The following diagram shows the various states and transitions in the lifecycle of a stream.
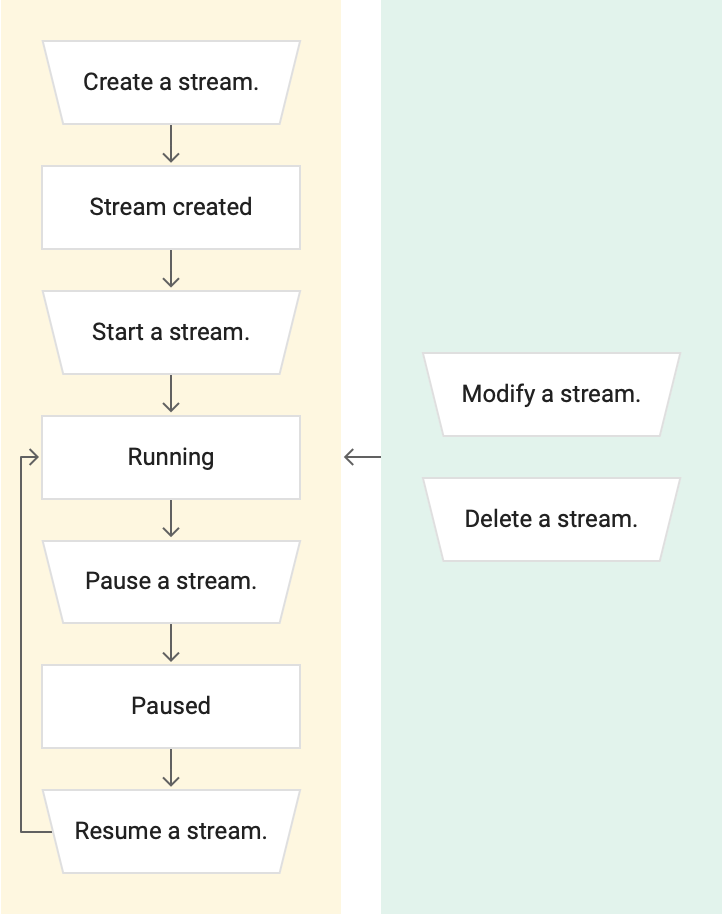
First, you create a stream. Datastream uses this stream to transfer data from a source database into a destination. After the stream is created, the state of the stream is Not started.
After creating the stream, you start it. The status of the stream changes to Starting. This signifies that the stream is in the process of being started and validated.
- If the stream is valid, then the status of the stream changes from
StartingtoRunning. - If the stream isn't valid, then the status of the stream changes from
Startingback toNot started. You can then rectify the problems of the stream. For example, if errors are associated with the connectivity information of the stream, then modify the stream definition. After resolving all problems of the stream, start it again, and the status changes toStarting, and then toRunning.
You can pause a stream. When a stream is paused, Datastream doesn't pull any new data from the source database into the destination. However, some data may continue to be written to the destination because in flight data continues to flow.
Therefore, after you pause a stream, the status of the stream changes from Running to Draining. Draining a stream is the process of emptying the stream so that it doesn't contain any data. After the stream is drained of all data, then the status of the stream changes from Draining to Paused.
When you resume a paused stream, the status of the stream changes from Paused to Running.
There are two actions that you can perform at any time during the lifecycle of the stream:
- Modify the stream. Any changes that you make to it take effect immediately.
- Delete the stream after you no longer need it.
Stream errors
A running stream can encounter errors which might cause the stream to change its state to Failed or Failed permanently:
- A
Failedstatus means that the stream encountered a recoverable error. This means that the stream is either still active, or continuously attempting to run. - A
Failed permanentlystream is a stream that ran into an unrecoverable error which prevents it from continuing to run. Such errors might cause data loss.
You can address the issues for a Failed stream, and the stream automatically resumes. Its state changes from Failed back to Running. For more information, see Troubleshoot a stream.
You can manually recover a Failed permanently stream. For more information, see Recover a stream.
What's next
- For information about running a stream, see Run a stream.
- For information about modifying your streams, see Modify a stream.
- For information about troubleshooting a stream, see Troubleshoot a stream.
- For information about recovering a stream, see Recover a stream.
- For information about deleting a stream, see Delete a stream.
