Das lokale Transcodieren von Daten auf einem Mainframe ist ein CPU-intensiver Vorgang, der zu einem hohen MIPS-Verbrauch (Millionen von Anweisungen pro Sekunde) führt. Um dies zu vermeiden, können Sie Cloud Run verwenden, um Mainframe-Daten aus der Ferne aufGoogle Cloudzu verschieben und zu transkodieren. So wird Ihr Mainframe für geschäftskritische Aufgaben freigegeben und der MIPS-Verbrauch wird reduziert.
Wenn Sie sehr große Datenmengen (mindestens 500 GB pro Tag) von Ihrem Mainframe zu Google Cloudverschieben möchten, aber Ihren Mainframe dafür nicht verwenden möchten, können Sie eine cloudfähige VTL-Lösung (Virtual Tape Library) verwenden, um die Daten in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket zu übertragen. Anschließend können Sie mit Cloud Run die im Bucket vorhandenen Daten transkodieren und in BigQuery verschieben.
Auf dieser Seite erfahren Sie, wie Sie Mainframe-Daten lesen, die in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket kopiert wurden, sie vom EBCDIC-Dataset (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) in das ORC-Format in UTF-8 umwandeln und den Datensatz in eine BigQuery-Tabelle laden.
Das folgende Diagramm zeigt, wie Sie Ihre Mainframe-Daten mit einer VTL-Lösung in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket verschieben, die Daten mit Cloud Run in das ORC-Format umwandeln und die Inhalte dann in BigQuery verschieben.
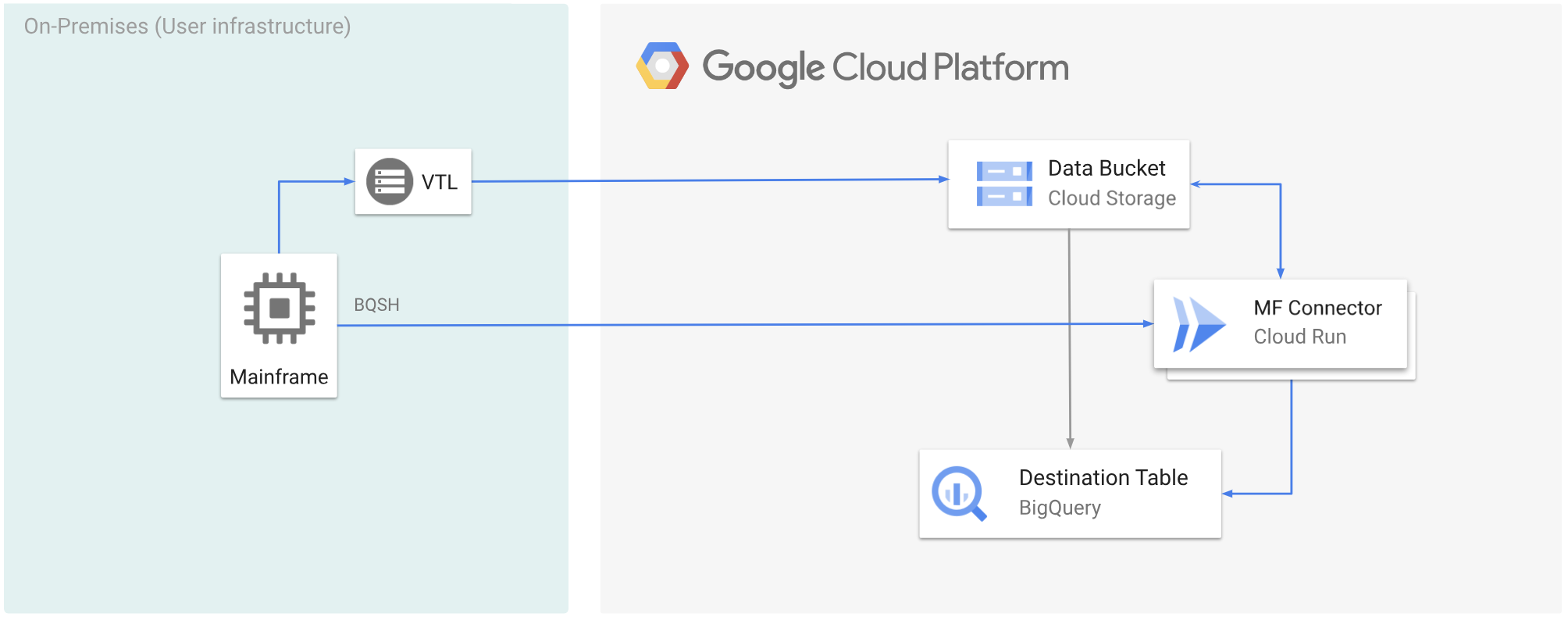
Hinweise
- Wählen Sie eine VTL-Lösung aus, die Ihren Anforderungen entspricht, und verschieben Sie Ihre Mainframe-Daten in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket und speichern Sie sie als
.dat. Achten Sie darauf, dass Sie der hochgeladenen.dat-Datei einen Metadatenschlüssel mit dem Namenx-goog-meta-lreclhinzufügen und dass die Länge des Metadatenschlüssels der Datensatzlänge der ursprünglichen Datei entspricht, z. B. 80. - Mainframe Connector in Cloud Run bereitstellen
- Legen Sie auf dem Mainframe die Umgebungsvariable
GCSDSNURIauf das Präfix fest, das Sie für Ihre Mainframe-Daten im Cloud Storage-Bucket verwendet haben.export GCSDSNURI="gs://BUCKET/PREFIX"
- BUCKET: Der Name des Cloud Storage-Buckets.
- PREFIX: Das Präfix, das Sie im Bucket verwenden möchten.
- Erstellen Sie ein Dienstkonto oder identifizieren Sie ein vorhandenes Dienstkonto, das mit Mainframe Connector verwendet werden soll. Dieses Dienstkonto muss Berechtigungen für den Zugriff auf Cloud Storage-Buckets, BigQuery-Datasets und alle anderen Google Cloud Ressourcen haben, die Sie verwenden möchten.
- Achten Sie darauf, dass dem von Ihnen erstellten Dienstkonto die Rolle Cloud Run-Aufrufer zugewiesen ist.
Mainframe-Daten, die in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket hochgeladen wurden, transkodieren
Wenn Sie Mainframe-Daten mithilfe von VTL zu Google Cloud verschieben und aus der Ferne transkodieren möchten, müssen Sie die folgenden Aufgaben ausführen:
- Daten in einem Cloud Storage-Bucket lesen und in das ORC-Format umwandeln. Bei der Transcodierung wird ein EBCDIC-Dataset eines Mainframes in das ORC-Format in UTF-8 konvertiert.
- Laden Sie das Dataset in eine BigQuery-Tabelle.
- Optional: Führen Sie eine SQL-Abfrage für die BigQuery-Tabelle aus.
- Optional: Daten aus BigQuery in eine Binärdatei in Cloud Storage exportieren.
So führen Sie diese Aufgaben aus:
Erstellen Sie auf Ihrem Mainframe einen Job, um die Daten aus einer
.dat-Datei in einem Cloud Storage-Bucket zu lesen und in das ORC-Format zu transkodieren. Gehen Sie dazu so vor:Eine vollständige Liste der vom Mainframe-Connector unterstützten Umgebungsvariablen finden Sie unter Umgebungsvariablen.
//STEP01 EXEC BQSH //COPYBOOK DD DISP=SHR,DSN=<HLQ>.COPYBOOK.FILENAME //STDIN DD * gsutil cp --replace gs://mybucket/tablename.orc \ --inDsn INPUT_FILENAME \ --remoteHost <mainframe-connector-url>.a.run.app \ --remotePort 443 \ --project_id PROJECT_NAME /*Ersetzen Sie Folgendes:
PROJECT_NAME: Der Name des Projekts, in dem Sie die Abfrage ausführen möchten.INPUT_FILENAME: Der Name der.dat-Datei, die Sie in einen Cloud Storage-Bucket hochgeladen haben.
Wenn Sie die während dieses Vorgangs ausgeführten Befehle protokollieren möchten, können Sie Ladestatistiken aktivieren.
Optional: Erstellen und senden Sie einen BigQuery-Abfragejob, der eine SQL-Leseoperation aus der QUERY-DD-Datei ausführt. Normalerweise handelt es sich bei der Abfrage um eine
MERGE- oderSELECT INTO DML-Anweisung, die zur Transformation einer BigQuery-Tabelle führt. Hinweis: Der Mainframe-Connector protokolliert Jobmesswerte, schreibt Abfrageergebnisse aber nicht in eine Datei.Sie können BigQuery auf verschiedene Arten abfragen: inline, mit einem separaten Dataset mit DD oder mit einem separaten Dataset mit DSN.
Example JCL //STEP03 EXEC BQSH //QUERY DD DSN=<HLQ>.QUERY.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //STDIN DD * PROJECT=PROJECT_NAME LOCATION=LOCATION bq query --project_id=$PROJECT \ --location=$LOCATION/* /*Ersetzen Sie Folgendes:
PROJECT_NAME: Der Name des Projekts, in dem Sie die Abfrage ausführen möchten.LOCATION: Der Ort, an dem die Abfrage ausgeführt wird. Wir empfehlen, die Abfrage an einem Ort auszuführen, der sich in der Nähe der Daten befindet.
Optional: Erstellen und senden Sie einen Exportjob, der eine SQL-Leseoperation aus der QUERY-DD-Datei ausführt und den resultierenden Datensatz als Binärdatei in Cloud Storage exportiert.
Example JCL //STEP04 EXEC BQSH //OUTFILE DD DSN=<HLQ>.DATA.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //COPYBOOK DD DISP=SHR,DSN=<HLQ>.COPYBOOK.FILENAME //QUERY DD DSN=<HLQ>.QUERY.FILENAME,DISP=SHR //STDIN DD * PROJECT=PROJECT_NAME DATASET_ID=DATASET_ID DESTINATION_TABLE=DESTINATION_TABLE BUCKET=BUCKET bq export --project_id=$PROJECT \ --dataset_id=$DATASET_ID \ --destination_table=$DESTINATION_TABLE \ --location="US" \ --bucket=$BUCKET \ --remoteHost <mainframe-connector-url>.a.run.app \ --remotePort 443 /*Ersetzen Sie Folgendes:
PROJECT_NAME: Der Name des Projekts, in dem Sie die Abfrage ausführen möchten.DATASET_ID: Die BigQuery-Dataset-ID, die die Tabelle enthält, die Sie exportieren möchten.DESTINATION_TABLE: Die BigQuery-Tabelle, die Sie exportieren möchten.BUCKET: Der Cloud Storage-Bucket, der die Ausgabedatei enthält.

