene Arten abfragen: inline, mit einem separaten Dataset mit DD oder mit einem separaten Dataset mit DSN.
Example JCL //STEP03 EXEC BQSH //QUERY DD DSN=<HLQ>.QUERY.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //STDIN DD * PROJECT=PROJECT_NAME LOCATION=LOCATION bq query --project_id=$PROJECT \ --location=$LOCATION \ --remoteHost <mainframe-connector-url>.a.run.app \ --remotePort 443/* /*Außerdem müssen Sie die Umgebungsvariable
BQ_QUERY_REMOTE_EXECUTION=truefestlegen.Ersetzen Sie Folgendes:
PROJECT_NAME: Der Name des Projekts, in dem Sie die Abfrage ausführen möchten.LOCATION: Der Ort, an dem die Abfrage ausgeführt wird. Wir empfehlen, die Abfrage an einem Ort auszuführen, der sich in der Nähe der Daten befindet.
Optional: Erstellen und senden Sie einen Exportjob, der eine SQL-Leseoperation aus der QUERY-DD-Datei ausführt und den resultierenden Datensatz als Binärdatei in Cloud Storage exportiert.
Example JCL //STEP04 EXEC BQSH //OUTFILE DD DSN=<HLQ>.DATA.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //COPYBOOK DD DISP=SHR,DSN=<HLQ>.COPYBOOK.FILENAME //QUERY DD DSN=<HLQ>.QUERY.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //STDIN DD * PROJECT=PROJECT_NAME DATASET_ID=DATASET_ID DESTINATION_TABLE=DESTINATION_TABLE BUCKET=BUCKET bq export --project_id=$PROJECT \ --dataset_id=$DATASET_ID \ --destination_table=$DESTINATION_TABLE \ --location="US" \ --bucket=$BUCKET \ --remoteHost <mainframe-connector-url>.a.run.app \ --remotePort 443 /*Ersetzen Sie Folgendes:
PROJECT_NAME: Der Name des Projekts, in dem Sie die Abfrage ausführen möchten.DATASET_ID: Die BigQuery-Dataset-ID, die die Tabelle enthält, die Sie exportieren möchten.DESTINATION_TABLE: Die BigQuery-Tabelle, die Sie exportieren möchten.BUCKET: Der Cloud Storage-Bucket, der die Ausgabedatei enthält.
Nächste Schritte
- Lokalisch transkribierte Mainframe-Daten zu Google Cloud verschieben
- Mainframe-Daten per Fernzugriff auf Google Cloud transcodieren
- Mainframe-Daten, die mit einer virtuellen Bandbibliothek zu Google Cloud verschoben wurden, transcodieren

