Clients can connect to a Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster from any Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network in your Google Cloud projects.
This page explains how networking is configured in Managed Service for Apache Kafka, how to enable connections between Kafka clients and your cluster, and how to enable cross-project connectivity.
Overview
When you create a cluster, the service places it in a VPC network that is managed by Google Cloud. This network is called the tenant network. Each Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster has its own isolated tenant network. To enable client applications to communicate with the cluster, you connect subnets within your VPC networks to the tenant network.
The following diagram shows two Google Cloud projects, project-1 and
project-2. A Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster is located in
project-1.
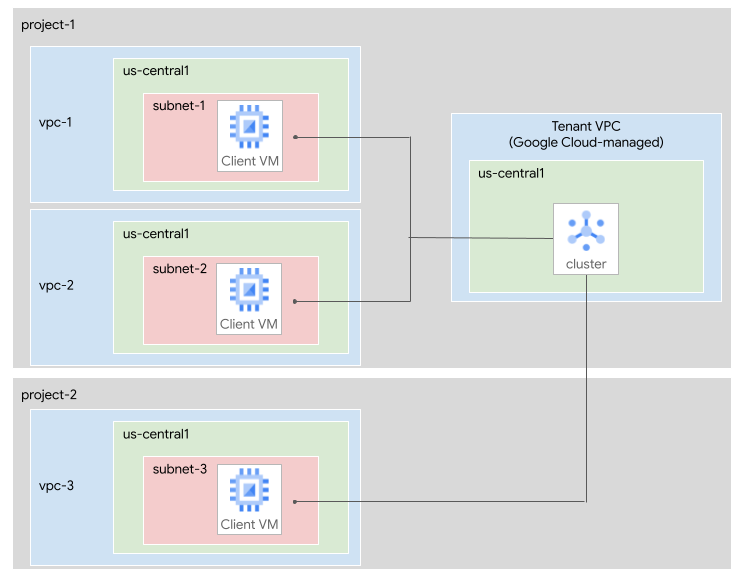
The following subnets are connected to the cluster:
subnet-1, in the VPC networkvpc-1inproject-1.subnet-2, in the VPC networkvpc-2inproject-1.subnet-3, in the VPC networkvpc-3inproject-2.
Connect subnets to a cluster
When you first create a Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster, you must specify at least one subnet. Later, you can update the cluster to add or remove subnets.
Connected subnets can belong to the same Google Cloud project as the cluster or a different project. Connected subnets must be in the same region as the cluster, but clients in any region within the same VPC can connect to the IP addresses in that subnet. At most one subnet per VPC network can be connected to the cluster.
To view the subnets that are connected to a cluster, see View a cluster's subnets.
Cluster DNS entries
When you connect a subnet to a cluster, the service creates DNS entries within that subnet network for the cluster's bootstrap address and brokers. Kafka clients use the bootstrap address to locate the brokers and establish a connection.
The DNS names are the same across all connected subnets, although they correspond to different IP addresses in each subnet. Because the DNS names are consistent, all of your Kafka client applications can use the same bootstrap address. To get the cluster's bootstrap address, see View a cluster's bootstrap address.
For examples of client applications that connect to Managed Service for Apache Kafka, see the following tutorials:
Subnet sizing
When you add a subnet to a cluster, the subnet must have enough IP addresses available. Each subnet requires one IP address for each Kafka broker, plus one IP address for the bootstrap address. The minimum cluster size for Managed Service for Apache Kafka has three brokers, so each subnet needs at least four usable IP addresses including the bootstrap address.
If your cluster has more than 45 vCPUs, then the cluster has one broker for every 15 vCPUs. In that case, calculate the minimum number of IP addresses for each subnet as follows:
- Divide the number of vCPUs by 15.
- Round up to the nearest whole number.
- Add 1 to account for the bootstrap address.
For example, a cluster with 60 vCPUs needs at least (60/15 + 1) = 5 usable IP addresses.
Google might change the ratio of brokers to vCPUs in the future. To accommodate any future changes, we recommended that you allocate 3x the number of IP addresses calculated in the previous step.
When you plan the subnet size, base your calculations on the maximum size that you expect to scale your cluster in the future.
Privately used public IP ranges
You can connect your cluster to subnets that use the non-RFC 1918 address space. Such IP address ranges are called privately used public IP (PUPI) ranges.
No additional configuration is required to connect to PUPI subnets. The PUPI subnets must use a valid IPv4 range that is not a prohibited IPv4 subnet range.
Connect clients and clusters across projects
If you have Kafka clients in different Google Cloud projects, you can connect them to your cluster in the following ways:
The next sections describe these options.
Connect a cluster across projects
You can connect subnets from other projects to your cluster. To enable cross-project access, you must grant permissions to the Google-managed service account that is associated with the cluster. For each project where you want Kafka clients to access the cluster, the service account must have the Managed Kafka Service Agent IAM role on that project. This role enables the cluster to access Google Cloud resources, so that it can create network resources and DNS entries.
Example: If project-1 contains the cluster, and you want clients in
project-2 to access the cluster, then grant the Managed Kafka service account
for project-1 the Managed Kafka Service Agent role on project-2. Then
connect a subnet from project-2 to the cluster, as described in
Connect subnets to the cluster.
To grant the necessary roles, perform the following steps:
Console
Determine the Google Cloud projects where you want your Kafka clients to access the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster.
For each project, in the Google Cloud console, go to the IAM page for that project:
Click Grant access.
In the New principals field, enter the following:
service-CLUSTER_PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-managedkafka.iam.gserviceaccount.comReplace CLUSTER_PROJECT_NUMBER with the project number of the project that contains the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster.
Click Add roles.
In the Search for roles field, enter
Managed Kafka Service Agent. The service agent name appears in the search results.In the search results, select Managed Kafka Service Agent.
Click Apply.
Click Save.
gcloud
Determine the Google Cloud projects where you want your Kafka clients to access the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster.
For each project, run the
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-bindingcommand:gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding CLIENT_PROJECT_ID \ --member=serviceAccount:service-CLUSTER_PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-managedkafka.iam.gserviceaccount.com \ --role=roles/managedkafka.serviceAgentReplace the following:
- CLIENT_PROJECT_ID: the name of the project that contains the VPC network to connect
- CLUSTER_PROJECT_NUMBER: the project number of the project that contains the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster
Use Shared VPC to connect projects
Shared VPC allows an organization to connect resources from multiple projects to a common VPC network. To use Shared VPC with Managed Service for Apache Kafka, perform the following steps:
Create a Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster.
Grant the Managed Kafka service account the required roles in the Shared VPC host project, as described in the previous section.
Connect the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster to a subnet in the Shared VPC network.
Clients in the Shared VPC host project or in the service projects can connect to the cluster.
For information about when to use Shared VPC in your network architectures, see Best practices and reference architectures for VPC design.
Network architecture of a cluster
This section describes the details of the networking architecture used in Managed Service for Apache Kafka.
A Kafka cluster spans a tenant network and one or more consumer networks.
In the tenant network, the cluster has a single bootstrap IP address and URL. This bootstrap address corresponds to a load balancer connected to all the brokers in the cluster. Each broker individually can also act as a bootstrap server, but we recommend you use the bootstrap address for reliability.
Within each consumer network, the service creates a Private Service Connect endpoint for the bootstrap address and one endpoint for each broker.
The URL for the bootstrap address is the same across the VPC networks to which a cluster is connected. The IP address is local to the consumer network.
Clients connect to Kafka brokers by using DNS names. These names are registered automatically in every VPC network to which a Kafka cluster is connected. The bootstrap address and its port number are available as a property of the cluster.
Clients use the bootstrap address to retrieve broker URLs. These URLs are resolved to IP addresses local to each VPC network. You can find the actual broker IP addresses and URLs in Cloud DNS.
The following diagram shows a sample architecture of a Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster network.
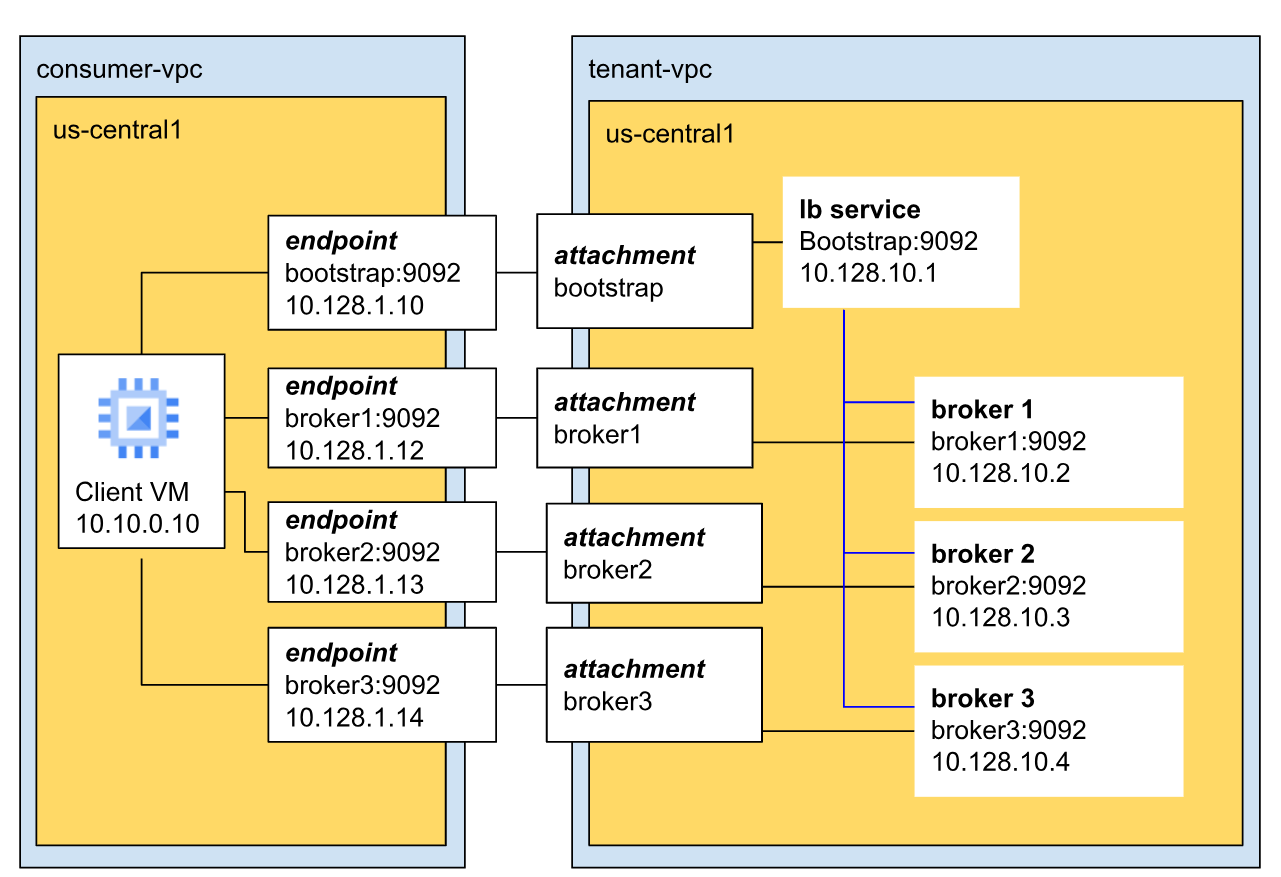
In this example, the cluster has three brokers and the cluster is in the tenant VPC.
Brokers communicate with clients over the default Kafka port (9092) and have unique IP addresses. In this example, the three brokers have IP addresses 10.128.10.2, 10.128.10.3, and 10.128.10.4 respectively.
All three brokers connect to the bootstrap load balancer. This ensures high availability and regional fault tolerance, because the bootstrap address isn't confined to a single broker or zone.
Troubleshoot VPC network configuration
If the service can't configure the consumer VPC network for access to Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster, it logs messages similar to the following:
Managed Service for Apache Kafka failed to set up networking in VPC subnet
to the cluster project.
If your Kafka clients fail to connect to a Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster, perform the following troubleshooting steps:
Enable the Compute Engine and Cloud DNS APIs in the parent project of the consumer VPC network.
If the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster and consumer VPC network are in different projects, configure the required permissions. See Connect a cluster across projects.
Ensure that no organization policy constraints prevent the service from creating the necessary resources in the consumer VPC network's project.
Make sure that clients are using the correct bootstrap address.
Ensure that the Kafka clients run in a VPC network that is configured to access the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster.
If you run the Kafka client on a computer or laptop, you can set up a Compute Engine instance to use as a proxy to access to the Managed Service for Apache Kafka cluster. For more information, see Set up a client machine.
