第 6 步:执行部署
本页介绍了部署 Cortex Framework 数据基础(Cortex Framework 的核心)的第六步。在此步骤中,您将执行 Cortex Framework Data Foundation 的部署。
构建流程
按照第 5 步:配置部署中的说明配置 config.json 文件后,请按照以下说明构建流程。
运行以下命令,将自己定位到克隆的代码库中:
cd cortex-data-foundation运行包含目标日志存储桶的 build 命令:
gcloud builds submit \ --substitutions=_GCS_BUCKET=LOGS_BUCKET,_BUILD_ACCOUNT='projects/SOURCE_PROJECT/serviceAccounts/SERVICE_ACCOUNT@SOURCE_PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com'替换以下内容:
- 将
LOGS_BUCKET替换为用于存储日志的存储桶名称。 Cloud Build 服务账号需要有权在此处写入这些文件。 SOURCE_PROJECT与源项目。- 将
SERVICE_ACCOUNT替换为服务账号 ID。
- 将
如果您有足够的权限,可以按照主要构建流程从终端或 Cloud Build 控制台中查看日志。如需了解更多参考信息,请参阅以下图片。
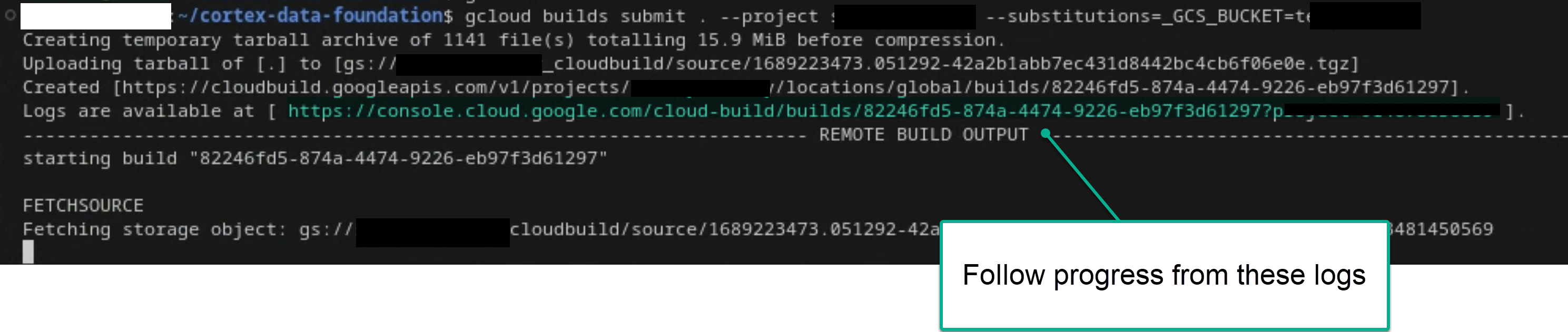
图 1。在终端中查看日志进度的示例。 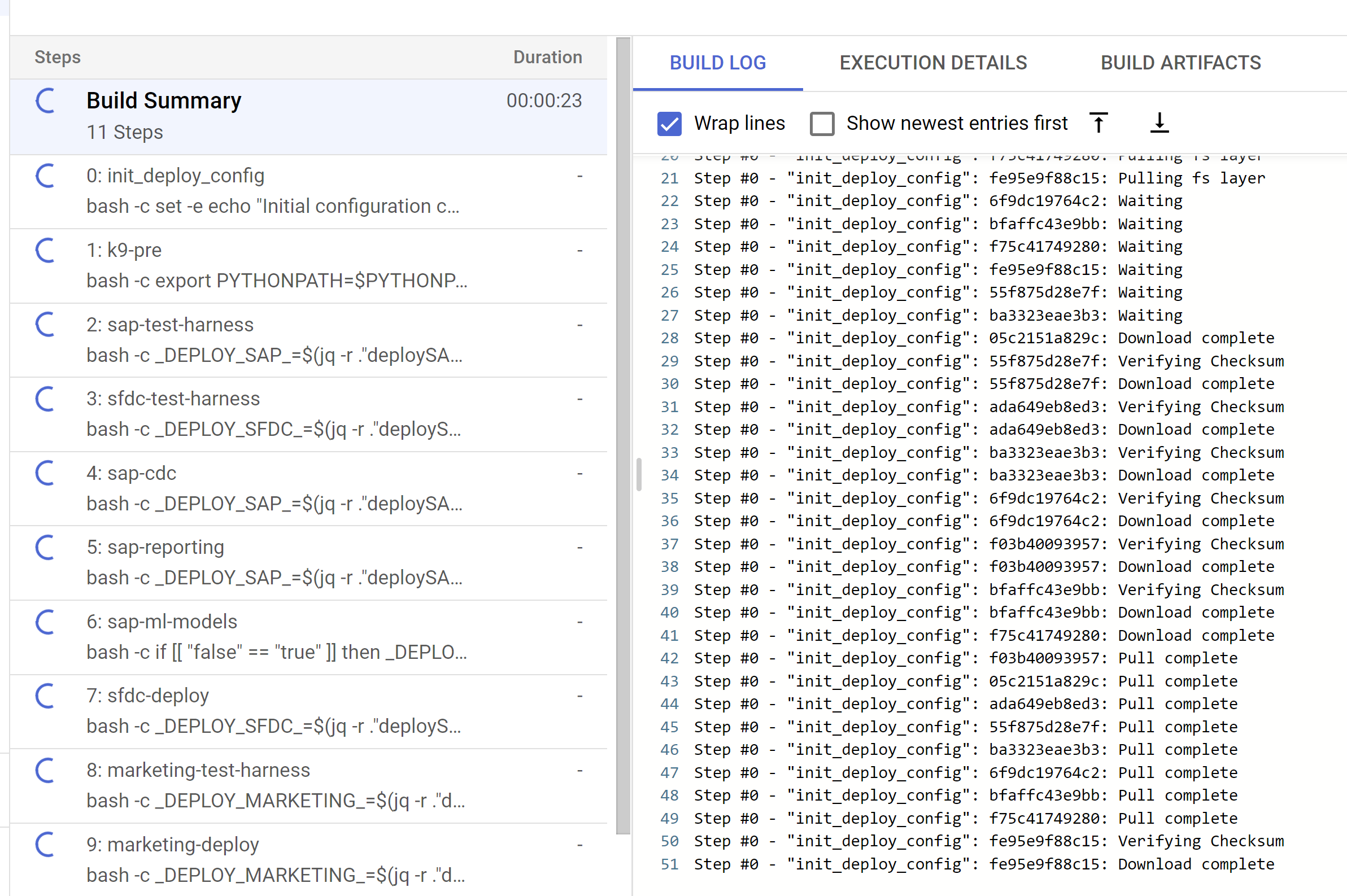
图 2。在控制台中查看日志进度的示例。 跟踪从 Cloud Build 控制台触发的子构建步骤,或在从这些步骤创建的日志中跟踪。如需更多参考信息,请参阅以下图片。
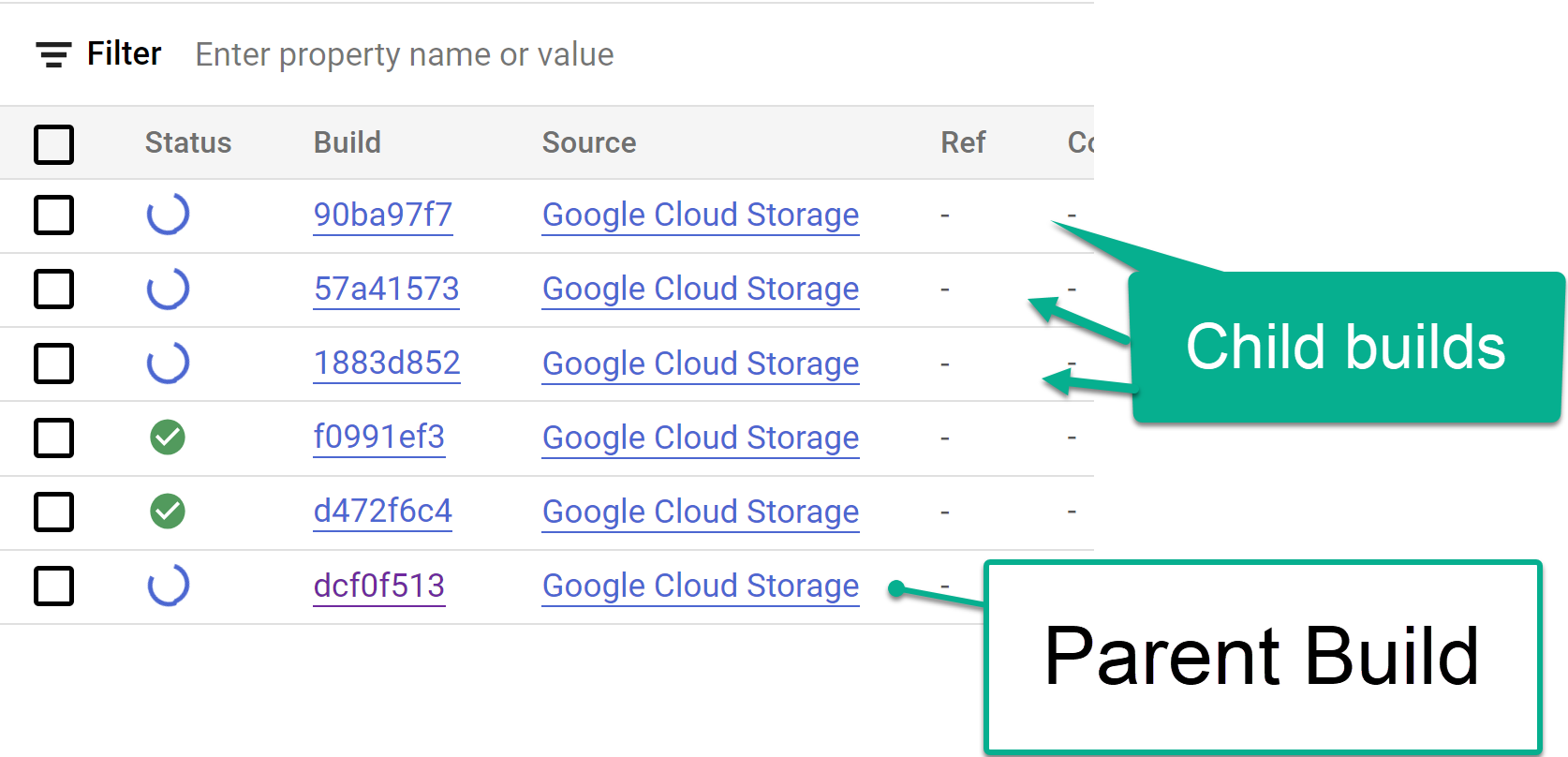
图 3. 在控制台中跟踪子 build 步骤的示例。 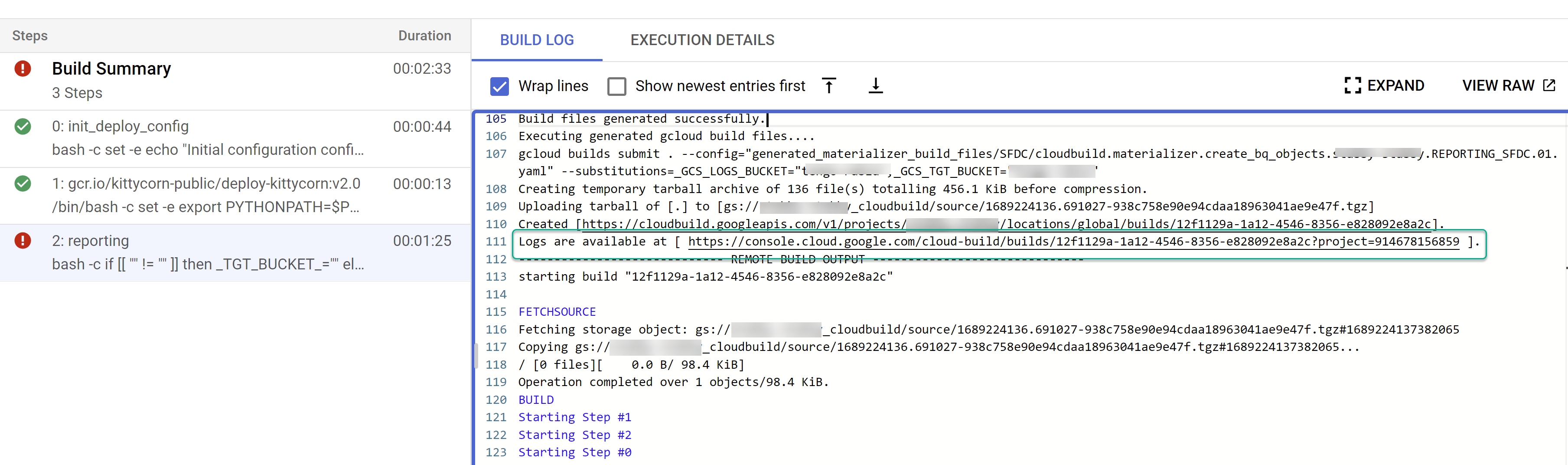
图 4。在日志中跟踪子 build 步骤的示例。 确定各个 build 是否存在任何问题。修正错误(如有)。建议将生成的 SQL 粘贴到 BigQuery 中,以识别并更正错误。大多数错误都与所选但未出现在复制源中的字段有关。BigQuery 界面有助于识别这些代码并将其注释掉。

图 5。通过 Cloud Build 日志识别问题的示例。
将文件移动到 Cloud Composer (Airflow) DAG 存储桶
如果您选择生成集成文件或 CDC 文件,并且拥有 Cloud Composer (Airflow) 实例,则可以使用以下命令将这些文件移至最终存储桶:
gcloud storage -m cp -r gs://OUTPUT_BUCKET/dags/ gs://COMPOSER_DAG_BUCKET/
gcloud storage -m cp -r gs://OUTPUT_BUCKET/data/ gs://COMPOSER_DAG_BUCKET/
替换以下内容:
- 将
OUTPUT_BUCKET替换为输出存储桶。 COMPOSER_DAG_BUCKET与 Cloud Composer (Airflow) DAG 存储桶。
自定义并为升级做好准备
许多企业客户对其系统进行了特定的自定义,例如在流程中添加了其他文档或特定类型的记录。这些规则是针对每个客户的,由功能分析师根据业务需求进行配置。
Cortex 会在代码中使用 ## CORTEX-CUSTOMER 标记来表示可能需要进行此类自定义的位置。使用命令 grep -R CORTEX-CUSTOMER 可检查所有应自定义的 ## CORTEX-CUSTOMER 注释。
除了 CORTEX-CUSTOMER 标记之外,您可能还需要进一步自定义以下内容,方法是将所有这些更改提交到您自己的派生或克隆的代码库,并在代码中添加清晰的标记:
- 添加业务规则。
- 添加其他数据集并将其与现有视图或表联接
- 重复使用提供的模板来调用其他 API。
- 修改部署脚本。
- 应用更多数据网格概念。
- 调整一些表格或已发布的 API,以包含标准中未包含的其他字段。
采用适合您组织的 CI/CD 流水线,以确保这些增强功能经过测试,并使整个解决方案处于可靠且稳健的状态。流水线可以重复使用 cloudbuild.yaml 脚本,以定期或根据 Git 操作触发端到端部署,具体取决于您选择的代码库,从而自动执行 build。
使用 config.json 文件为开发、预演和生产环境定义不同的项目和数据集。使用您自己的样本数据进行自动化测试,以确保模型始终能生成您期望的结果。
在代码库的分叉或克隆中明显标记您自己的更改,并结合一些部署和测试自动化功能,有助于执行升级。
支持
如果您遇到任何问题,或者有与这些模型或部署程序相关的功能请求,请在 Cortex Framework Data Foundation 代码库中创建问题。为了帮助您收集必要的信息,请从克隆的目录中执行 support.sh。此脚本会引导您完成一系列步骤,帮助您排查问题。
如有任何 Cortex Framework 请求或问题,请前往概览页面中的支持部分。
Looker 块和信息中心
充分利用可用的 Looker Block 和信息中心。这些是 Cortex Framework 的常见分析模式和数据源的可重复使用的数据模型。如需了解详情,请参阅 Looker Block 和信息中心概览。

