It's common for users to want to interact with short numbers. For example, they prefer $2.5M to a long string like $2,523,093.25. You can build short-number displays by creating multiple defined LookML measures, such as one to display as-is, one divided by 1,000, or one with limited decimal places, and so on.
LookML can achieve these displays automatically with some more advanced value_format syntax.
Syntax
Use this pattern to set value formats with conditions:
[if_condition]format; [if_condition]format; else_format
Since the value of the value_format parameter is already enclosed in double quotes in LookML, any nested double quotes will need to be escaped using the backslash \ character.
Example with large numbers
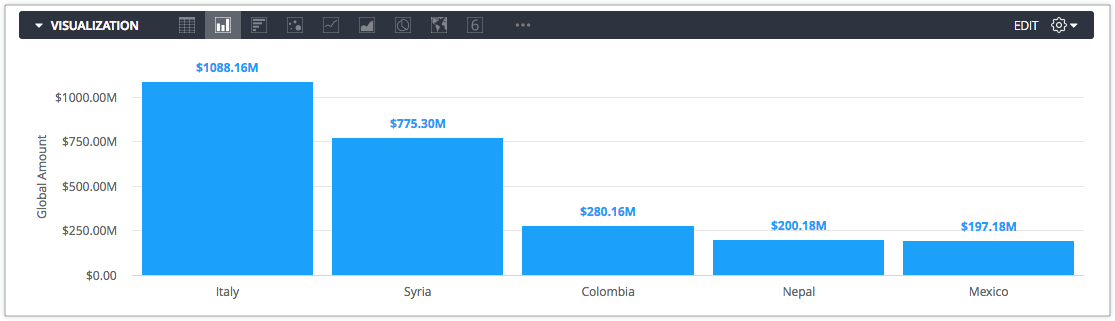
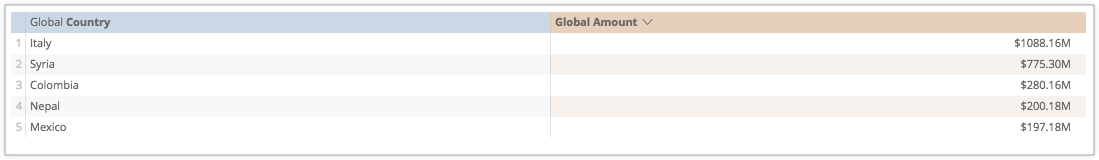
To make numbers such as 12.23M or 2.33K, you can use the following code:
[>=1000000]0.00,,\"M\";[>=1000]0.00,\"K\";
Or with no decimal places:
[>=1000000]0,,\"M\";[>=1000]0,\"K\";0
Here is the measure in LookML using this format, with dollar signs added:
measure: global_amount {
type: sum
sql: ${TABLE}.total
value_format: "[>=1000000]$0.00,,\"M\";[>=1000]$0.00,\"K\";$0.00"
drill_fields: invoices*
}
Example with large negative numbers
You can use similar syntax with negative numbers. To make numbers such as -12.23M or -2.33K, you can use the following code:
[<=-1000000]0.00,,\"M\";[<=-1000]0.00,\"K\";
Or with no decimal places:
[<=-1000000]0,,\"M\";[<=-1000]0,\"K\";0
Here is the measure in LookML using this format, with dollar signs added:
measure: global_amount_negative {
type: sum
sql: ${TABLE}.total
value_format: "[<=-1000000]$0.00,,\"M\";[<=-1000]$0.00,\"K\";$0.00"
drill_fields: invoices*
}
