Change Data Capture (CDC) processing
This page guides you through Change Data Capture (CDC) within Google Cloud Cortex Framework in BigQuery. BigQuery is designed for efficiently storing and analyzing new data.
CDC process
When data changes in your source data system (like SAP), BigQuery doesn't modify existing records. Instead, the updated information is added as a new record. To avoid duplicates, a merge operation needs to be applied afterwards. This process is called Change Data Capture (CDC) processing.
The Data Foundation for SAP includes the option to create scripts for
Cloud Composer or Apache Airflow to merge
or upsert the new records resulting from updates and only keep the
latest version in a new dataset. For these scripts to work the tables
need to have some specific fields:
operation_flag: This flag tells the script whether a record was inserted, updated, or deleted.recordstamp: This timestamp helps identify the most recent version of a record. This flag indicates whether the record is:- Inserted (I)
- Updated (U)
- Deleted (D)
By utilizing CDC processing, you can ensure that your BigQuery data accurately reflects the latest state of your source system. This eliminates duplicate entries and provides a reliable foundation for your data analysis.
Dataset structure
For all supported data sources, data from upstream systems are first replicated
into a BigQuery dataset (source or replicated dataset),
and the updated or merged results are inserted into another dataset
(CDC dataset). The reporting views select data from the CDC dataset,
to ensure the reporting tools and applications always have the latest version
of a table.
The following flow shows how the CDC processing for SAP, dependent on
the operational_flag and recordstamp.
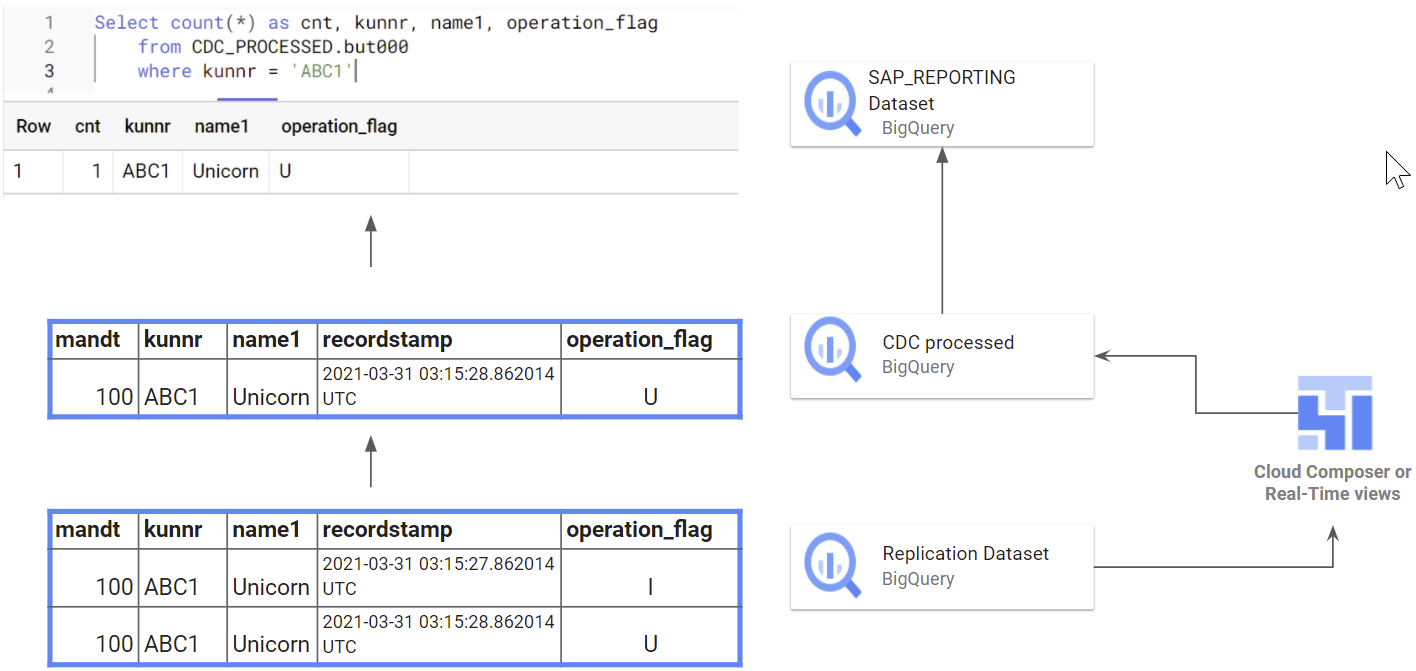
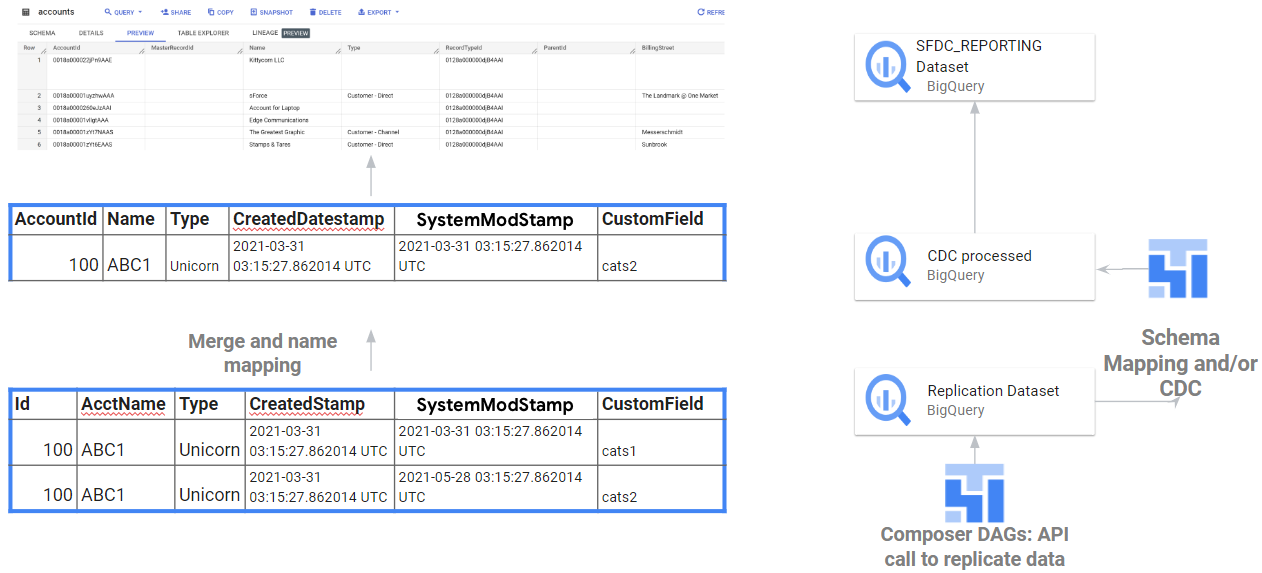
The following flow depicts the integration from APIs into Raw data and
CDC processing for Salesforce, dependent on the Id and SystemModStamp
fields produced by Salesforce APIs.
Some replication tools can merge or upsert the records when inserting them into BigQuery, so the generation of these scripts is optional. In this case, the setup only has a single dataset. The reporting dataset fetches updated records for reporting from that dataset.
