Kasus penggunaan: Memecahkan masalah konektivitas jaringan
Dalam kasus penggunaan ini, Anda adalah administrator jaringan yang mendukung jaringan yang menyertakan beberapa aplikasi yang di-load balance. Anda telah diberi tahu tentang masalah latensi dan telah diberi tahu bahwa aplikasi seluler organisasi Anda secara berkala lambat dan waktu tunggunya habis. Anda tahu bahwa sejumlah pengguna yang berbeda terpengaruh, dan belum ada deployment aplikasi baru-baru ini. Masalah ini kemungkinan terkait dengan perubahan lingkungan, bukan aplikasi.
Kasus penggunaan berikut menunjukkan cara Topologi Jaringan dapat membantu Anda memecahkan masalah dan menyelidiki masalah dalam deployment dengan cepat.
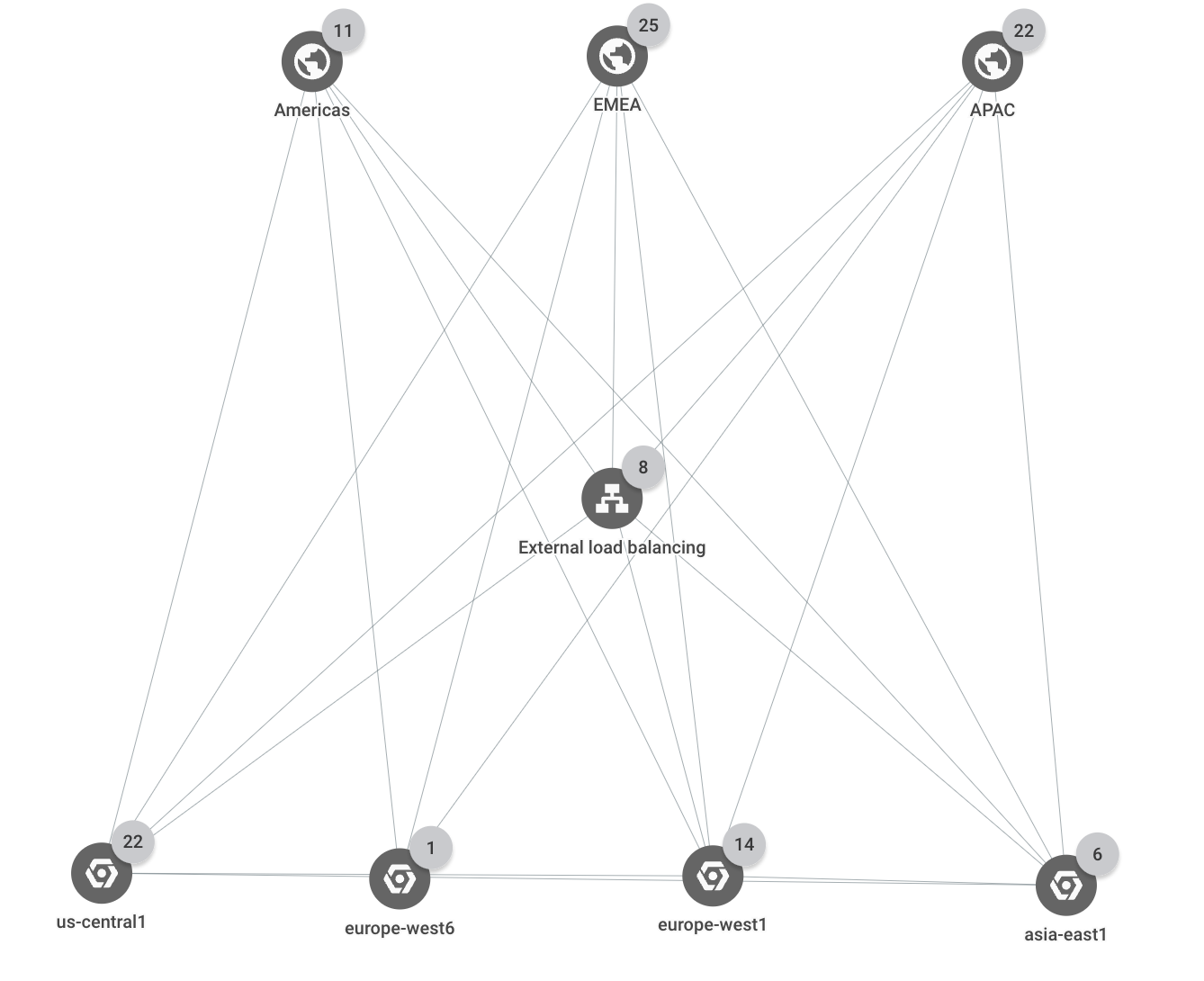
Detail topologi
Deployment ini mencakup tiga Google Cloud region (us-central1,
europe-west1, dan asia-east1). Semua permintaan klien eksternal ditayangkan oleh
satu Load Balancer Aplikasi eksternal yang memiliki beberapa backend di setiap dari tiga
region tersebut. Permintaan klien yang berasal dari salah satu dari tiga region bisnis (Amerika,
EMEA, dan APAC) ditayangkan oleh instance aplikasi di regionGoogle Cloud
terdekat.
Topologi berikut menunjukkan hierarki tingkat teratas untuk deployment:
Latensi jaringan
Dalam skenario ini, asumsikan Anda memiliki load balancer bernama shopping-site-lb.
Anda memeriksa latensi antara klien eksternal dan load balancer untuk melihat apakah
latensi di antara keduanya telah berubah. Anda mendapati bahwa hal itu telah terjadi dan memutuskan untuk
menyelidiki backend load balancer lebih lanjut.
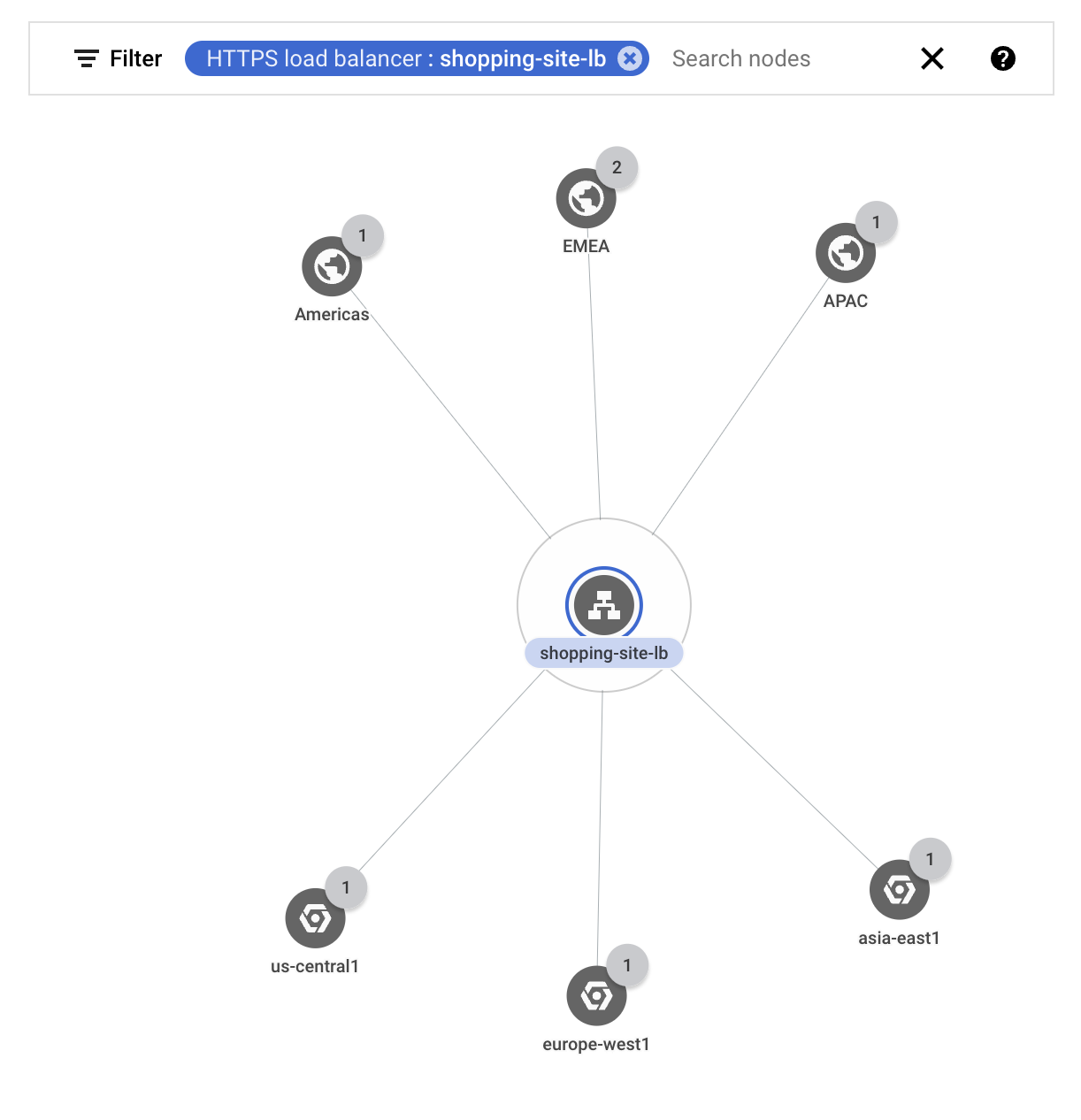
Anda memfilter topologi untuk hanya menampilkan traffic untuk load balancer eksternal
shopping-site-lb.Setelah Anda menerapkan filter, Network Topology hanya akan menampilkan koneksi yang terkait dengan load balancer, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam contoh berikut.
Mulai dari klien eksternal di Amerika, Anda mengklik metrik traffic antara region bisnis Amerika dan load balancer.
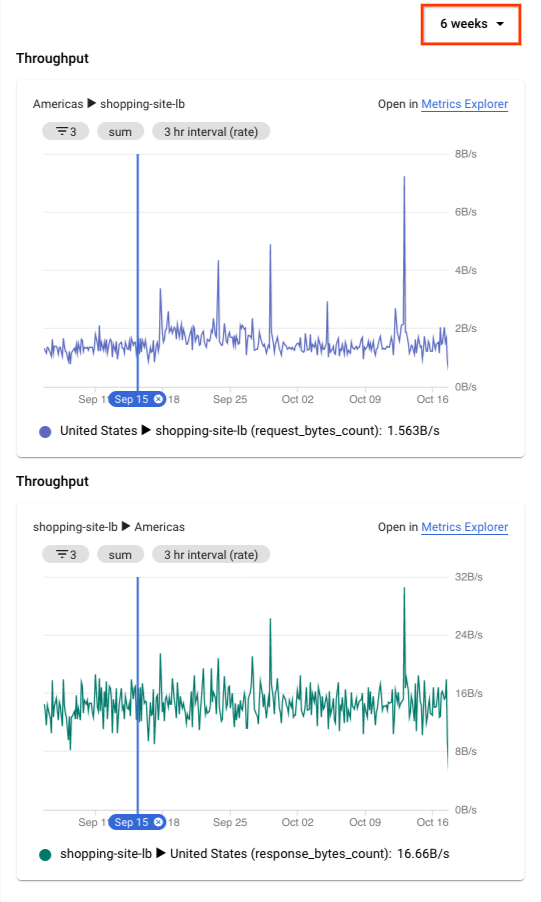
Topologi Jaringan menampilkan diagram di panel detail. Informasi ini mencakup traffic masuk dan keluar antara entity yang Anda pilih dan entity yang terhubung. Misalnya, Topologi Jaringan memberikan nilai terbaru untuk kueri per detik (QPS) dan latensi permintaan HTTP.
Dalam diagram latensi permintaan, Anda akan melihat nilai untuk persentil ke-50, ke-95, dan ke-99. Dalam contoh ini, asumsikan bahwa semua nilai latensi lebih tinggi dari yang Anda harapkan.
Untuk meluaskan diagram deret waktu menjadi 6 minggu, di bagian atas panel detail, pilih 6 minggu.
1Gambar ini hanya untuk referensi. Datanya tidak mencerminkan kasus penggunaan.
Anda melihat lonjakan signifikan yang terjadi sekitar dua jam yang lalu, kira-kira saat masalah pertama dilaporkan. Anda yakin bahwa masalah tersebut terkait dengan peningkatan latensi pada load balancer.
Setelah memiliki gambaran umum tentang masalah tersebut, Anda akan menyelidiki load balancer lebih lanjut dengan membuka halaman Load balancing di konsol Google Cloud . Anda akhirnya mendapati bahwa instance dalam layanan backend load balancer memerlukan waktu lebih lama dari biasanya untuk merespons. Anda menghentikan instance tersebut, yang akan menyelesaikan masalah.
Langkah berikutnya
- Memantau konfigurasi jaringan dengan Topologi Jaringan
- Kasus penggunaan: Mengaudit performa jaringan
- Memecahkan Masalah Topologi Jaringan