本文档介绍了如何保护和管理对 Dataplex Universal Catalog 数据湖的访问权限。
借助 Dataplex Universal Catalog 安全模型,您可以管理用户权限,以执行以下任务:
- 管理数据湖(创建和附加资产、区域和其他数据湖)
- 通过映射资产(例如,Cloud Storage 存储桶和 BigQuery 数据集等Google Cloud 资源)访问与数据湖关联的数据
- 访问与数据湖关联的数据的相关元数据
数据湖的管理员可以通过授予基本角色和预定义角色来控制对 Dataplex Universal Catalog 资源(例如数据湖、区域和资产)的访问权限。
基本角色
| 角色 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Dataplex Viewer ( roles/dataplex.viewer) |
能够查看(但不能修改)数据湖及其配置的区域和资产。 |
| Dataplex Editor ( roles/dataplex.editor) |
能够修改数据湖。可以创建和配置数据湖、区域、资产和任务。 |
| Dataplex Administrator ( roles/dataplex.administrator) |
能够完全管理数据湖。 |
| Dataplex Developer ( roles/dataplex.developer) |
能够在数据湖上运行数据分析工作负载。 * |
如需运行 Spark 作业,请在您希望将计算计入的项目中创建 Dataproc 集群并提交 Dataproc 作业。
预定义角色
Google Cloud 管理可为 Dataplex Universal Catalog 提供精细访问权限的预定义角色。
元数据角色
元数据角色能够查看表架构等元数据。
| 角色 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Dataplex Metadata Writer ( roles/dataplex.metadataWriter) |
能够更新特定资源的元数据。 |
| Dataplex Metadata Reader ( roles/dataplex.metadataReader) |
能够读取元数据(例如,查询表)。 |
数据角色
向主账号授予数据角色后,该主账号便能够读取或写入数据湖的资产所指向的底层资源中的数据。
Dataplex Universal Catalog 会将其角色映射到每个底层存储资源(例如 Cloud Storage 和 BigQuery)的数据角色。
Dataplex Universal Catalog 会转换 Dataplex Universal Catalog 数据角色并将其传播到底层存储资源,从而为每个存储资源设置正确的角色。您可以在数据湖层次结构(例如,数据湖)中授予单个 Dataplex Universal Catalog 数据角色,并且 Dataplex Universal Catalog 会维护对关联到该数据湖的所有资源(例如,Cloud Storage 存储桶和 BigQuery 数据集由底层区域中的资产引用)的数据的指定访问权限。
例如,为主账号授予数据湖的 dataplex.dataWriter 角色后,该主账号便拥有对数据湖及其底层区域和资产中所有数据的写入权限。在较低级层(区域)授予的数据访问角色会在数据湖层次结构中继承到底层资产。
| 角色 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Dataplex Data Reader ( roles/dataplex.dataReader) |
能够从附加到资产的存储空间(包括存储桶和 BigQuery 数据集及其内容)读取数据。* |
| Dataplex Data Writer ( roles/dataplex.dataWriter) |
能够将数据写入相应资产所指向的底层资源。* |
| Dataplex Data Owner ( roles/dataplex.dataOwner) |
向底层资源授予 Owner 角色,包括能够管理子资源。例如,作为 BigQuery 数据集的数据所有者,您可以管理底层表。 |
确保您的数据湖安全无虞
您可以保护和管理对数据湖及其附加的数据的访问权限。在 Google Cloud 控制台中,使用以下视图之一:
- 权限标签页上的 Dataplex Universal Catalog 管理视图
- Dataplex Universal Catalog 安全视图
使用管理视图
权限标签页可让您管理数据湖资源的所有权限,并显示所有权限(包括继承的权限)的未过滤视图。
如需保护数据湖,请按照以下步骤操作:
在 Google Cloud 控制台中,前往 Dataplex Universal Catalog。
导航到管理视图。
点击您创建的数据湖的名称。
点击权限标签页。
点击按角色查看标签页。
点击添加以添加新角色。添加 Dataplex Data Reader、Data Writer 和 Data Owner 角色。
验证 Dataplex Data Reader、Data Writer 和 Data Owner 角色是否显示。
使用安全视图
Google Cloud 控制台中的 Dataplex Universal Catalog 安全视图提供以下功能:
- 仅包含以特定资源为中心的 Dataplex Universal Catalog 角色的可过滤视图
- 将数据角色与数据湖资源角色分开
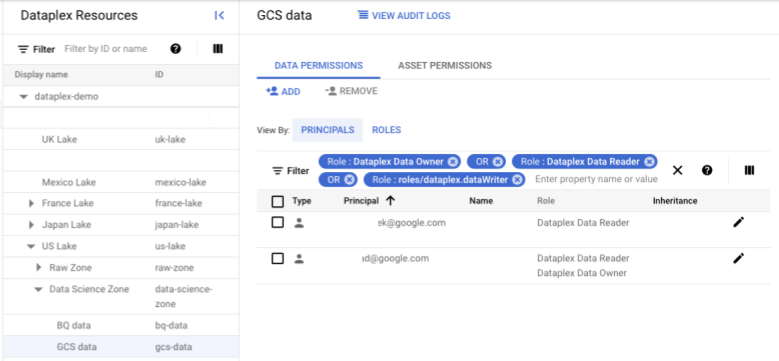
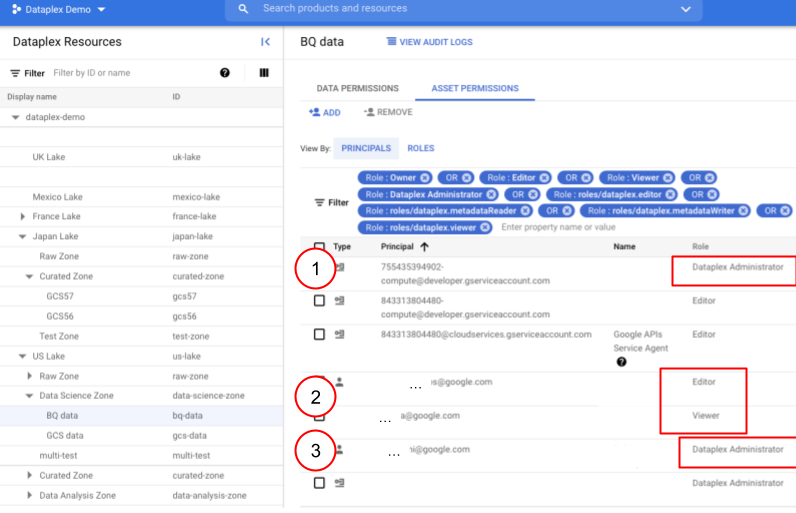
- 从项目继承 Dataplex Administrator 角色的服务账号。
- 从项目继承 Dataplex Editor 和 Viewer 角色的主账号(邮箱)。这些角色适用于所有资源。
- 从项目继承 Dataplex Administrator 角色的主账号(邮箱)。
政策管理
指定安全政策后,Dataplex Universal Catalog 会将权限传播到托管式资源的 IAM 政策。
在数据湖级层配置的安全政策会传播到该数据湖内管理的所有资源。Dataplex Universal Catalog 在 Dataplex Universal Catalog 的 管理 > 权限 标签页上提供传播状态,并可让您了解这些大规模传播。它会持续监控托管式资源,以了解 Dataplex Universal Catalog 外部的 IAM 政策是否发生任何更改。
如果用户已拥有资源的权限,则在资源附加到 Dataplex Universal Catalog 数据湖后,用户仍会拥有这些权限。同样,在将资源附加到 Dataplex Universal Catalog 后创建或更新的非 Dataplex Universal Catalog 角色绑定保持不变。
设置列级、行级和表级政策
Cloud Storage 存储桶附加了关联的 BigQuery 外部表。
您可以升级 Cloud Storage 存储桶资产,这意味着 Dataplex Universal Catalog 会移除附加的外部表,并改为附加 BigLake 表。
您可以使用 BigLake 表而不是外部表来提供精细的访问权限控制,包括行级控制、列级控制和列数据遮盖。
元数据安全性
元数据主要是指与数据湖管理的资源中存在的用户数据相关联的架构信息。
Dataplex Universal Catalog 发现功能会检查托管式资源中的数据,并提取表格架构信息。这些表会发布到 BigQuery、Dataproc Metastore 和 Data Catalog(已弃用)系统。
BigQuery
每个发现的表都有一个在 BigQuery 中注册的关联表。对于每个区域,都有一个关联的 BigQuery 数据集,与该数据区域中发现的表关联的所有外部表都会在该数据集下注册。
发现的 Cloud Storage 托管表会在为该区域创建的数据集下注册。
Dataproc Metastore
数据库和表可在与 Dataplex Universal Catalog 数据湖实例关联的 Dataproc Metastore 中提供。每个数据区域都有一个关联的数据库,每个资产可以有一个或多个关联的表。
通过配置 VPC-SC 网络,可以确保 Dataproc Metastore 服务中的数据安全无虞。在创建数据湖期间,Dataproc Metastore 实例会提供给 Dataplex Universal Catalog,已使其成为用户管理的资源。
Data Catalog
每个发现的表在 Data Catalog(已弃用)中都有一个关联的条目,以启用搜索和发现功能。
Data Catalog 在创建条目期间需要使用 IAM 政策名称。因此,Dataplex Universal Catalog 会提供条目应关联的 Dataplex Universal Catalog 资产资源的 IAM 政策名称。因此,Dataplex Universal Catalog 条目的权限由资产资源的权限决定。授予资产资源的 Dataplex Metadata Reader 角色 (roles/dataplex.metadataReader) 和 Dataplex Metadata Writer 角色 (roles/dataplex.metadataWriter)。
后续步骤
- 详细了解 Dataplex Universal Catalog IAM。
- 详细了解 Dataplex Universal Catalog IAM 角色。
- 详细了解 Dataplex Universal Catalog IAM 权限。
