This page describes how customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK) work with Memorystore for Valkey. To begin using this feature, see Use customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK).
By default, Memorystore for Valkey encrypts customer content at rest. Memorystore for Valkey handles encryption for you without any additional actions on your part. This option is called Google default encryption.
If you want to control your encryption keys, then you can use customer-managed encryption keys (CMEKs) in Cloud KMS with CMEK-integrated services including Memorystore for Valkey. Using Cloud KMS keys gives you control over their protection level, location, rotation schedule, usage and access permissions, and cryptographic boundaries. Using Cloud KMS also lets you track key usage, view audit logs, and control key lifecycles. Instead of Google owning and managing the symmetric key encryption keys (KEKs) that protect your data, you control and manage these keys in Cloud KMS.
After you set up your resources with CMEKs, the experience of accessing your Memorystore for Valkey resources is similar to using Google default encryption. For more information about your encryption options, see Customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK).
Who should use CMEK?
CMEK is intended for organizations that have sensitive or regulated data that must be encrypted. For more information about whether to use CMEK to encrypt this data, see Decide whether to use CMEK.
Google-managed encryption versus customer-managed encryption
The CMEK feature lets you use your own cryptographic keys for data at rest in Memorystore for Valkey. For CMEK-enabled Memorystore for Valkey instances, Google uses your keys to access all data at rest.
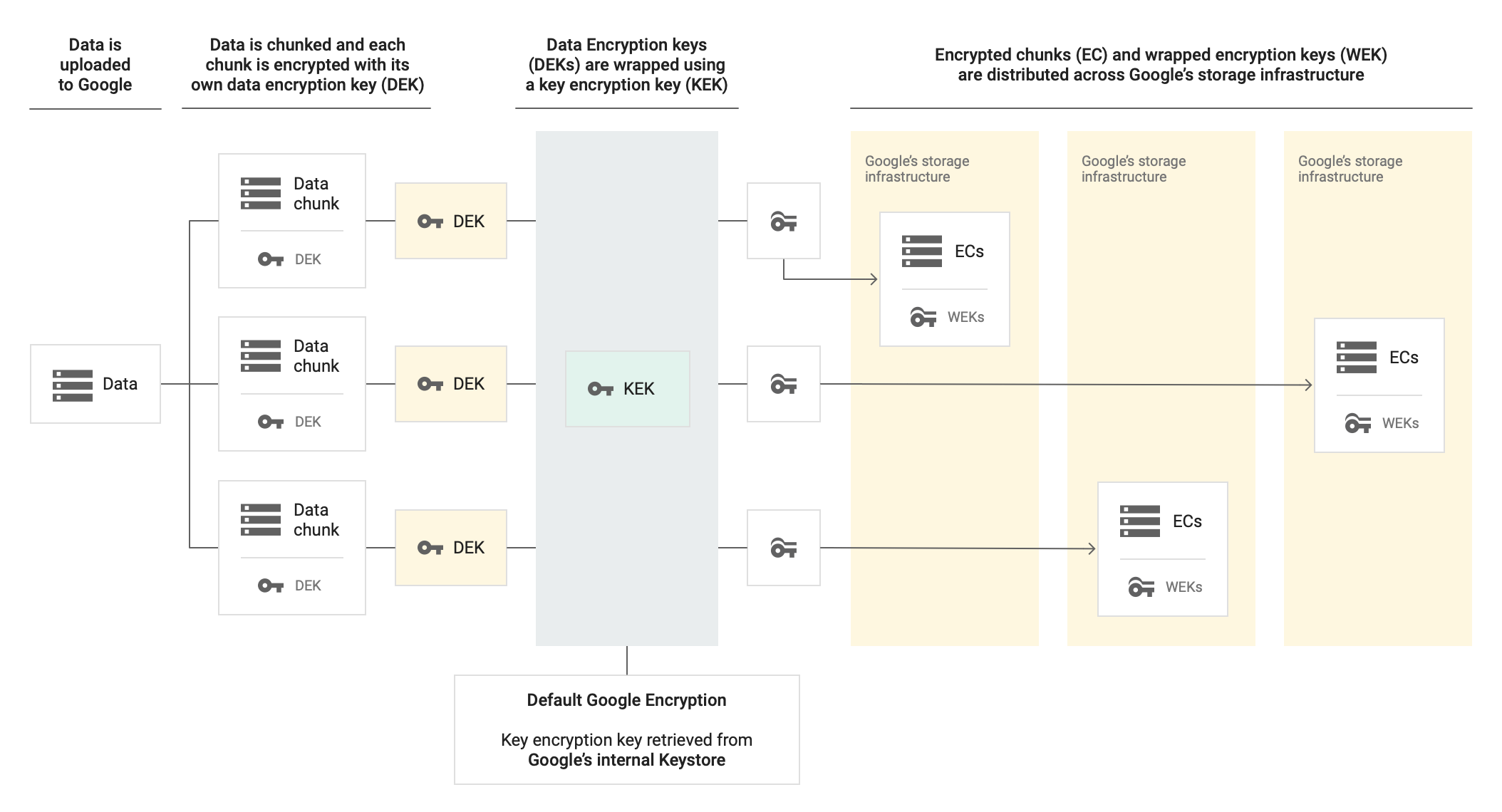
Memorystore uses Google-managed data encryption keys (DEK) and key encryption keys (KEK) to encrypt data in Memorystore for Valkey. There are two levels of encryption:
- DEK encryption: Memorystore uses DEKs to encrypt data in Memorystore for Valkey.
- KEK encryption: Memorystore uses KEKs to encrypt DEKs.
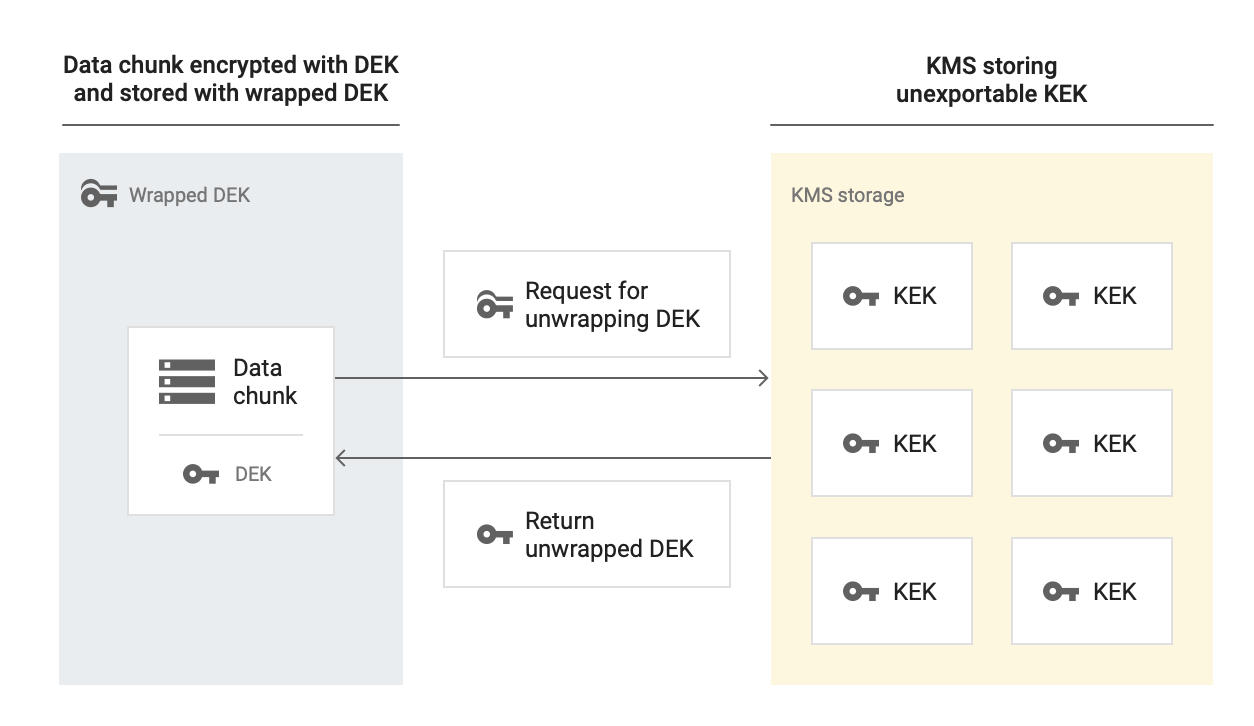
The Memorystore for Valkey instance stores the encrypted DEK alongside the encrypted data on disk and Google manages the Google KEK. The CMEK is the KEK that wraps the DEK. CMEK lets you create, disable or destroy, rotate, and enable or restore the KEK.
The following diagrams show how data-at-rest encryption works inside a Memorystore for Valkey instance when using default Google-managed encryption versus CMEK.
Without CMEK
With CMEK
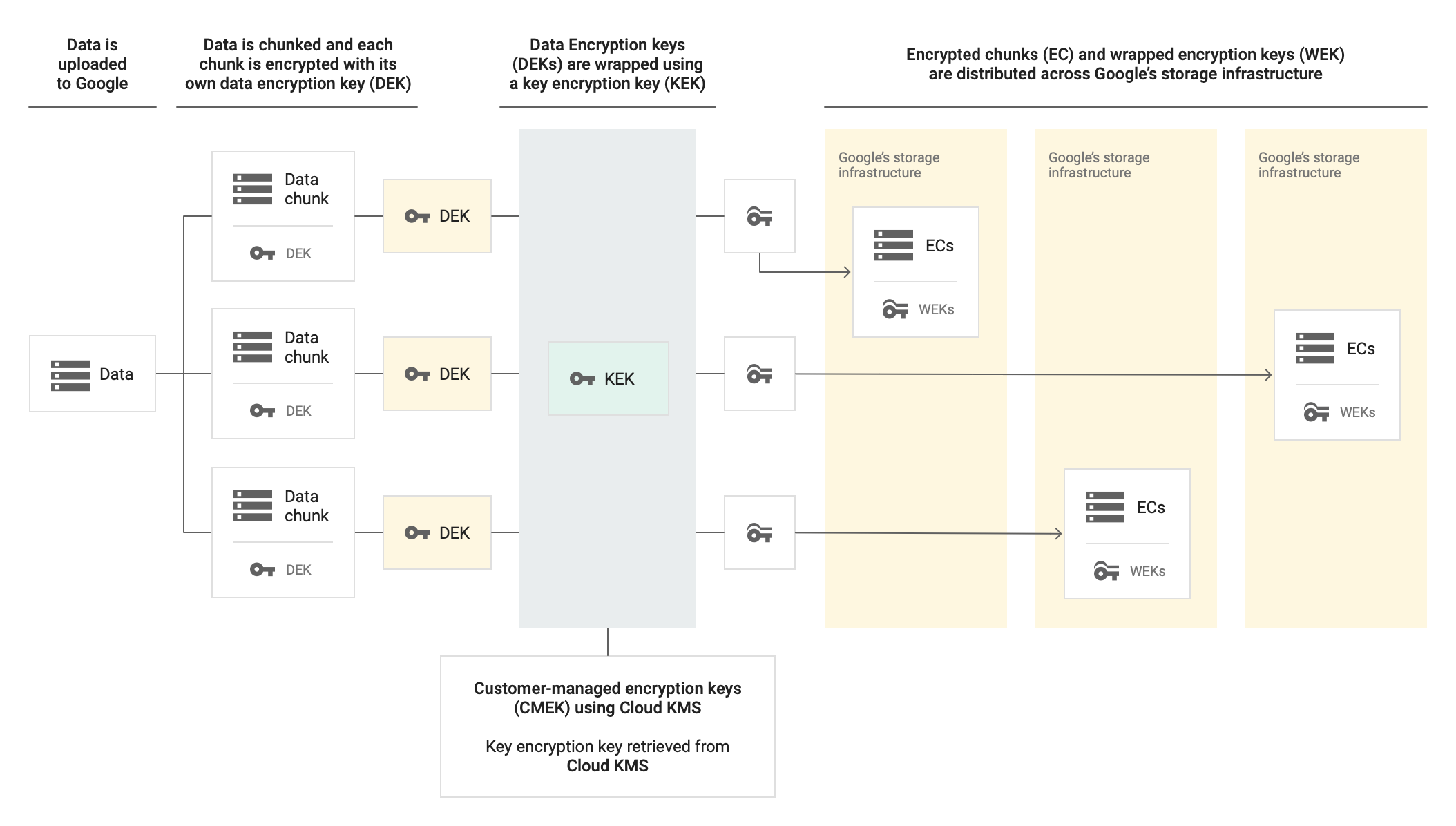
When decrypting data wrapped with CMEK, Memorystore uses the KEK from Cloud Key Management Service to decrypt the DEK and the unencrypted DEK to decrypt data at rest.
Pricing
Memorystore for Valkey bills for a CMEK-enabled instance just like any other instance; there are no additional costs. For more information, see Memorystore for Valkey pricing.
You use the Cloud KMS API to manage CMEK. When you create a Memorystore for Valkey instance with CMEK, Memorystore uses the key periodically to encrypt data.
You're billed by Cloud KMS for the cost of the key and for encryption and decryption operations when Memorystore for Valkey uses the key. For more information, see Cloud KMS pricing.
Which data is encrypted using CMEK?
CMEK encrypts the following types of customer data that are stored in persistent storage:
- Backups: Backups let you recover your data to a point in time, and export and analyze data. Backups are also useful for disaster recovery, data migration, data sharing, and compliance scenarios.
- Persistence:
Memorystore for Valkey supports two types of persistence:
- RDB persistence: This feature protects your data by saving snapshots of your data on durable storage.
- AOF persistence: This feature prioritizes data durability. It stores data durably by recording every write command to a log file called the Append-Only File (AOF). If a system failure or restart occurs, then the server replays AOF file commands sequentially to restore your data.
About service accounts
When creating an instance with CMEK you must grant the
cloudkms.cryptoKeyEncrypterDecrypter role to the Memorystore for Valkey
service account that has the following format:
service-PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-memorystore.iam.gserviceaccount.com
Granting this permission allows the service account to request key access from Cloud KMS.
For instructions on granting this permission to the service account, see Grant the Memorystore for Valkey service account access to the key.
About keys
In Cloud KMS, you need to create a key ring with a cryptographic key that uses a symmetric encryption algorithm. When you create a new Memorystore for Valkey instance, you select this key to encrypt the instance. You can create one project for both your keys and instances, or different projects for each of them.
CMEK is available in all Memorystore for Valkey instance locations. You must create the key ring and key in the same region where you want to create the instance. For a multi-region instance, you must set the key ring and key to the same location as the instance. If the regions or locations don't match, then a request for creating the instance fails.
For the resource ID of the key, CMEK uses the following format:
projects/CMEK_ENABLED_PROJECT/locations/REGION/keyRings/KEY_RING_NAME/cryptoKeys/KEY_NAME
External keys
You can use Cloud External Key Manager (Cloud EKM) to encrypt data within Google Cloud using external keys that you manage.
When you use a Cloud EKM key, Google has no control over the availability of your externally managed key. If the key isn't available when you create your instance, then the instance isn't created.
For more considerations when using external keys, see Cloud External Key Manager.
How do you make CMEK-encrypted data inaccessible permanently?
You might have situations where you want to destroy data encrypted with CMEK permanently. To do this, you destroy the key version. For more information about destroying versions of the key, see Destroy and restore key versions.
Behavior of a CMEK key version
This section provides information about what happens when you disable, destroy, rotate, enable, and restore a key version.
Disable or destroy a CMEK key version
If you disable or destroy the primary key version of your CMEK, then the following conditions apply for backups and persistence.
Backups
- You can't create on-demand or automated backups. However, if you enable an older key version, then you can access any backups that you created using this key version.
- You can't update or re-enable automated backups until you enable or restore the primary key version.
Persistence
- If you configure your instance to use persistence, then Memorystore for Valkey deactivates the persistence feature when the key version becomes unavailable. You're no longer charged for this feature.
- Memorystore for Valkey doesn't flush new data to persistent storage using the CMEK.
- Memorystore for Valkey can't read existing data that's present in the persistent storage.
- You can't update or re-enable persistence until you enable or restore the primary key version.
If you enable the primary key version of your CMEK, but you disable or destroy an older key version, then the following conditions apply for backups and persistence:
- You can create backups. However, if a backup is encrypted with an older key version that's disabled or destroyed, then the backup remains inaccessible.
- If you enable persistence, then this feature remains enabled. If the older key version that's used in persistence is disabled or destroyed, then Memorystore for Valkey performs an update that's similar to the one that's used in maintenance and re-encrypts the data with the primary key version.
Rotate the primary CMEK key version
If you rotate the primary key version of your CMEK and create a new primary key version, then the following conditions apply for backups and persistence:
- The latest primary key version of your CMEK encrypts new backups.
- For existing backups, no re-encryption is done.
- For persistence, the nodes don't take any action. The nodes continue to use the older key version until the next maintenance event.
Enable or restore the primary CMEK key version
If you enable or restore the primary key version of your CMEK, then the following conditions apply for backups and persistence:
- You can create on-demand and automated backups again.
- Memorystore for Valkey performs an update that's similar to the one used in maintenance and re-enables persistence.
Limitations
The following limitations apply when using CMEK with Memorystore for Valkey:
- You can't enable CMEK on an existing Memorystore for Valkey instance.
- The region for the key, key ring, and instance must all be the same.
- You must use the symmetric encryption algorithm for your key.
- Cloud KMS encryption and decryption rates are subject to a quota.
